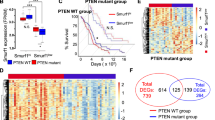
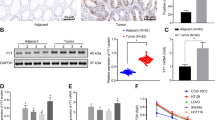
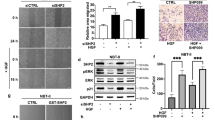
Abstract
Overexpression of HECT-type E3 ubiquitin ligase SMURF1 is correlated with poor prognosis in patients with various cancers, such as glioblastoma, colon cancer, and clear cell renal cell carcinoma. SMURF1 acts as a tumor promoter by ubiquitination modification and/or degradation of tumor-suppressing proteins. Combined treatment of Smurf1 knockdown with rapamycin showed collaborative antitumor effects in mice. This review described the role of HECT, WW, and C2 domains in regulating SMURF1 substrate selection. We summarized up to date SMURF1 substrates regulating different type cell signaling, thus, accelerating tumor progression, invasion, and metastasis. Furthermore, the downregulation of SMURF1 expression, inhibition of its E3 activity and regulation of its specificity to substrates prevent tumor progression. The potential application of SMURF1 regulators, specifically, wisely choose certain drugs by blocking SMURF1 selectivity in tumor suppressors, to develop novel anticancer treatments.
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 12 print issues and online access
$259.00 per year
only $21.58 per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on Springer Link
- Instant access to full article PDF
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout


Similar content being viewed by others
References
Chen C, Matesic LE. The Nedd4-like family of E3 ubiquitin ligases and cancer. Cancer Metastasis Rev. 2007;26:587–604.
Shao G, Wang R, Sun A, Wei J, Peng K, Dai Q, et al. The E3 ubiquitin ligase NEDD4 mediates cell migration signaling of EGFR in lung cancer cells. Mol Cancer. 2018;17:24.
Fukushima T, Yoshihara H, Furuta H, Hakuno F, Iemura SI, Natsume T, et al. USP15 attenuates IGF-I signaling by antagonizing Nedd4-induced IRS-2 ubiquitination. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 2017;484:522–8.
Wang X, Trotman LC, Koppie T, Alimonti A, Chen Z, Gao Z, et al. NEDD4-1 is a proto-oncogenic ubiquitin ligase for PTEN. Cell. 2007;128:129–39.
Zhou Y, Tao F, Cheng Y, Xu F, Yao F, Feng D, et al. Up-regulation of ITCH is associated with down-regulation of LATS1 during tumorigenesis and progression of cervical squamous cell carcinoma. Clin Invest Med Med Clin et Exp. 2014;37:E384–94.
Zhang Q, Huang AZ, Shen FJ, Yu JP, Qin CZ. [WWP1 promotes cell proliferation in hepatocellular carcinoma through ubiquitin-degradation EI24]. Zhonghua zhong liu za zhi [Chin J Oncol]. 2020;42:203–9.
Shimazu J, Wei J, Karsenty G. Smurf1 inhibits osteoblast differentiation, bone formation, and glucose homeostasis through Serine 148. Cell Rep. 2016;15:27–35.
Cao Y, Zhang L. A Smurf1 tale: function and regulation of an ubiquitin ligase in multiple cellular networks. Cell Mol Life Sci. 2013;70:2305–17.
Khammanivong A, Gopalakrishnan R, Dickerson EB. SMURF1 silencing diminishes a CD44-high cancer stem cell-like population in head and neck squamous cell carcinoma. Mol Cancer. 2014;13:260.
Kwei KA, Shain AH, Bair R, Montgomery K, Karikari CA, van de Rijn M, et al. SMURF1 amplification promotes invasiveness in pancreatic cancer. PLoS ONE. 2011;6:e23924.
Zhu H, Kavsak P, Abdollah S, Wrana JL, Thomsen GHA. SMAD ubiquitin ligase targets the BMP pathway and affects embryonic pattern formation. Nature. 1999;400:687–93.
Feng X, Jia Y, Zhang Y, Ma F, Zhu Y, Hong X, et al. Ubiquitination of UVRAG by SMURF1 promotes autophagosome maturation and inhibits hepatocellular carcinoma growth. Autophagy. 2019;15:1130–49.
Critchley DR. Smurf1 zaps the talin head. Nat Cell Biol. 2009;11:538–40.
Huang C, Rajfur Z, Yousefi N, Chen Z, Jacobson K, Ginsberg MH. Talin phosphorylation by Cdk5 regulates Smurf1-mediated talin head ubiquitylation and cell migration. Nat Cell Biol. 2009;11:624–30.
Wei X, Wang X, Zhan J, Chen Y, Fang W, Zhang L, et al. Smurf1 inhibits integrin activation by controlling Kindlin-2 ubiquitination and degradation. J Cell Biol. 2017;216:1455–71.
