Abstract
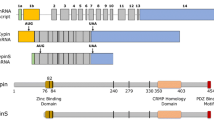
The members of the collapsin response mediator protein (CRMP) family—five cytosolic phosphoproteins—are highly expressed throughout brain development. The first member to be cloned, CRMP2, was identified as an intracellular messenger required for the growth cone-collapse induced by semaphorin 3A (Sema3A). A rapidly expanding body of study indicates that the functions of CRMPs are not solely limited to the signaling transduction of the Sema3A guidance cue. They are probably involved in multiple cellular and molecular events involved in apoptosis/proliferation, cell migration, and differentiation. In the adult brain, the expression of CRMPs is dramatically downregulated. However, they remain expressed in structures that retain their capacity for differentiation and plasticity and also in a subpopulation of oligodendrocytes (CRMP2 and CRMP5). Moreover, the expression of CRMPs is altered in neurodegenerative diseases, and these proteins may be of key importance in the physiopathology of the adult nervous system.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Goshima Y., Nakamura F., Strittmatter P., and Strittmatter S.M. (1995) Collapsin-induced growth cone collapse mediated by an intracellular protein related to UNC-33. Nature 376(6540), 509–514.
Luo Y., Raible D., and Raper J.A. (1993) Collapsin: a protein in brain that induces the collapse and paralysis of neuronal growth cones. Cell 75(2), 217–227.
Minturn J.E., Geschwind D.H., Fryer H.J.L., and Hockfield S. (1995) Early postmitotic neurons transiently express TOAD-64, a neural specific protein. J. Comp. Neurol. 355(3), 369–379.
Minturn J.E., Fryer H.J.L., Geschwind D.H., and Hockfield S. (1995) TOAD-64, a gene expressed early in neuronal differentiation in the rat, is related to unc-33, a C. elegans gene involved in axon outgrowth. J. Neurosci. 15(10), 6757–6766.
Gaetano C., Matsuo T., and Thiele C.J. (1997) Identification and characterisation of a retinoïc acid-regulated human homologue of the hUlip from neuroblastoma cells. J. Biol. Chem. 272(18), 12,195–12,201.
Scott B.W., Wang S., Burnham W.M., De Boni U., and Wojtowicz J.M. (1998) Kindling-induced neurogenesis in the dentate gyrus of the rat. Neurosci. Lett. 248(2), 73–76.
Nacher J., Rosell D.R., and McEwen B.S. (2000) Widespread expression of rat collapsin response-mediated protein 4 in the telencephalon and other areas of the adult rat central nervous system. J. Comp. Neurol. 424(4), 628–639.
Cameron H.A. and McKay R.D. (2001) Adult neurogenesis produces a large pool of new granule cells in the dentate gyrus. J. Comp. Neurol. 435(4), 406–417.
Byk T., Dobransky T., Cifluentes-Diaz C., and Sobel A. (1996) Identification and molecular characterization of Unc-33-like phosphoprotein (Ulip), a putative mammalian homolog of the axonal guidance-associated unc-33 gene product. J. Neurosci. 16(2), 688–701.
Wang L.H. and Strittmatter S.M. (1996) A family of rat CRMP genes is differentially expressed in the nervous system. J. Neurosci. 16(19), 6197–6207.
Hamajima N., Matsuda K., Sakata S., Tamaki M., and Nonaka M. (1996) A novel gene family defined by human dihydropyrimidinase and three related proteins with differential tissue distribution. Gene 180(1–2), 157–163.
Byk T., Ozon S., and Sobel A. (1998) The Ulip family phosphoproteins. Eur. J. Biochem. 254(1), 14–24.
Horiuchi M., El Far O., and Betz H. (2000) Ulip6, a novel unc-33 and dihydropyrimidinase related protein highly expressed in developing rat brain. FEBS Lett. 480(2–3), 283–286.
Fukada M., Watakabe I., Yuasa-Kawada J., Kawachi H., Kuroiwa A., Matsuda Y., et al. (2000) Molecular characterization of CRMP5, a novel member of the collapsin response mediator protein family. J. Biol. Chem. 275(48), 37,957–37,965.
