Abstract
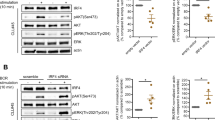
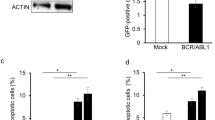
B-cell CLL/lymphoma 6 (BCL6) exerts oncogenic effects in several human hematopoietic malignancies including chronic myeloid leukemia (CML), where BCL6 expression was shown to be essential for CML stem cell survival and self-renewal during imatinib mesylate (IM) treatment. As several lines of evidence suggest that interferon γ (IFNγ) production in CML patients might have a central role in the response to tyrosine kinase inhibitor (TKI) therapy, we analyzed if IFNγ modulates BCL6 expression in CML cells. Although separate IFNγ or IM treatment only slightly upregulated BCL6 expression, combined treatment induced remarkable BCL6 upregulation in CML lines and primary human CD34+ CML stem cells. We proved that during combined treatment, inhibition of constitutive signal transducer and activator of transcription (STAT) 5 activation by IM allowed the specific enhancement of the STAT1 dependent, direct upregulation of BCL6 by IFNγ in CML cells. By using colony-forming assay, we found that IFNγ enhanced the ex vivo colony or cluster-forming capacity of human CML stem cells in the absence or presence of IM, respectively. Furthermore, inhibition of the transcriptional repressor function of BCL6 in the presence of IM and IFNγ almost completely blocked the cluster formation of human CML stem cells. On the other hand, by using small interfering RNA knockdown of BCL6, we demonstrated that in an IM-treated CML line the antiapoptotic effect of IFNγ was independent of BCL6 upregulation. We found that IFNγ also upregulated several antiapoptotic members of the BCL2 and BIRC gene families in CML cells, including the long isoform of MCL1, which proved to be essential for the antiapoptotic effect of IFNγ in an IM-treated CML line. Our results suggest that combination of TKIs with BCL6 and MCL1 inhibitors may potentially lead to the complete eradication of CML stem cells.
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 50 print issues and online access
$259.00 per year
only $5.18 per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on Springer Link
- Instant access to full article PDF
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout








Similar content being viewed by others
References
Chomel JC, Turhan AG . Chronic myeloid leukemia stem cells in the era of targeted therapies: resistance, persistence and long-term dormancy. Oncotarget 2011; 2: 713–727.
O’Hare T, Zabriskie MS, Eiring AM, Deininger MW . Pushing the limits of targeted therapy in chronic myeloid leukaemia. Nat Rev Cancer 2012; 12: 513–526.
Basso K, Dalla-Favera R . BCL6: master regulator of the germinal center reaction and key oncogene in B cell lymphomagenesis. Adv Immunol 2010; 105: 193–210.
Basso K, Dalla-Favera R . Roles of BCL6 in normal and transformed germinal center B cells. Immunol Rev 2012; 247: 172–183.
Bunting KL, Melnick AM . New effector functions and regulatory mechanisms of BCL6 in normal and malignant lymphocytes. Curr Opin Immunol 2013; 25: 339–346.
Kurosu T, Fukuda T, Miki T, Miura O . BCL6 overexpression prevents increase in reactive oxygen species and inhibits apoptosis induced by chemotherapeutic reagents in B-cell lymphoma cells. Oncogene 2003; 22: 4459–4468.
Tsuyama N, Danjoh I, Otsuyama K, Obata M, Tahara H, Ohta T et al. IL-6-induced Bcl6 variant 2 supports IL-6-dependent myeloma cell proliferation and survival through STAT3. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 2005; 337: 201–208.
Hideshima T, Mitsiades C, Ikeda H, Chauhan D, Raje N, Gorgun G et al. A proto-oncogene BCL6 is up-regulated in the bone marrow microenvironment in multiple myeloma cells. Blood 2010; 115: 3772–3775.
