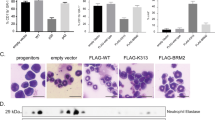
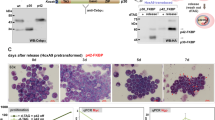
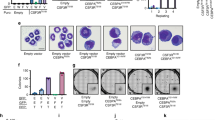
Key Points
-
CCAAT/enhancer-binding protein-α (C/EBPα) is a transcription factor that coordinates cellular differentiation with growth arrest.
-
Patients with acute myeloid leukaemia carry specific combinations of point mutations in the gene encoding C/EBPα.
-
C/EBPα represses the E2F transcription factor. Patient-derived C/EBPα mutants generally loose the ability to bind DNA or to repress E2F activity.
-
C/EBPα expression inhibits the malignant potential of myeloid leukaemia cells by inducing their differentiation.
-
E2F repression and DNA binding by C/EBPα are required for the C/EBP-induced differentiation of leukaemia cells.
-
Reconstituting C/EBPα-mediated E2F repression has the potential to revert leukaemogenesis in vivo.
Abstract
Specific mutations in the gene that encodes the multifunctional transcription factor C/EBPα are frequently associated with acute myeloid leukaemias. Are only a specific subset of the functions of C/EBPα therefore involved in leukaemogenesis?
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 12 print issues and online access
$209.00 per year
only $17.42 per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on Springer Link
- Instant access to full article PDF
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout




Similar content being viewed by others
References
Tenen, D. G. Disruption of differentiation in human cancer: AML shows the way. Nature Rev. Cancer 3, 89–101 (2003).
Wang, N. D. et al. Impaired energy homeostasis in C/EBPα knockout mice. Science 269, 1108–1112 (1995). This paper demonstrates the requirement for C/EBPα during white-fat adipogenesis.
Zhang, D. E. et al. Absence of granulocyte colony-stimulating factor signaling and neutrophil development in CCAAT enhancer binding protein α-deficient mice. Proc. Natl Acad. Sci. USA 94, 569–574 (1997). This paper provided the first demonstration of a block in granulopoiesis in the absence of the C/EBPα protein.
Freytag, S. O., Paielli, D. L. & Gilbert, J. D. Ectopic expression of the CCAAT/enhancer-binding protein α promotes the adipogenic program in a variety of mouse fibroblastic cells. Genes Dev. 8, 1654–1663 (1994).
Radomska, H. S. et al. CCAAT/enhancer binding protein α is a regulatory switch sufficient for induction of granulocytic development from bipotential myeloid progenitors. Mol. Cell. Biol. 18, 4301–4314 (1998).
Nerlov, C., McNagny, K. M., Doderlein, G., Kowenz-Leutz, E. & Graf, T. Distinct C/EBP functions are required for eosinophil lineage commitment and maturation. Genes Dev. 12, 2413–2423 (1998).
Lin, F. T., MacDougald, O. A., Diehl, A. M. & Lane, M. D. A 30-kDa alternative translation product of the CCAAT/enhancer binding protein α message: transcriptional activator lacking antimitotic activity. Proc. Natl Acad. Sci. USA 90, 9606–9610 (1993).
Calkhoven, C. F., Muller, C. & Leutz, A. Translational control of C/EBPα and C/EBPβ isoform expression. Genes Dev. 14, 1920–1932 (2000). An elegant demonstration of how translational control can alter the function of a transcription factor by selectively including or excluding functional domains in response to extracellular signalling.
Rosenwald, I. B., Rhoads, D. B., Callanan, L. D., Isselbacher, K. J. & Schmidt, E. V. Increased expression of eukaryotic translation initiation factors eIF-4E and eIF-2α in response to growth induction by c-myc. Proc. Natl Acad. Sci. USA 90, 6175–6178 (1993).
D'Alo', F. et al. The amino terminal and E2F interaction domains are critical for C/EBPα-mediated induction of granulopoietic development of hematopoietic cells. Blood 102, 3163–3171 (2003).