Inatome R., Tsujimura T., Hitomi T., Hermann P., Kuroda S., Yamamura H., et al. (2000) Identification of CRAM, a novel Unc33 gene family that associates with CRMP3 and protein-tyrosine kinase(s) in the developing rat brain. J. Biol. Chem. 275(35), 27,291–27,302.
Ricard D., Rogemond V., Charrier E., Aguera M., Bagnard D., Belin M.F., et al. (2001) Isolation and expression pattern of human Unc-33-Like Phosphoprotein 6/Collapsin Response Mediator Protein 5 (Ulip6/CRMP5): coexistence with Ulip2/CRMP2 in Sema3A-sensitive oligodendrocytes. J. Neurosci. 21(18), 7203–7214.
Quach T.T., Rong Y., Belin M.F., Duchemin A.M., Akakoa H., Ding S., et al. (1997) Molecular cloning and expression of a new unc-33 like cDNA from rat brain and its relation to paraneoplastic neurological syndromes. Brain Res. Mol. Brain Res. 46(1–2), 329–332.
Antoine J.C., Honnorat J., Vocanson C., Koenig F., Aguera M., Belin M.F. (1993) Posterior uveitis, paraneoplastic encephalomyelitis and auto-antibodies reacting with developmental protein of brain and retina. J. Neurol. Sci. 117(1–2), 215–223.
Honnorat J., Antoine J.C., Derrington E.A., Aguera M., and Belin M.F. (1996) Antibodies to a subpopulation of glial cells and a 66 kD developmental protein in patients with paraneoplastic neurological syndromes. J. Neurol. Neurosurg. Psychiatry 61(3), 270–278.
Honnorat J., Rogemond, V., Byk T., Kusters I., Aguera M., Ricard D., Rogemend V., et al. (1999) Ulip/CRMP proteins are recognized by autoantibodies in paraneoplasic neurological syndromes. Eur. J. Neurosci. 11(12), 4226–4232.
Quach T.T., Mosinger B. Jr, Ricard D., Copeland N.G., Gilbert D.J., Jenkins N.A., et al. (2000) Collapsin response mediator protein-3/unc-33-like protein-4 gene: organization, chromosomal mapping and expression in the developing mouse brain. Gene 242(1–2), 175–182.
Wang L.H. and Strittmatter S.M. (1997) Brain CRMP forms heterotetramers similar to liver dihydropyrimidinase. J. Neurochem. 69(6), 2261–2269.
Kamata T., Subleski M., Hara Y., Yuhki N., Kung H., Copeland N.G., Jenkins N.A., Yoshimura T., Modi W., and Copeland T.D. (1998) Isolation and characterization of a bovine neural specific protein (CRMP-2) cDNA homologous to unc-33, a C. elegans gene implicated in axonal outgrowth and guidance. Brain Res. Mol. Brain Res. 54(2), 219–236.
Takemoto T., Sasaki Y., Hamajima N., Goshima Y., Nonaka M., and Kimura H. (2000) Cloning and characterization of the Caenorhabditis elegans CeCRMP/DHP-1 and -2; common ancestors of CRMP and dihydropyrimidinase? Gene 261(2), 259–267.
Geschwind D.H., Kelly G.M., Fryer H., Feeser-Bhatt H., and Hockfield S. (1996) Identification and characterization of novel developmentally regulated proteins in rat spinal cord. Brain Res. Dev. Brain Res. 97(1), 62–75.
Honnorat J., Aguera M., Zalc B., Goujet C., Quach T., Antoine J.C., et al. (1998) POP66, a paraneoplastic encephalomyelitis-related antigen, is a marker of adult oligodendrocytes. J. Neuropathol. Exp. Neurol. 57(4), 311–322.
Yoshida H., Watanabe A., and Ihara Y. (1998) CRMP-2 is associated with neurofibrillary tangles in Alzheimer’s disease. J. Biol. Chem. 273(16), 9761–9768.
Kamata T., Daar I.O., Subleski M., Copeland T., Kung H.F., and Xu R.H. (1998) Xenopus CRMP-2 is an early response gene to neural induction. Brain Res. Mol. Brain Res. 57(2), 201–210.