Boyer L, Turchi L, Desnues B, Doye A, Ponzio G, Mege JL, et al. CNF1-induced ubiquitylation and proteasome destruction of activated RhoA is impaired in Smurf1-/- cells. Mol Biol Cell. 2006;17:2489–97.
Wang HR, Zhang Y, Ozdamar B, Ogunjimi AA, Alexandrova E, Thomsen GH, et al. Regulation of cell polarity and protrusion formation by targeting RhoA for degradation. Science. 2003;302:1775–9.
Ozdamar B, Bose R, Barrios-Rodiles M, Wang HR, Zhang Y, Wrana JL. Regulation of the polarity protein Par6 by TGFbeta receptors controls epithelial cell plasticity. Science. 2005;307:1603–9.
Townsend TA, Robinson JY, Deig CR, Hill CR, Misfeldt A, Blobe GC, et al. BMP-2 and TGFbeta2 shared pathways regulate endocardial cell transformation. Cells Tissues Organs. 2011;194:1–12.
Townsend TA, Wrana JL, Davis GE, Barnett JV. Transforming growth factor-beta-stimulated endocardial cell transformation is dependent on Par6c regulation of RhoA. J Biol Chem. 2008;283:13834–41.
Vohra BP, Fu M, Heuckeroth RO. Protein kinase Czeta and glycogen synthase kinase-3beta control neuronal polarity in developing rodent enteric neurons, whereas SMAD specific E3 ubiquitin protein ligase 1 promotes neurite growth but does not influence polarity. J Neurosci. 2007;27:9458–68.
Cheng PL, Lu H, Shelly M, Gao H, Poo MM. Phosphorylation of E3 ligase Smurf1 switches its substrate preference in support of axon development. Neuron. 2011;69:231–43.
Bryan B, Cai Y, Wrighton K, Wu G, Feng XH, Liu M. Ubiquitination of RhoA by Smurf1 promotes neurite outgrowth. FEBS Lett. 2005;579:1015–9.
Chang H, Zhang J, Miao Z, Ding Y, Xu X, Zhao X, et al. Suppression of the Smurf1 expression inhibits tumor progression in gliomas. Cell Mol Neurobiol. 2018;38:421–30.
Lu L, Wu M, Lu Y, Zhao Z, Liu T, Fu W, et al. MicroRNA-424 regulates cisplatin resistance of gastric cancer by targeting SMURF1 based on GEO database and primary validation in human gastric cancer tissues. Onco Targets Ther. 2019;12:7623–36.
Tao Y, Sun C, Zhang T, Song Y. SMURF1 promotes the proliferation, migration and invasion of gastric cancer cells. Oncol Rep. 2017;38:1806–14.
Xie P, Zhang M, He S, Lu K, Chen Y, Xing G, et al. The covalent modifier Nedd8 is critical for the activation of Smurf1 ubiquitin ligase in tumorigenesis. Nat Commun. 2014;5:3733.
Ke M, Mo L, Li W, Zhang X, Li F, Yu H. Ubiquitin ligase SMURF1 functions as a prognostic marker and promotes growth and metastasis of clear cell renal cell carcinoma. FEBS Open Bio. 2017;7:577–86.
Nie J, Liu L, Wu M, Xing G, He S, Yin Y, et al. HECT ubiquitin ligase Smurf1 targets the tumor suppressor ING2 for ubiquitination and degradation. FEBS Lett. 2010;584:3005–12.
Yang H, Yu N, Xu J, Ding X, Deng W, Wu G, et al. SMURF1 facilitates estrogen receptor a signaling in breast cancer cells. J Exp Clin Cancer Res. 2018;37:24.
Stiess M, Bradke F. Controlled demolition: Smurf1 regulates neuronal polarity by substrate switching. Neuron. 2011;69:183–5.
Zarrinpar A, Lim WA. Converging on proline: the mechanism of WW domain peptide recognition. Nat Struct Biol. 2000;7:611–3.
Macias MJ, Gervais V, Civera C, Oschkinat H. Structural analysis of WW domains and design of a WW prototype. Nat Struct Biol. 2000;7:375–9.
Li S, Lu K, Wang J, An L, Yang G, Chen H. et al. Ubiquitin ligase Smurf1 targets TRAF family proteins for ubiquitination and degradation. Mol Cell Biochem. 2010;338:11–7.
Ma X, Wang D, Li N, Gao P, Zhang M, Zhang Y. Hippo kinase NDR2 inhibits IL-17 signaling by promoting Smurf1-mediated MEKK2 ubiquitination and degradation. Mol Immunol. 2019;105:131–6.
Kanelis V, Farrow NA, Kay LE, Rotin D, Forman-Kay JD. NMR studies of tandem WW domains of Nedd4 in complex with a PY motif-containing region of the epithelial sodium channel. Biochem Cell Biol=Biochim Biol Cell. 1998;76:341–50.