Green MR, Vicente-Dueñas C, Romero-Camarero I, Long Liu C, Dai B, González-Herrero I et al. Transient expression of Bcl6 is sufficient for oncogenic function and induction of mature B-cell lymphoma. Nat Commun 2014; 5: 3904.
Duy C, Hurtz C, Shojaee S, Cerchietti L, Geng H, Swaminathan S et al. BCL6 enables Ph+ acute lymphoblastic leukaemia cells to survive BCR-ABL1 kinase inhibition. Nature 2011; 473: 384–388.
Hurtz C, Hatzi K, Cerchietti L, Braig M, Park E, Kim YM et al. BCL6-mediated repression of p53 is critical for leukemia stem cell survival in chronic myeloid leukemia. J Exp Med 2011; 208: 2163–2174.
Boehm U, Klamp T, Groot M, Howard JC . Cellular responses to interferon-gamma. Annu Rev Immunol 1997; 15: 749–795.
Schroder K, Hertzog PJ, Ravasi T, Hume DA . Interferon-gamma: an overview of signals, mechanisms and functions. J Leukoc Biol 2004; 75: 163–189.
Dunn GP, Koebel CM, Schreiber RD . Interferons, immunity and cancer immunoediting. Nat Rev Immunol 2006; 6: 836–848.
Held SAE, Heine A, Kesper AR, Schönberg K, Beckers A, Wolf D et al. Interferon gamma modulates sensitivity of CML cells to tyrosine kinase inhibitors. OncoImmunology 2016; 5: e1065368.
Aswald JM, Lipton JH, Aswald S, Messner HA . Increased IFN-gamma synthesis by T cells from patients on imatinib therapy for chronic myeloid leukemia. Cytokines Cell Mol Ther 2002; 7: 143–149.
Kim DH, Kong JH, Byeun JY, Jung CW, Xu W, Liu X et al. The IFNG (IFN-gamma) genotype predicts cytogenetic and molecular response to imatinib therapy in chronic myeloid leukemia. Clin Cancer Res 2010; 16: 5339–5350.
Zhou G, Ono SJ . Induction of BCL-6 gene expression by interferon-gamma and identification of an IRE in exon I. Exp Mol Pathol 2005; 78: 25–35.
Lee SK, Silva DG, Martin JL, Pratama A, Hu X, Chang PP et al. Interferon-γ excess leads to pathogenic accumulation of follicular helper T cells and germinal centers. Immunity 2012; 37: 880–892.
Huang BB, Bonish BK, Chaturvedi V, Qin JZ, Nickoloff BJ . Keratinocyte CDw60 expression is modulated by both a Th-1 type cytokine IFN-gamma and Th-2 cytokines IL-4 and IL-13: relevance to psoriasis. J Invest Dermatol 2001; 116: 305–312.
Ohashi K, Miki T, Hirosawa S, Aoki N . Characterization of the promoter region of human BCL-6 gene. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 1995; 214: 461–467.
Walker SR, Nelson EA, Frank DA . STAT5 represses BCL6 expression by binding to a regulatory region frequently mutated in lymphomas. Oncogene 2007; 26: 224–233.
Gough DJ, Levy DE, Johnstone RW, Clarke CJ . IFNgamma signaling-does it mean JAK-STAT? Cytokine Growth Factor Rev 2008; 19: 383–394.
Warsch W, Walz C, Sexl V . JAK of all trades: JAK2-STAT5 as novel therapeutic targets in BCR-ABL1+ chronic myeloid leukemia. Blood 2013; 122: 2167–2175.
Mandal PK, Morlacchi P, Knight JM, Link TM, Lee GR IV, Nurieva R et al. Targeting the Src homology 2 (SH2) domain of signal transducer and activator of transcription 6 (STAT6) with cell-permeable, phosphatase-stable phosphopeptide mimics potently inhibits Tyr641 phosphorylation and transcriptional activity. J Med Chem 2015; 58: 8970–8984.