Ricard D., Stankoff B., Bagnard D., Aguera M., Rogemond V., Antoine J.C., et al. (2000) Differential expression of CRMP/Ulip proteins in subsets of oligodendrocytes in the post-natal rodent brain. Mol. Cell. Neurosci. 16(4), 324–337.
Pasterkamp R.J., De Winter F., Holtmaat A.J.G.D., and Verhaagen J. (1998) Evidence for a role of the chemorepellent semaphorin III and its receptor neuropilin-1 in the regeneration of primary olfactory axons. J. Neurosci. 18(23), 9962–9976.
Jourdan F., Veyrac A., Charrier E., Reymond-Marron I., Aguera M., Belin M. F., et al. (2002) Differential neuronal expression of Ulip/CRMP in the regenerating olfactory epithelium following lesions of the olfactory nerve in the adult mouse. Abstract 3rd Forum of European Neuroscience, Paris, 2002.
Antoine J.C., Honnorat J., Camdessanche J.P., Magistris M., Absi L., Mosnier J.F., et al. (2001) Paraneoplastic anti-CV2 antibodies react with peripheral nerve and are associated with a mixed axonal and demyelinating peripheral neuropathy. Ann. Neurol. 49(2), 214–221.
Taketo M.M., Araki Y., Matsunaga A., Yokoi A., Tsuchida J., Nishina Y., et al. (1997) Mapping of eight testis specific genes to mouse chromosomes. Genomics 46(1), 138–142.
Kato Y., Hamajima N., Inagaki H., Okumura N., Koji T., Sasaki M., et al. (1998) Post-meiotic expression of the mouse dihydropyrimidinase related protein 3 gene during spermiogenesis. Mol. Reprod. Dev. 51(1), 105–111.
Branda C.S. and Stern M. J. (2000) Mechanisms controlling sex myoblast migration in Caenorhabditis elegans hermaphrodites. Dev. Biol. 226(1), 137–151.
Ito T., Kagoshima M., Sasaki Y., Li C., Udaka N., Kitsukawa T., et al. (2000) Repulsive axon guidance molecule Sema3A inhibits branching morphogenesis of fetal mouse lung. Mech. Dev. 97(1–2), 35–45.
Rouzaut A., Lopez-Moratalla N., and De Miguel C. (2000) Differential gene expression in the activation and maturation of human monocytes. Arch. Biochem. Biophys. 374(2), 153–160.
Inagaki N., Chihara K., Arimura N., Menager C., Kawano Y., Matsuo N., et al. (2001) CRMP-2 induces axons in cultured hippocampal neurons. Nat. Neurosci. 4(8), 781–782.
Lee S., Kim J.H., Lee C.S., Kim J.H., Kim Y., Heo K., et al. (2002) Collapsin response mediator protein-2 inhibits neuronal phospholipase D(2) activity by direct interaction. J. Biol. Chem. 277(8), 6542–6549.
Hedgecock E.M., Culotti J.G., Thomson J.N., and Perkins L.A. (1985) Axonal guidance mutants of Caenorhabditis elegans identified by filling sensory neurons with fluorescein dyes. Dev. Biol. 111(1), 158–170.
Bagnard D., Lohrum M., Uziel D., Püschel A.W., and Bolz J. (1998) Semaphorins as attractive and repulsive guidance signals during the development of cortical projections. Development 125(24), 5043–5053.
Tessier-lavigne M. and Goodman C.S. (1996) The molecular biology of axon guidance. Science 274(5290), 1123–1133.
Liu B.P. and Strittmatter S.M. (2001) Semaphorinmediated axonal guidance via Rho-related G proteins. Curr. Opin. Cell. Biol. 13(5), 619–626.
He Z. and Tessier-Lavigne M. (1997) Neuropilin is a receptor for the axonal chemorepellent Semaphorin III. Cell 90(4), 739–751.
Kolodkin A.L., Levengood D.V., Rowe E.G., Tai Y.T., Giger R.J., and Ginty D.D. (1997) Neuropilin is a semaphorin III receptor. Cell 90(4), 753–762.