Huang X, Poy F, Zhang R, Joachimiak A, Sudol M, Eck MJ. Structure of a WW domain containing fragment of dystrophin in complex with beta-dystroglycan. Nat Struct Biol. 2000;7:634–8.
Verdecia MA, Bowman ME, Lu KP, Hunter T, Noel JP. Structural basis for phosphoserine-proline recognition by group IV WW domains. Nat Struct Biol. 2000;7:639–43.
Kanelis V, Rotin D, Forman-Kay JD. Solution structure of a Nedd4 WW domain-ENaC peptide complex. Nat Struct Biol. 2001;8:407–12.
Pires JR, Taha-Nejad F, Toepert F, Ast T, Hoffmüller U, Schneider-Mergener J, et al. Solution structures of the YAP65 WW domain and the variant L30 K in complex with the peptides GTPPPPYTVG, N-(n-octyl)-GPPPY and PLPPY and the application of peptide libraries reveal a minimal binding epitope. J Mol Biol. 2001;314:1147–56.
Aragón E, Goerner N, Zaromytidou AI, Xi Q, Escobedo A, Massagué J, et al. A Smad action turnover switch operated by WW domain readers of a phosphoserine code. Genes Dev. 2011;25:1275–88.
Lu PJ, Zhou XZ, Shen M, Lu KP. Function of WW domains as phosphoserine- or phosphothreonine-binding modules. Science. 1999;283:1325–8.
Qiu L, Joazeiro C, Fang N, Wang HY, Elly C, Altman Y, et al. Recognition and ubiquitination of Notch by Itch, a hect-type E3 ubiquitin ligase. J Biol Chem. 2000;275:35734–7.
Courbard JR, Fiore F, Adelaide J, Borg JP, Birnbaum D, Ollendorff V. Interaction between two ubiquitin-protein isopeptide ligases of different classes, CBLC and AIP4/ITCH. J Biol Chem. 2002;277:45267–75.
Murillas R, Simms KS, Hatakeyama S, Weissman AM, Kuehn MR. Identification of developmentally expressed proteins that functionally interact with Nedd4 ubiquitin ligase. J Biol Chem. 2002;277:2897–907.
Nie J, Xie P, Liu L, Xing G, Chang Z, Yin Y, et al. Smad ubiquitylation regulatory factor 1/2 (Smurf1/2) promotes p53 degradation by stabilizing the E3 ligase MDM2. J Biol Chem. 2010;285:22818–30.
Scott JL, Frick CT, Johnson KA, Liu H, Yong SS, Varney AG, et al. Molecular analysis of membrane targeting by the C2 domain of the E3 ubiquitin ligase Smurf1. Biomolecules. 2020;10:229. https://doi.org/10.3390/biom10020229.
Yamaguchi K, Ohara O, Ando A, Nagase T. Smurf1 directly targets hPEM-2, a GEF for Cdc42, via a novel combination of protein interaction modules in the ubiquitin-proteasome pathway. Biol Chem. 2008;389:405–13.
Tian M, Bai C, Lin Q, Lin H, Liu M, Ding F, et al. Binding of RhoA by the C2 domain of E3 ligase Smurf1 is essential for Smurf1-regulated RhoA ubiquitination and cell protrusive activity. FEBS Lett. 2011;585:2199–204.
Lu K, Li P, Zhang M, Xing G, Li X, Zhou W, et al. Pivotal role of the C2 domain of the Smurf1 ubiquitin ligase in substrate selection. J Biol Chem. 2011;286:16861–70.
Hynes RO. Integrins: bidirectional, allosteric signaling machines. Cell. 2002;110:673–87.
Al-Hakim AK, Zagorska A, Chapman L, Deak M, Peggie M, Alessi DR. Control of AMPK-related kinases by USP9X and atypical Lys(29)/Lys(33)-linked polyubiquitin chains. Biochemical J. 2008;411:249–60.
Huang H, Jeon MS, Liao L, Yang C, Elly C, Yates JR 3rd, et al. K33-linked polyubiquitination of T cell receptor-zeta regulates proteolysis-independent T cell signaling. Immunity. 2010;33:60–70.
Plow EF, Qin J, Byzova T. Kindling the flame of integrin activation and function with kindlins. Curr Opin Hematol. 2009;16:323–8.
Lai-Cheong JE, Parsons M, McGrath JA. The role of kindlins in cell biology and relevance to human disease. Int J Biochem Cell Biol. 2010;42:595–603.
Montanez E, Ussar S, Schifferer M, Bosl M, Zent R, Moser M, et al. Kindlin-2 controls bidirectional signaling of integrins. Genes Dev. 2008;22:1325–30.
Meves A, Stremmel C, Gottschalk K, Fassler R. The Kindlin protein family: new members to the club of focal adhesion proteins. Trends Cell Biol. 2009;19:504–13.
Narimatsu M, Bose R, Pye M, Zhang L, Miller B, Ching P, et al. Regulation of planar cell polarity by Smurf ubiquitin ligases. Cell. 2009;137:295–307.