Lazaris-Karatzas, A., Montine, K. S. & Sonenberg, N. Malignant transformation by a eukaryotic initiation factor subunit that binds to mRNA 5′ cap. Nature 345, 544–547 (1990).
Pabst, T. et al. Dominant-negative mutations of CEBPA, encoding CCAAT/enhancer binding protein-α (C/EBPα), in acute myeloid leukemia. Nature Genet. 27, 263–270 (2001). The first demonstration of mutations in a lineage-specific transcriptional regulator in patients with AML.
Gombart, A. F. et al. Mutations in the gene encoding the transcription factor CCAAT/enhancer binding protein α in myelodysplastic syndromes and acute myeloid leukemias. Blood 99, 1332–1340 (2002).
Preudhomme, C. et al. Favorable prognostic significance of CEBPA mutations in patients with de novo acute myeloid leukemia: a study from the Acute Leukemia French Association (ALFA). Blood 100, 2717–2723 (2002).
Van Waalwijk Van Doorn-Khosrovani, S. B. et al. Biallelic mutations in the CEBPA gene and low CEBPA expression levels as prognostic markers in intermediate-risk AML. Hematol. J. 4, 31–40 (2003).
Kaeferstein, A. et al. The emergence of a C/EBPα mutation in the clonal evolution of MDS towards secondary AML. Leukemia 17, 343–349 (2003).
Snaddon, J. et al. Mutations of CEBPA in acute myeloid leukemia FAB types M1 and M2. Genes Chromosom. Cancer 37, 72–78 (2003).
Asou, H. et al. Establishment of the acute myeloid leukemia cell line Kasumi-6 from a patient with a dominant-negative mutation in the DNA-binding region of the C/EBPα gene. Genes Chromosom. Cancer 36, 167–174 (2003).
Pabst, T. et al. AML1–ETO downregulates the granulocytic differentiation factor C/EBPα in t(8;21) myeloid leukemia. Nature Med. 7, 444–451 (2001).
Cilloni, D. et al. Down-modulation of the C/EBPα transcription factor in core binding factor acute myeloid leukemias. Blood 102, 2705–2706 (2003).
Perrotti, D. et al. BCR–ABL suppresses C/EBPα expression through inhibitory action of hnRNP E2. Nature Genet. 30, 48–58 (2002).
Friedman, A. D., Landschulz, W. H. & McKnight, S. L. CCAAT/enhancer binding protein activates the promoter of the serum albumin gene in cultured hepatoma cells. Genes Dev. 3, 1314–1363 (1989).
Christy, R. J. et al. Differentiation-induced gene expression in 3T3-L1 preadipocytes: CCAAT/enhancer binding protein interacts with and activates the promoters of two adipocyte-specific genes. Genes Dev. 3, 1323–1335 (1989).
Tenen, D. G., Hromas, R., Licht, J. D. & Zhang, D. E. Transcription factors, normal myeloid development, and leukemia. Blood 90, 489–519 (1997).
McNagny, K. M., Sieweke, M. H., Doderlein, G., Graf, T. & Nerlov, C. Regulation of eosinophil-specific gene expression by a C/EBP–Ets complex and GATA-1. EMBO J. 17, 3669–3680 (1998).
Nerlov, C. & Ziff, E. B. CCAAT/enhancer binding protein-α amino acid motifs with dual TBP and TFIIB binding ability co-operate to activate transcription in both yeast and mammalian cells. EMBO J. 14, 4318–4328 (1995).
Kovacs, K. A., Steinmann, M., Magistretti, P. J., Halfon, O. & Cardinaux, J. R. CCAAT/enhancer-binding protein family members recruit the coactivator CREB-binding protein and trigger its phosphorylation. J. Biol. Chem. 278, 36959–36965 (2003).
Schwartz, C. et al. Recruitment of p300 by C/EBPβ triggers phosphorylation of p300 and modulates coactivator activity. EMBO J. 22, 882–892 (2003).
Pedersen, T. A., Kowenz-Leutz, E., Leutz, A. & Nerlov, C. Cooperation between C/EBPα TBP/TFIIB and SWI/SNF recruiting domains is required for adipocyte differentiation. Genes Dev. 15, 3208–3216 (2001).