Takahashi T., Fournier A., Nakamura F., Wang L.H., Murakami Y., Kalb R.G., et al. (1999) Plexin-neuropilin-1 complexes form functional semaphorin-3A receptors. Cell 99(1), 59–69.
Nakamura F., Kalb R.G., and Strittmatter S. M. (2000) Molecular basis of semaphorin-mediated axon guidance. J. Neurobiol. 44(2), 219–229.
Rohm B., Ottemeyer A., Lohrum M., and Püschel A.W. (2000) Plexin/neuropilin complexes mediate repulsion by the axonal guidance signal semaphorin 3A. Mech. Dev. 93(1–2), 95–104.
Takahashi T. and Strittmatter S.M. (2001) Plexin A1 autoinhibition by the plexin sema domain. Neuron 29(2), 429–439.
Mitsui N., Inatome R., Takahashi S., Goshima Y., Yamamura H., and Yanagi S. (2002) Involvement of Fes/FPS tyrosine kinase in semaphorin3A signaling. EMBO J. 21(13), 3274–3285.
Moolenaar W.H. (2000) Development of our current understanding of bioactive lysophospholipids. Ann. NY Acad. Sci. 905, 1–10.
Chun J., Weiner J.A., Fukushima N., Contos J.J., Zhang G., Kimura Y., et al. (2000) Neurobiology of receptor-mediated lysophospholipid signaling. From the first lysophospholipid receptor to roles in nervous system function and development. Ann. NY Acad. Sci. 905, 110–117.
Arimura N., Inagaki N., Chihara K., Ménager C., Nakamura N., Iwamatsu A., et al. (2000) Phosphorylation of CRMP-2 by Rho-kinase:evidence for two separate signaling pathways for growth cone collapse. J. Biol. Chem. 275(31), 23,973–23,980.
Jin Z. and Strittmatter S.M. (1997) Rac1 mediates collapsin1 induced growth cone collapse. J. Neurosci. 17(16), 6256–6263.
Kuhn T.B., Brown M.D., Wilcox C.L., Raper J.A., and Bamburg J.R. (1999) Myelin and collapsin-1 induce motor neuron growth cone collapse through different pathways: inhibition of collapse by opposing mutants of Rac1. J. Neurosci. 19(6), 1965–1975.
Nishiki T., Narumiya S., Morii N., Yamamoto M., Fujiwara M., Kamata Y., et al. (1990) ADP-ribosylation of the rho/rac proteins induces growth inhibition, neurite outgrowth and acetylcholine esterase in cultured PC-12 cells. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 167(1), 265–272.
Jalink K., Van Corven E.J., Hengeveld T., Morii N., Narumiya S., and Moolenaar W.H. (1994) Inhibition of lysophosphatidate-and thrombin-induced neurite retraction and neuronal cell rounding by ADP ribosylation of the small GTP-binding protein Rho. J. Cell. Biol. 126(3), 801–810.
Tigyi G., Fischer D.J., Sebok A., Yang C., Dyer D.L., and Miledi R. (1996) Lysophosphatidic acid-induced neurite retraction in PC12 cells: control by phosphoinositide-Ca2+ signaling and Rho. J. Neurochem. 66(2), 537–548.
Amano M., Chihara K., Nakamura N., Fukata Y., Yano T., Shibata M., et al. (1998) Myosin II activation promotes neurite retraction during the action of Rho and Rho-kinase Genes Cells 3(3), 177–188.
Kranenburg O., Poland M., Van Horck F.P., Drechsel D., Hall A., and Moolenaar W.H. (1999) Activation of RhoA by lysophosphatidic acid and G alpha12/13 subunits in neuronal cells: induction of neurite retraction. Mol. Biol. Cell. 10(6), 1851–1857.
Hall C., Brown M., Jacobs T., Ferrari G., Cann N., Teo M., et al. (2001) Collapsin response mediator protein switches RhoA and Rac1 morphology in N1E-115 neuroblastoma cells and is regulated by Rho kinase. J. Biol. Chem. 276(46), 43,482–43,486.