Hong-Rui W, Yue Z, Barish O, Ogunjimi AA, Evguenia A, Thomsen GH, et al. Regulation of cell polarity and protrusion formation by targeting RhoA for degradation. Science. 2003;302:1775–9.
Zhang Y, Chang C, Gehling DJ, Hemmati-Brivanlou A, Derynck R. Regulation of Smad degradation and activity by Smurf2, an E3 ubiquitin ligase. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 2001;98:974–9.
Lee YS, Park JS, Kim JH, Jung SM, Lee JY, Kim S-J, et al. Smad6-specific recruitment of Smurf E3 ligases mediates TGF-β1-induced degradation of MyD88 in TLR4 signalling. Nat Commun. 2011;2:460.
Xia Q, Zhang H, Zhang P, Li Y, Xu M, Li X, et al. Oncogenic Smurf1 promotes PTEN wild-type glioblastoma growth by mediating PTEN ubiquitylation. Oncogene. 2020;39:5902–15.
Lee WS, Yoo WH, Chae HJ. ER stress and autophagy. Curr Mol Med. 2015;15:735–45.
Guo X, Shen S, Song S, He S, Cui Y, Xing G, et al. The E3 ligase Smurf1 regulates Wolfram syndrome protein stability at the endoplasmic reticulum. J Biol Chem. 2011;286:18037–47.
Fei C, He X, Xie S, Miao H, Zhou Z, Li L. Smurf1-mediated axin ubiquitination requires Smurf1 C2 domain and is cell cycle-dependent. J Biol Chem. 2014;289:14170–7.
Wei R, Guo J, Li M, Yang X, Zhu R, Huang H, et al. Smurf1 controls S phase progression and tumorigenesis through Wee1 degradation. FEBS Lett. 2017;591:1150–8.
Penas C, Ramachandran V, Simanski S, Lee C, Madoux F, Rahaim RJ, et al. Casein kinase 1delta-dependent Wee1 protein degradation. J Biol Chem. 2014;289:18893–903.
Moren A, Imamura T, Miyazono K, Heldin CH, Moustakas A. Degradation of the tumor suppressor Smad4 by WW and HECT domain ubiquitin ligases. J Biol Chem. 2005;280:22115–23.
Sangadala S, Metpally RP, Reddy BV. Molecular interaction between Smurf1 WW2 domain and PPXY motifs of Smad1, Smad5, and Smad6-modeling and analysis. J Biomol Struct Dyn. 2007;25:11–23.
Miyazono K, Kamiya Y, Morikawa M. Bone morphogenetic protein receptors and signal transduction. J Biochem. 2010;147:35–51.
Ebisawa T, Fukuchi M, Murakami G, Chiba T, Tanaka K, Imamura T, et al. Smurf1 interacts with transforming growth factor-beta type I receptor through Smad7 and induces receptor degradation. J Biol Chem. 2001;276:12477–80.
Murakami G, Watabe T, Takaoka K, Miyazono K, Imamura T. Cooperative inhibition of bone morphogenetic protein signaling by Smurf1 and inhibitory Smads. Mol Biol Cell. 2003;14:2809–17.
Chen Y, Huang Q, Liu W, Zhu Q, Cui CP, Xu L, et al. Mutually exclusive acetylation and ubiquitylation of the splicing factor SRSF5 control tumor growth. Nat Commun. 2018;9:2464.
Yu H, Li D, Zhou P, Li W. Smurf1-positive expression indicates favorable survival for resected non-small cell lung cancer patients. Int J Clin Exp Pathol. 2018;11:399–405.
Xu S, Tong M, Huang J, Zhang Y, Qiao Y, Weng W, et al. TRIB2 inhibits Wnt/beta-Catenin/TCF4 signaling through its associated ubiquitin E3 ligases, beta-TrCP, COP1 and Smurf1, in liver cancer cells. FEBS Lett. 2014;588:4334–41.
Wang J, Park JS, Wei Y, Rajurkar M, Cotton JL, Fan Q, et al. TRIB2 acts downstream of Wnt/TCF in liver cancer cells to regulate YAP and C/EBPalpha function. Mol Cell. 2013;51:211–25.
Keeshan K, Bailis W, Dedhia PH, Vega ME, Shestova O, Xu L, et al. Transformation by Tribbles homolog 2 (Trib2) requires both the Trib2 kinase domain and COP1 binding. Blood. 2010;116:4948–57.
Wang M, Guo L, Wu Q, Zeng T, Lin Q, Qiao Y, et al. ATR/Chk1/Smurf1 pathway determines cell fate after DNA damage by controlling RhoB abundance. Nat Commun. 2014;5:4901.
Dahlem C, Barghash A, Puchas P, Haybaeck J, Kessler SM. The insulin-like growth factor 2 mRNA binding protein IMP2/IGF2BP2 is overexpressed and correlates with poor survival in pancreatic cancer. Int J Mol Sci. 2019;20:3204. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms20133204.