Zhang, D. E. et al. CCAAT enhancer-binding protein (C/EBP) and AML1 (CBF α2) synergistically activate the macrophage colony-stimulating factor receptor promoter. Mol. Cell. Biol. 16, 1231–1240 (1996).
Yamaguchi, Y., Nishio, H., Kishi, K., Ackerman, S. J. & Suda, T. C. EBPβ and GATA-1 synergistically regulate activity of the eosinophil granule major basic protein promoter: implication for C/EBPβ activity in eosinophil gene expression. Blood 94, 1429–1439 (1999).
Reddy, V. A. et al. Granulocyte inducer C/EBPα inactivates the myeloid master regulator PU. 1: possible role in lineage commitment decisions. Blood 100, 483–490 (2002).
Umek, R. M., Friedman, A. D. & McKnight, S. L. CCAAT-enhancer binding protein: a component of a differentiation switch. Science 251, 288–292 (1991).
Muller, C. et al. Separation of C/EBPα-mediated proliferation arrest and differentiation pathways. Proc. Natl Acad. Sci. USA 96, 7276–7281 (1999).
Timchenko, N. A. et al. CCAAT/enhancer binding protein α regulates p21 protein and hepatocyte proliferation in newborn mice. Mol. Cell. Biol. 17, 7353–7361 (1997).
Wang, H. et al. C/EBPα arrests cell proliferation through direct inhibition of Cdk2 and Cdk4. Mol. Cell 8, 817–828 (2001).
Harbour, J. W. & Dean, D. C. The Rb/E2F pathway: expanding roles and emerging paradigms. Genes Dev. 14, 2393–2409 (2000).
Slomiany, B. A., D'Arigo, K. L., Kelly, M. M. & Kurtz, D. T. C/EBPα inhibits cell growth via direct repression of E2F-DP-mediated transcription. Mol. Cell. Biol. 20, 5986–5997 (2000). The first demonstration of the capacity of C/EBPα to repress E2F-dependent transcription.
Porse, B. T. et al. E2F repression by C/EBPα is required for adipogenesis and granulopoiesis in vivo. Cell 107, 247–258 (2001). An in vivo demonstration of the coupling between cell-cycle control and terminal differentiation by C/EBPα.
Johansen, L. M. et al. c-Myc is a critical target for c/EBPα in granulopoiesis. Mol. Cell. Biol. 21, 3789–3806 (2001).
Hendricks-Taylor, L. R. & Darlington, G. J. Inhibition of cell proliferation by C/EBPα occurs in many cell types, does not require the presence of p53 or Rb, and is not affected by large T-antigen. Nucleic Acids Res. 23, 4726–4733 (1995).
Wang, Q. F., Cleaves, R., Kummalue, T., Nerlov, C. & Friedman, A. D. Cell cycle inhibition mediated by the outer surface of the C/EBPα basic region is required but not sufficient for granulopoiesis. Oncogene 22, 2548–2557 (2003).
Muller, C., Calkhoven, C. F., Sha, X. & Leutz, A. The CCAAT enhancer-binding protein α (C/EBPα) requires a SWI/SNF complex for proliferation arrest. J. Biol. Chem. 279, 7353–7358 (2004).
Zhang, H. S. & Dean, D. C. Rb-mediated chromatin structure regulation and transcriptional repression. Oncogene 20, 3134–3138 (2001).
Strom, D. K., Cleveland, J. L., Chellappan, S., Nip, J. & Hiebert, S. W. E2F-1 and E2F-3 are functionally distinct in their ability to promote myeloid cell cycle progression and block granulocyte differentiation. Cell Growth Differ. 9, 59–69 (1998).
Bjerregaard, M. D., Jurlander, J., Klausen, P., Borregaard, N. & Cowland, J. B. The in vivo profile of transcription factors during neutrophil differentiation in human bone marrow. Blood 101, 4322–4332 (2003).