Leung T., Ng Y., Cheong A., Ng C.H., Tan I., Hall C., et al. (2002) p80 ROKalpha binding protein is a navel variant of CRMP1 which associates with CRMP2 and modulates Rho-A-induced neuronal morphology. FEBS Lett. 523(3), 445–449.
Cole R.N. and Hart G.W. (2001) Cytosolic O-glycosylation is abundant in nerve terminals. J. Neurochem. 79(5), 1080–1089.
Li W., Herman R.K., and Shaw J.E. (1992) Analysis of the Caenorhabditis elegans axonal guidance and outgrowth gene unc-33. Genetics 132(3), 675–689.
Gu Y. and Ihara Y. (2000) Evidence that CRMP2 is involved in the dynamics of microtubules. J. Biol. Chem. 275(24), 17,917–17,920.
Fukata Y., Itoh T.J., Kimura T., Ménager C., Nishimura T., Shiromizu T., et al. (2002) CRMP-2 binds to tubulin heterodimers to promote microtubule assembly. Nature Cell. Biol. 4(8), 583–591.
Fukata Y., Kimura T., and Kaibuchi K. (2002) Axon specification in hippocampal neurons. Neurosci. Res. 43(4), 305–315.
Goshima Y., Kawakami T., Hori H., Sugiyama Y., Takasawa S., Hashimoto Y., et al. (1997) A novel action of collapsin: collapsin-1 increases antero- and retrograde axoplasmic transport independently of growth cone collapse. J. Neurobiol. 33(3), 316–328.
Shirvan A., Fleminger G., Shina R., He Z., Brudo I., Melamed E., et al. (1999) Semaphorins as mediators of neuronal apoptosis. J. Neurochem. 73(3), 961–971.
Galiardini V. and Fankhauser C. (1999) Semaphorin III can induce death in sensory neurons. Mol. Cell. Neurosci. 14(4–5), 301–316.
Barzilai A., Zilkha-Falb R., Daily D., Stern N., Offen D., Ziv I., et al. (2000) The molecular mechanism of dopamine-induced apoptosis: identification and characterization of genes that mediate dopamine toxicity. J. Neural Transm. Suppl. 60, 59–76.
Bagnard D., Vaillant C., Khuth S., Dufay N., Lohrum M., Püschel A., et al. (2001) Sema3A/VEGF165 balance mediates migration and apoptosis of neural progenitor cells by the recrutment of shared receptors. J. Neurosci. 21(10), 3332–3341.
Franken S., Junghans U., Rosslenbroich V., Baader S.L., Hoffman R., Gieselmann V., et al. (2002) Collapsin Response Mediator Proteins of neonatal brain interact with chondroitin sulfate. J. Biol. Chem. 278(5), 3241–3250.
Bermingham J.R. Jr, Shumas S., Whisenhunt T., Rosenfeld M.G., and Scherer S.S. (2001) Modification of representational difference analysis applied to the isolation of forskolin-regulated genes from Schwann cells. J. Neurosci. Res. 63(6), 516–524.
Weiner J.A., Hecht J.H., and Chun J. (1998) Lysophosphatidic receptor gene vzg-1/lpA1/edg-2 is expressed by mature oligodendrocytes during myelination in the postnatal murine brain. J. Comp. Neurol. 398(4), 587–598.
Cervera P., Tirard M., Barron S., Allard J., Trottier S., Lacombe J., et al. (2002) Immunohistological localization of the myelinating cell-specific receptor LP (A1). Glia 38(2), 126–136.
Stankoff B., Barron S., Allard J., Barbin G., Noel F., Aigrot M.S., et al. (2002) Oligodendroglial expression of Edg-2 receptor: developmental analysis and pharmacological responses to lysophosphatidic acid. Mol. Cell. Neurosci. 20(3), 415–428.
Weiner J.A. and Chun J. (1999) Schwann cells survival mediated by the signaling phospholipid lysophosphatidic acid. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 96(9), 5233–5238.
Möller T., Musante D.B., and Ransom B.R. (1999) Lysophosphatidic acid-induced calcium signals in cultured rat oligodendrocytes. NeuroReport 10(14), 2929–2932.