Fukunaga E, Inoue Y, Komiya S, Horiguchi K, Goto K, Saitoh M, et al. Smurf2 induces ubiquitin-dependent degradation of Smurf1 to prevent migration of breast cancer cells. J Biol Chem. 2008;283:35660–7.
Fan X, Wang Y, Fan J, Chen R. Deletion of SMURF 1 represses ovarian cancer invasion and EMT by modulating the DAB2IP/AKT/Skp2 feedback loop. J Cell Biochem. 2019;120:10643–51.
Wang W, Du H, Liu H, Hu F, Liu G. SMAD specific E3 ubiquitin protein ligase 1 promotes ovarian cancer cell migration and invasion via the activation of the RhoA/ROCK signaling pathway. Oncol Rep. 2019;41:668–76.
Pastushenko I, Blanpain C. EMT transition states during tumor progression and metastasis. Trends Cell Biol. 2019;29:212–26.
Yeung KT, Yang J. Epithelial-mesenchymal transition in tumor metastasis. Mol Oncol. 2017;11:28–39.
Wu Q, Li G, Wen C, Zeng T, Fan Y, Liu C, et al. Monoubiquitination of p120-catenin is essential for TGFbeta-induced epithelial-mesenchymal transition and tumor metastasis. Sci Adv. 2020;6:eaay9819.
Zhan F, Zhong Y, Qin Y, Li L, Wu W, Yao M. SND1 facilitates the invasion and migration of cervical cancer cells by Smurf1-mediated degradation of FOXA2. Exp Cell Res. 2020;388:111809.
Yan C, Su H, Song X, Cao H, Kong L, Cui W. Smad ubiquitination regulatory factor 1 (Smurf1) promotes thyroid cancer cell proliferation and migration via ubiquitin-dependent degradation of Kisspeptin-1. Cell Physiol Biochem: Int J Exp Cell Physiol, Biochem, Pharmacol. 2018;49:2047–59.
Sahai E, Garcia-Medina R, Pouysségur J, Vial E. Smurf1 regulates tumor cell plasticity and motility through degradation of RhoA leading to localized inhibition of contractility. J Cell Biol. 2007;176:35–42.
Koganti P, Levy-Cohen G, Blank M. Smurfs in protein homeostasis, signaling, and cancer. Front Oncol. 2018;8:295.
Yu L, Liu X, Cui K, Di Y, Xin L, Sun X, et al. SND1 acts downstream of TGFβ1 and upstream of Smurf1 to promote breast cancer metastasis. Cancer Res. 2015;75:1275–86.
Chen X, Chen S, Li Y, Gao Y, Huang S, Li H, et al. SMURF1-mediated ubiquitination of ARHGAP26 promotes ovarian cancer cell invasion and migration. Exp Mol Med. 2019;51:1–12.
Yamashita M, Ying SX, Zhang GM, Li C, Cheng SY, Deng CX, et al. Ubiquitin ligase Smurf1 controls osteoblast activity and bone homeostasis by targeting MEKK2 for degradation. Cell. 2005;121:101–13.
Lin X, Liang M, Feng XH. Smurf2 is a ubiquitin E3 ligase mediating proteasome-dependent degradation of Smad2 in transforming growth factor-beta signaling. J Biol Chem. 2000;275:36818–22.
Kavsak P, Rasmussen RK, Causing CG, Bonni S, Zhu H, Thomsen GH, et al. Smad7 binds to Smurf2 to form an E3 ubiquitin ligase that targets the TGF beta receptor for degradation. Mol Cell. 2000;6:1365–75.
Zhao M, Qiao M, Oyajobi BO, Mundy GR, Chen D. E3 ubiquitin ligase Smurf1 mediates core-binding factor alpha1/Runx2 degradation and plays a specific role in osteoblast differentiation. J Biol Chem. 2003;278:27939–44.
Jin YH, Jeon EJ, Li QL, Lee YH, Choi JK, Kim WJ, et al. Transforming growth factor-beta stimulates p300-dependent RUNX3 acetylation, which inhibits ubiquitination-mediated degradation. J Biol Chem. 2004;279:29409–17.
Izzi L, Attisano L. Regulation of the TGFbeta signalling pathway by ubiquitin-mediated degradation. Oncogene. 2004;23:2071–8.
Manikoth Ayyathan D, Koganti P, Marcu-Malina V, Litmanovitch T, Trakhtenbrot L, Emanuelli A, et al. SMURF2 prevents detrimental changes to chromatin, protecting human dermal fibroblasts from chromosomal instability and tumorigenesis. Oncogene. 2020;39:3396–410.
Blank M, Tang Y, Yamashita M, Burkett SS, Cheng SY, Zhang YE. A tumor suppressor function of Smurf2 associated with controlling chromatin landscape and genome stability through RNF20. Nat Med. 2012;18:227–34.