Jaras M, Johnels P, Hansen N, Agerstam H, Tsapogas P, Rissler M et al. Isolation and killing of candidate chronic myeloid leukemia stem cells by antibody targeting of IL-1 receptor accessory protein. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 2010; 107: 16280–16285.
Petzer AL, Zandstra PW, Piret JM, Eaves CJ . Differential cytokine effects on primitive (CD34+CD38-) human hematopoietic cells: novel responses to Flt3-ligand and thrombopoietin. J Exp Med 1996; 183: 2551–2558.
Schürch C, Riether C, Amrein MA, Ochsenbein AF . Cytotoxic T cells induce proliferation of chronic myeloid leukemia stem cells by secreting interferon-γ. J Exp Med 2013; 210: 605–621.
Cardenas MG, Yu W, Beguelin W, Teater MR, Geng H, Goldstein RL et al. Rationally designed BCL6 inhibitors target activated B cell diffuse large B cell lymphoma. J Clin Invest 2016; 126: 3351–3362.
Kuroda J, Puthalakath H, Cragg MS, Kelly PN, Bouillet P, Huang DC et al. Bim and Bad mediate imatinib-induced killing of Bcr/Abl+ leukemic cells, and resistance due to their loss is overcome by a BH3 mimetic. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 2006; 103: 14907–14912.
Youle RJ, Strasser A . The BCL-2 protein family: opposing activities that mediate cell death. Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol 2008; 9: 47–59.
Srinivasula SM, Ashwell JD . IAPs: what’s in a name? Mol Cell 2008; 30: 123–135.
Aichberger KJ, Mayerhofer M, Krauth MT, Skvara H, Florian S, Sonneck K et al. Identification of mcl-1 as a BCR/ABL-dependent target in chronic myeloid leukemia (CML): evidence for cooperative antileukemic effects of imatinib and mcl-1 antisense oligonucleotides. Blood 2005; 105: 3303–3311.
Opferman JT, Iwasaki H, Ong CC, Suh H, Mizuno S, Akashi K et al. Obligate role of anti-apoptotic MCL-1 in the survival of hematopoietic stem cells. Science 2005; 307: 1101–1104.
Leverson JD, Zhang H, Chen J, Tahir SK, Phillips DC, Xue J et al. Potent and selective small-molecule MCL-1 inhibitors demonstrate on-target cancer cell killing activity as single agents and in combination with ABT-263 (navitoclax). Cell Death Dis 2015; 6: e1590.
Walker SR, Nelson EA, Yeh JE, Pinello L, Yuan GC, Frank DA . STAT5 outcompetes STAT3 to regulate the expression of the oncogenic transcriptional modulator BCL6. Mol Cell Biol 2013; 33: 2879–2890.
Ritz O, Rommel K, Dorsch K, Kelsch E, Melzner J, Buck M et al. STAT6-mediated BCL6 repression in primary mediastinal B-cell lymphoma (PMBL). Oncotarget 2013; 4: 1093–1102.
Nakayamada S, Poholek AC, Lu KT, Takahashi H, Kato M, Iwata S et al. Type I IFN induces binding of STAT1 to Bcl6: divergent roles of STAT family transcription factors in the T follicular helper cell genetic program. J Immunol 2014; 192: 2156–2166.
Fernández de Mattos S, Essafi A, Soeiro I, Pietersen AM, Birkenkamp KU, Edwards CS et al. FoxO3a and BCR-ABL regulate cyclin D2 transcription through a STAT5/BCL6-dependent mechanism. Mol Cell Biol 2004; 24: 10058–10071.
Bonmort M, Ullrich E, Mignot G, Jacobs B, Chaput N, Zitvogel L . Interferon-gamma is produced by another player of innate immune responses: the interferon-producing killer dendritic cell (IKDC). Biochimie 2007; 89: 872–877.
Zoubir M, Tursz T, Ménard C, Zitvogel L, Chaput N . Imatinib mesylate (Gleevec): targeted therapy against cancer with immune properties. Endocr Metab Immune Disord Drug Targets 2010; 10: 1–7.