Duprez, E., Wagner, K., Koch, H. & Tenen, D. G. C/EBPβ: a major PML–RARA-responsive gene in retinoic acid-induced differentiation of APL cells. EMBO J. 22, 5806–5816 (2003).
Gery, S., Gombart, A. F., Fung, Y. K. & Koeffler, H. P. C/EBPε interacts with retinoblastoma and E2F1 during granulopoiesis. Blood 103, 828–835 (2003).
Verbeek, W., Wachter, M., Lekstrom-Himes, J. & Koeffler, H. P. C/EBPε−/− mice: increased rate of myeloid proliferation and apoptosis. Leukemia 15, 103–111 (2001).
Jones, L. C. et al. Expression of C/EBPβ from the C/ebpα gene locus is sufficient for normal hematopoiesis in vivo. Blood 99, 2032–2036 (2002).
Truong, B. T. et al. CCAAT/Enhancer binding proteins repress the leukemic phenotype of acute myeloid leukemia. Blood 101, 1141–1148 (2003).
Timchenko, N. A., Wilde, M., Nakanishi, M., Smith, J. R. & Darlington, G. J. CCAAT/enhancer-binding protein α (C/EBPα) inhibits cell proliferation through the p21 (WAF-1/CIP-1/SDI-1) protein. Genes Dev. 10, 804–815 (1996).
Timchenko, N. A., Wilde, M. & Darlington, G. J. C/EBPα regulates formation of S-phase-specific E2F–107 complexes in livers of newborn mice. Mol. Cell. Biol. 19, 2936–2945 (1999).
Iakova, P., Awad, S. S. & Timchenko, N. A. Aging reduces proliferative capacities of liver by switching pathways of C/EBPα growth arrest. Cell 113, 495–506 (2003).
Ross, S. E., Erickson, R. L., Hemati, N. & MacDougald, O. A. Glycogen synthase kinase 3 is an insulin-regulated C/EBPα kinase. Mol. Cell. Biol. 19, 8433–8441 (1999).
Behre, G. et al. Ras signaling enhances the activity of C/EBPα to induce granulocytic differentiation by phosphorylation of serine 248. J. Biol. Chem. 277, 26293–26299 (2002).
Weinstein, H. & Griffin, J. D. in Blood, Principles and Practice of Hematology (eds Handin, R. I., Lux, S. E. & Stossel, T. P.) 543–574 (J.B. Lippincott Company, Philadelphia, USA, 1995).
Acknowledgements
The author thanks B. Porse, A. Leutz and D. Tenen for helpful discussions, and present as well as former members of the Nerlov lab for their contributions to this article.
Correction: The DOI number given for this article in the May 2004 print issue of Nature Reviews Cancer was wrong. The correct DOI number is: doi:10.1038/nrc1363.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Ethics declarations
Competing interests
The author declares no competing financial interests.
Glossary
- BASELINE GRANULOPOIESIS
-
Normal physiological granulopoiesis, in which a myeloblast matures into a fully differentiated granulocyte, typically takes about 11–12 days. This is opposed to the accelerated granulopoiesis that occurs under conditions of stress, such as in the case of severe infection, when granulocytes are produced much more rapidly.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Nerlov, C. C/EBPα mutations in acute myeloid leukaemias. Nat Rev Cancer 4, 394–400 (2004). https://doi.org/10.1038/nrc1363
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/nrc1363
This article is cited by
-
Targeting C/EBPα overcomes primary resistance and improves the efficacy of FLT3 inhibitors in acute myeloid leukaemia
Nature Communications (2023)
-
Identification and interrogation of the gene regulatory network of CEBPA-double mutant acute myeloid leukemia
Leukemia (2023)
-
Sporadic and Familial Acute Myeloid Leukemia with CEBPA Mutations
Current Hematologic Malignancy Reports (2023)
-
Identification of gene targets of mutant C/EBPα reveals a critical role for MSI2 in CEBPA-mutated AML
Leukemia (2021)
-
The AML-associated K313 mutation enhances C/EBPα activity by leading to C/EBPα overexpression
Cell Death & Disease (2021)