Tan Y, Chen Y, Du M, Peng Z, Xie P. USF2 inhibits the transcriptional activity of Smurf1 and Smurf2 to promote breast cancer tumorigenesis. Cell Signal. 2019;53:49–58.
Sato Y, Heuckeroth RO. Retinoic acid regulates murine enteric nervous system precursor proliferation, enhances neuronal precursor differentiation, and reduces neurite growth in vitro. Dev Biol. 2008;320:185–98.
Panchenko MP, Siddiquee Z, Dombkowski DM, Alekseyev YO, Lenburg ME, Walker JD, et al. Protein kinase CK1alphaLS promotes vascular cell proliferation and intimal hyperplasia. Am J Pathol. 2010;177:1562–72.
Kwon A, Lee HL, Woo KM, Ryoo HM, Baek JH. SMURF1 plays a role in EGF-induced breast cancer cell migration and invasion. Mol Cell. 2013;36:548–55.
Gang X, Wang G, Huang H. Androgens regulate SMAD ubiquitination regulatory factor-1 expression and prostate cancer cell invasion. Prostate. 2015;75:561–72.
Chen P, Zhao D, Li J, Liang X, Li J, Chang A, et al. Symbiotic macrophage-glioma cell interactions reveal synthetic lethality in PTEN-Null glioma. Cancer Cell. 2019;35:868–884.e6.
Xu S, Hui L, Yang N, Wang Y, Zhao N, Jiang XJ. Upregulation of microRNA‑194‑5p inhibits hypopharyngeal carcinoma cell proliferation, migration and invasion by targeting SMURF1 via the mTOR signaling pathway. Int J Oncol. 2019;54:1245–55.
Li T, Xing Y, Yang F, Sun Y, Zhang S, Wang Q, et al. LncRNA SNHG3 sponges miR-577 to up-regulate SMURF1 expression in prostate cancer. Cancer Med. 2020;9:3852–62. https://doi.org/10.1002/cam4.2992. Epub 2020 Apr 5.
Jiang M, Shi L, Yang C, Ge Y, Lin L, Fan H, et al. miR-1254 inhibits cell proliferation, migration, and invasion by down-regulating Smurf1 in gastric cancer. Cell Death Dis. 2019;10:32.
Bian S. miR-4319 inhibited the development of thyroid cancer by modulating FUS-stabilized SMURF1. J Cell Biochem. 2020;121:174–82.
Liu J, Chen Y, Huang Q, Liu W, Ji X, Hu F, et al. IRAK2 counterbalances oncogenic Smurf1 in colon cancer cells by dictating ER stress. Cell Signal. 2018;48:69–80.
Chan MC, Nguyen PH, Davis BN, Ohoka N, Hayashi H, Du K, et al. A novel regulatory mechanism of the bone morphogenetic protein (BMP) signaling pathway involving the carboxyl-terminal tail domain of BMP type II receptor. Mol Cell Biol. 2007;27:5776–89.
Cui Y, He S, Xing C, Lu K, Wang J, Xing G, et al. SCFFBXL(1)(5) regulates BMP signalling by directing the degradation of HECT-type ubiquitin ligase Smurf1. EMBO J. 2011;30:2675–89.
Nie J, Wu M, Wang J, Xing G, He F, Zhang L. REGgamma proteasome mediates degradation of the ubiquitin ligase Smurf1. FEBS Lett. 2010;584:3021–7.
Kannan M, Lee SJ, Schwedhelm-Domeyer N, Stegmüller J. The E3 ligase Cdh1-anaphase promoting complex operates upstream of the E3 ligase Smurf1 in the control of axon growth. Development. 2012;139:3600–12.
Lu K, Yin X, Weng T, Xi S, Li L, Xing G, et al. Targeting WW domains linker of HECT-type ubiquitin ligase Smurf1 for activation by CKIP-1. Nat Cell Biol. 2008;10:994–1002.
Nie J, Liu L, Xing G, Zhang M, Wei R, Guo M, et al. CKIP-1 acts as a colonic tumor suppressor by repressing oncogenic Smurf1 synthesis and promoting Smurf1 autodegradation. Oncogene. 2014;33:3677–87.
Wan L, Zou W, Gao D, Inuzuka H, Fukushima H, Berg AH, et al. Cdh1 regulates osteoblast function through an APC/C-independent modulation of Smurf1. Mol Cell. 2011;44:721–33.
Ji CD, Wang YX, Xiang DF, Liu Q, Zhou ZH, Qian F, et al. Kir2.1 interaction with Stk38 promotes invasion and metastasis of human gastric cancer by enhancing MEKK2-MEK1/2-ERK1/2 signaling. Cancer Res. 2018;78:3041–53.
Seo D, Jung SM, Park JS, Lee J, Ha J, Kim M, et al. The deubiquitinating enzyme PSMD14 facilitates tumor growth and chemoresistance through stabilizing the ALK2 receptor in the initiation of BMP6 signaling pathway. EBioMedicine. 2019;49:55–71.