Krusch M, Salih HR . Effects of BCR-ABL inhibitors on anti-tumor immunity. Curr Med Chem 2011; 18: 5174–5184.
Christiansson L, Söderlund S, Mangsbo S, Hjorth-Hansen H, Höglund M, Markevärn B et al. The tyrosine kinase inhibitors imatinib and dasatinib reduce myeloid suppressor cells and release effector lymphocyte responses. Mol Cancer Ther 2015; 14: 1181–1191.
Prost S, Relouzat F, Spentchian M, Ouzegdouh Y, Saliba J, Massonnet G et al. Erosion of the chronic myeloid leukaemia stem cell pool by PPARγ agonists. Nature 2015; 525: 380–383.
Cunard R, Eto Y, Muljadi JT, Glass CK, Kelly CJ, Ricote M . Repression of IFN-gamma expression by peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor gamma. J Immunol 2004; 172: 7530–7536.
Zhang X, Rodriguez-Galán MC, Subleski JJ, Ortaldo JR, Hodge DL, Wang JM et al. Peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor-gamma and its ligands attenuate biologic functions of human natural killer cells. Blood 2004; 104: 3276–3284.
Nelson EA, Walker SR, Weisberg E, Bar-Natan M, Barrett R, Gashin LB et al. The STAT5 inhibitor pimozide decreases survival of chronic myelogenous leukemia cells resistant to kinase inhibitors. Blood 2011; 117: 3421–3429.
Warsch W, Kollmann K, Eckelhart E, Fajmann S, Cerny-Reiterer S, Hölbl A et al. High STAT5 levels mediate imatinib resistance and indicate disease progression in chronic myeloid leukemia. Blood 2011; 117: 3409–3420.
Kubonishi I, Miyoshi I . Establishment of a Ph1 chromosome-positive cell line from chronic myelogenous leukemia in blast crisis. Int J Cell Cloning 1983; 1: 105–117.
Di Noto R, Luciano L, Lo Pardo C, Ferrara F, Frigeri F, Mercuro O et al. JURL-MK1 (c-kit(high)/CD30-/CD40-) and JURL-MK2 (c-kit(low)/CD30+/CD40+) cell lines: ‘two-sided’ model for investigating leukemic megakaryocytopoiesis. Leukemia 1997; 11: 1554–1564.
Klein E, Klein G, Nadkarni JS, Nadkarni JJ, Wigzell H, Clifford P . Surface IgM-kappa specificity on a Burkitt lymphoma cell in vivo and in derived culture lines. Cancer Res 1968; 28: 1300–1310.
Acknowledgements
This work was supported by grants from the the Swedish Cancer Society (Cancerfonden), Adolf H Lundin Charitable Foundation and Karolinska Institutet. HM, NN, TK and DS are or were recipients of Cancer Research Fellowship of the Cancer Research Institute (New York)/Concern Foundation (Los Angeles).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Competing interests
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Additional information
Supplementary Information accompanies this paper on the Oncogene website
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Madapura, H., Nagy, N., Ujvari, D. et al. Interferon γ is a STAT1-dependent direct inducer of BCL6 expression in imatinib-treated chronic myeloid leukemia cells. Oncogene 36, 4619–4628 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1038/onc.2017.85
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/onc.2017.85
This article is cited by
-
Eliminating chronic myeloid leukemia stem cells by IRAK1/4 inhibitors
Nature Communications (2022)
-
Combination of tyrosine kinase inhibitors and the MCL1 inhibitor S63845 exerts synergistic antitumorigenic effects on CML cells
Cell Death & Disease (2021)
-
Infliximab therapy together with tyrosine kinase inhibition targets leukemic stem cells in chronic myeloid leukemia
BMC Cancer (2019)
-
Chronic myeloid leukemia stem cells
Leukemia (2019)