Weiner J.A., Fukushima N., Contos J.J., and Chun J. (2001) Regulation of Schwann cells morphology and adhesion by receptor-mediated lysophosphatidic acid signaling. J. Neurosci. 21(18), 7069–7078.
Yoshimura Y., Shinkawa T., Taoka M., Kobayashi K., Isobe T., and Yamauchi T. (2002) Identification of protein substrates of Ca(2+)/calmodulin-dependent protein kinase Il in the postsynaptic density by protein sequencing and mass spectrometry. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 290(3), 948–954.
Wong C.C. and Leung M.S. (2001) Effects of neonatal hypothyroidism on the expressions of growth cone proteins and axon guidance molecules related genes in the hippocampus. Mol. Cell. Endocrinol. 184(1–2), 143–150.
Lubec G., Nonaka M., Krapfenbauer K., Gratzer M., Cairns N., and Fountoulakis M. (1999) Expression of the dihydropyrimidinase related protein 2 (DRP-2) in Down syndrome and Alzheimer’s disease brain is downregulated at the mRNA and dysregulated at the protein level. J. Neural Transm. Suppl. 57, 161–177.
Gu Y., Hamajima N., and Ihara Y. (2000) Neurofibrillary tangle associated CRMP-2 is highly phosphorylated on thr-509, ser-518 and ser-552. Biochemistry 39(15), 4267–4275.
Castegna A., Aksenov M., Thongboonkerd V., Klein J.B., Pierce W.M., Booze R., et al. (2002) Proteomic identification of oxidatively modified proteins in Alzheimer’s disease brain. Part II: dihydropyrimidinase-related-protein 2, alpha-enolase and heat shock cognate 71. J. Neurochem. 82(6), 1524–1532.
Bulliard C., Zurbriggen R., Tornare J., Faty M., Dastoor Z., and Dreyer J.L. (1997) Purification of a dichlorophenol-indophenol oxidoreductase from rat and bovine synaptic membranes: tight complex association of a glyceraldehyde-3-phosphate dehydrogenase isoform, TOAD64, enolase-gamma and aldolase C. Biochem. J. 324, 555–563.
Rogemond V. and Honnorat J. (2000) Anti-CV2 autoantibodies and paraneoplastic neurological syndromes. Clin. Rev. Allergy Immunol. 19(1), 51–59.
Yu Z., Kryzer T.J., Griesmann G.E., Kim K., Benarroch E.E., and Lennon V.A. (2001) CRMP-5 neuronal autoantibody: marker of lung cancer and thymoma-related autoimmunity. Ann. Neurol. 49(2), 146–154.
Shih J.Y., Yang S.C., Hong T.M., Yuan A., Chen J.J., Yu C.J., et al. (2001) Collapsin response mediator protein-1 and the invasion and metastasis of cancer cells. J. Natl. Cancer Inst. 93(18), 1392–1400.
Eickholt B.J., Mackenzie S.L., Graham A., Walsh F.S., and Doherty P. (1999) Evidence for collapsin-1 functioning in the control of neural crest migration in both trunk and hindbrain regions. Development 126(10), 2181–2189.
Miao H.Q., Soker S., Feiner L., Alonso J.L., Raper J.A., Klagsbrun M. (1999) Neuropilin-1 mediates collapsin-1/semaphorin III inhibition of endothelial cell motility: functional competition of collapsin-1 and vascular endothelial growth factor-165. J. Cell. Biol. 146(1), 233–242.
Johnston-Wilson N.L., Sims C.D., Hofmann J.P., Anderson L., Shore A.D., Torrey E.F., et al. (2000) Disease-specific alterations in frontal cortex brain proteins in schizophrenia, bipolar disorder, and major depressive disorder. The Stanley Neuropathology Consortium. Mol. Psychiatry 5(2), 142–149.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Charrier, E., Reibel, S., Rogemond, V. et al. Collapsin response mediator proteins (CRMPs). Mol Neurobiol 28, 51–63 (2003). https://doi.org/10.1385/MN:28:1:51
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1385/MN:28:1:51