Chen YL, Liu B, Zhou ZN, Hu RY, Fei C, Xie ZH, et al. Smad6 inhibits the transcriptional activity of Tbx6 by mediating its degradation. J Biol Chem. 2009;284:23481–90.
Jiao J, Zhang R, Li Z, Yin Y, Fang X, Ding X, et al. Nuclear Smad6 promotes gliomagenesis by negatively regulating PIAS3-mediated STAT3 inhibition. Nat Commun. 2018;9:2504.
Wang Z, Wang J, Li X, Xing L, Ding Y, Shi P, et al. Bortezomib prevents oncogenesis and bone metastasis of prostate cancer by inhibiting WWP1, Smurf1 and Smurf2. Int J Oncol. 2014;45:1469–78.
Cao Y, Wang C, Zhang X, Xing G, Lu K, Gu Y, et al. Selective small molecule compounds increase BMP-2 responsiveness by inhibiting Smurf1-mediated Smad1/5 degradation. Sci Rep. 2014;4:4965.
Liu L, Zheng W, Song Y, Du X, Tang Y, Nie J, et al. miRNA-497 enhances the sensitivity of colorectal cancer cells to neoadjuvant chemotherapeutic drug. Curr Protein Pept Sci. 2015;16:310–5.
Lin H, Lin Q, Liu M, Lin Y, Wang X, Chen H, et al. PKA/Smurf1 signaling-mediated stabilization of Nur77 is required for anticancer drug cisplatin-induced apoptosis. Oncogene. 2014;33:1629–39.
Churcher I. Protac-induced protein degradation in drug discovery: breaking the rules or just making new ones? J Med Chem. 2018;61:444–52.
Neklesa TK, Winkler JD, Crews CM. Targeted protein degradation by PROTACs. Pharmacol Therapeut. 2017;174:138–44.
Smith BE, Wang SL, Jaime-Figueroa S, Harbin A, Wang J, Hamman BD, et al. Differential PROTAC substrate specificity dictated by orientation of recruited E3 ligase. Nat Commun. 2019;10:131.
Sakamoto KM, Kim KB, Kumagai A, Mercurio F, Crews CM, Deshaies RJ. Protacs: chimeric molecules that target proteins to the Skp1-Cullin-F box complex for ubiquitination and degradation. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 2001;98:8554–9.
Tian M, Zeng T, Liu M, Han S, Lin H, Lin Q, et al. A cell-based high-throughput screening method based on a ubiquitin-reference technique for identifying modulators of E3 ligases. J Biol Chem. 2019;294:2880–91.
Kaneki H, Guo R, Chen D, Yao Z, Schwarz EM, Zhang YE, et al. Tumor necrosis factor promotes Runx2 degradation through up-regulation of Smurf1 and Smurf2 in osteoblasts. J Biol Chem. 2006;281:4326–33.
Choi SH, Seo GY, Nam EH, Jeon SH, Kim HA, Park JB, et al. Opposing effects of Arkadia and Smurf on TGFbeta1-induced IgA isotype expression. Mol Cell. 2007;24:283–7.
Fei C, Li Z, Li C, Chen Y, Chen Z, He X, et al. Smurf1-mediated Lys29-linked nonproteolytic polyubiquitination of axin negatively regulates Wnt/beta-catenin signaling. Mol Cell Biol. 2013;33:4095–105.
Wang X, Jin C, Tang Y, Tang LY, Zhang YE. Ubiquitination of tumor necrosis factor receptor-associated factor 4 (TRAF4) by Smad ubiquitination regulatory factor 1 (Smurf1) regulates motility of breast epithelial and cancer cells. J Biol Chem. 2013;288:21784–92.
Zhang L, Liu J, Qian L, Feng Q, Wang X, Yuan Y, et al. Induction of OTUD1 by RNA viruses potently inhibits innate immune responses by promoting degradation of the MAVS/TRAF3/TRAF6 signalosome. PLoS Pathog. 2018;14:e1007067.
Li Z, Li L, Zhang H, Zhou HJ, Ji W, Min W. Short AIP1 (ASK1-Interacting Protein-1) isoform localizes to the mitochondria and promotes vascular dysfunction. Arterioscler Thromb Vasc Biol. 2020;40:112–27.
Wang J, Zhang Y, Weng W, Qiao Y, Ma L, Xiao W, et al. Impaired phosphorylation and ubiquitination by p70 S6 kinase (p70S6K) and Smad ubiquitination regulatory factor 1 (Smurf1) promote tribbles homolog 2 (TRIB2) stability and carcinogenic property in liver cancer. J Biol Chem. 2013;288:33667–81.
Li X, Dai X, Wan L, Inuzuka H, North BJ. Smurf1 regulation of DAB2IP controls cell proliferation and migration. Oncotarget. 2014;7:26057–69.
Yuan C, Qi J, Zhao X, Gao C. Smurf1 protein negatively regulates interferon-? signaling through promoting STAT1 protein ubiquitination and degradation. J Biol Chem. 2012;287:17006–15.
Xie P, Tang Y, Shen S, Wang Y, Xing G, Yin Y, et al. Smurf1 ubiquitin ligase targets Kruppel-like factor KLF2 for ubiquitination and degradation in human lung cancer H1299 cells. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 2011;407:254–9.
Shu L, Zhang H, Boyce BF, Xing L. Ubiquitin E3 ligase Wwp1 negatively regulates osteoblast function by inhibiting osteoblast differentiation and migration. J Bone Min Res. 2013;28:1925–35.
Li H, Xiao N, Wang Y, Wang R, Chen Y, Pan W, et al. Smurf1 regulates lung cancer cell growth and migration through interaction with and ubiquitination of PIPKIγ. Oncogene. 2017;36:5668–80.
Liu Y, Liu W, Hu C, Xue Z, Wang G, Ding B, et al. MiR-17 modulates osteogenic differentiation through a coherent feed-forward loop in mesenchymal stem cells isolated from periodontal ligaments of patients with periodontitis. Stem Cells. 2011;29:1804–16.
Liu W, Qi M, Konermann A, Zhang L, Jin F, Jin Y. The p53/miR-17/Smurf1 pathway mediates skeletal deformities in an age-related model via inhibiting the function of mesenchymal stem cells. Aging. 2015;7:205–18.
Guo R, Yamashita M, Zhang Q, Zhou Q, Chen D, Reynolds DG, et al. Ubiquitin ligase Smurf1 mediates tumor necrosis factor-induced systemic bone loss by promoting proteasomal degradation of bone morphogenetic signaling proteins. J Biol Chem. 2008;283:23084–92.
Gong W, Chen Z, Zou Y, Zhang L, Huang J, Liu P, et al. CKIP-1 affects the polyubiquitination of Nrf2 and Keap1 via mediating Smurf1 to resist HG-induced renal fibrosis in GMCs and diabetic mice kidneys. Free Radic Biol Med. 2018;115:338–50.
Tang X, Chen X, Xu Y, Qiao Y, Zhang X, Wang Y, et al. CD166 positively regulates MCAM via inhibition to ubiquitin E3 ligases Smurf1 and betaTrCP through PI3K/AKT and c-Raf/MEK/ERK signaling in Bel-7402 hepatocellular carcinoma cells. Cell Signal. 2015;27:1694–702.
Ito I, Hanyu A, Wayama M, Goto N, Katsuno Y, Kawasaki S, et al. Estrogen inhibits transforming growth factor beta signaling by promoting Smad2/3 degradation. J Biol Chem. 2010;285:14747–55.
Wen M, Ma X, Cheng H, Jiang W, Xu X, Zhang Y, et al. Stk38 protein kinase preferentially inhibits TLR9-activated inflammatory responses by promoting MEKK2 ubiquitination in macrophages. Nat Commun. 2015;6:7167.
Asanuma K, Yanagida-Asanuma E, Faul C, Tomino Y, Kim K, Mundel P. Synaptopodin orchestrates actin organization and cell motility via regulation of RhoA signalling. Nat Cell Biol. 2006;8:485–91.
Lee MG, Jeong SI, Ko KP, Park SK, Ryu BK, Kim IY, et al. RASSF1A directly antagonizes RhoA activity through the assembly of a Smurf1-mediated destruction complex to suppress tumorigenesis. Cancer Res. 2016;76:1847–59.
Sangadala S, Boden SD, Viggeswarapu M, Liu Y, Titus L. LIM mineralization protein-1 potentiates bone morphogenetic protein responsiveness via a novel interaction with Smurf1 resulting in decreased ubiquitination of Smads. J Biol Chem. 2006;281:17212–9.
Sangadala S, Yoshioka K, Enyo Y, Liu Y, Titus L, Boden SD. Characterization of a unique motif in LIM mineralization protein-1 that interacts with jun activation-domain-binding protein 1. Mol Cell Biochem. 2014;385:145–57.
Acknowledgements
This work was supported by grants from Beijing Natural Science Foundation (Z190018), The Natural Science Foundation of China (81870123), China Postdoctoral Science Foundation Grant (2018M641206), and the National Science Foundation for Young Scientists of China (81902545).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
All authors reviewed and approved the final manuscript. Q.X. and Y.L. contributed to the conception and design of paper. Y.L. drafted the paper. Q.X. provided useful comments and suggestions. L.D. and Q.X. revised the paper.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Additional information
Publisher’s note Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Xia, Q., Li, Y., Han, D. et al. SMURF1, a promoter of tumor cell progression?. Cancer Gene Ther 28, 551–565 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1038/s41417-020-00255-8
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/s41417-020-00255-8