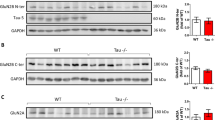
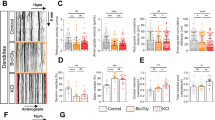
Abstract
Amyloid-β peptide is elevated in the brains of patients with Alzheimer disease and is believed to be causative in the disease process. Amyloid-β reduces glutamatergic transmission and inhibits synaptic plasticity, although the underlying mechanisms are unknown. We found that application of amyloid-β promoted endocytosis of NMDA receptors in cortical neurons. In addition, neurons from a genetic mouse model of Alzheimer disease expressed reduced amounts of surface NMDA receptors. Reducing amyloid-β by treating neurons with a γ-secretase inhibitor restored surface expression of NMDA receptors. Consistent with these data, amyloid-β application produced a rapid and persistent depression of NMDA-evoked currents in cortical neurons. Amyloid-β–dependent endocytosis of NMDA receptors required the α-7 nicotinic receptor, protein phosphatase 2B (PP2B) and the tyrosine phosphatase STEP. Dephosphorylation of the NMDA receptor subunit NR2B at Tyr1472 correlated with receptor endocytosis. These data indicate a new mechanism by which amyloid-β can cause synaptic dysfunction and contribute to Alzheimer disease pathology.
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 12 print issues and online access
$209.00 per year
only $17.42 per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on Springer Link
- Instant access to full article PDF
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout







Similar content being viewed by others
References
Perdahl, E., Wu, W.C., Browning, M.D., Winblad, B. & Greengard, P. Protein III, a neuron-specific phosphoprotein: variant forms found in human brain. Neurobehav. Toxicol. Teratol. 6, 425–431 (1984).
Terry, R.D. et al. Physical basis of cognitive alterations in Alzheimer's disease: synapse loss is the major correlate of cognitive impairment. Ann. Neurol. 30, 572–580 (1991).
Takahashi, R.H. et al. Oligomerization of Alzheimer's β-amyloid within processes and synapses of cultured neurons and brain. J. Neurosci. 24, 3592–3599 (2004).
Selkoe, D.J. Alzheimer's disease is a synaptic failure. Science 298, 789–791 (2002).
Hardy, J. & Selkoe, D.J. The amyloid hypothesis of Alzheimer's disease: progress and problems on the road to therapeutics. Science 297, 353–356 (2002).
Chapman, P.F. et al. Impaired synaptic plasticity and learning in aged amyloid precursor protein transgenic mice. Nat. Neurosci. 2, 271–276 (1999).
Freir, D.B., Holscher, C. & Herron, C.E. Blockade of long-term potentiation by β-amyloid peptides in the CA1 region of the rat hippocampus in vivo. J. Neurophysiol. 85, 708–713 (2001).
Kim, J.H., Anwyl, R., Suh, Y.H., Djamgoz, M.B. & Rowan, M.J. Use-dependent effects of amyloidogenic fragments of (β)-amyloid precursor protein on synaptic plasticity in rat hippocampus in vivo. J. Neurosci. 21, 1327–1333 (2001).
Malenka, R.C. Synaptic plasticity and AMPA receptor trafficking. Ann. NY Acad. Sci. 1003, 1–11 (2003).
Naslund, J. et al. Correlation between elevated levels of amyloid β-peptide in the brain and cognitive decline. J. Am. Med. Assoc. 283, 1571–1577 (2000).
Kamenetz, F. et al. APP processing and synaptic function. Neuron 37, 925–937 (2003).
Snyder, E.M. et al. Internalization of ionotropic glutamate receptors in response to mGluR activation. Nat. Neurosci. 4, 1079–1085 (2001).
Roche, K.W. et al. Molecular determinants of NMDA receptor internalization. Nat. Neurosci. 4, 794–802 (2001).
Nong, Y. et al. Glycine binding primes NMDA receptor internalization. Nature 422, 302–307 (2003).
Scott, D.B., Michailidis, I., Mu, Y., Logothetis, D. & Ehlers, M.D. Endocytosis and degradative sorting of NMDA receptors by conserved membrane-proximal signals. J. Neurosci. 24, 7096–7109 (2004).
Mammen, A.L., Huganir, R.L. & O'Brien, R.J. Redistribution and stabilization of cell surface glutamate receptors during synapse formation. J. Neurosci. 17, 7351–7358 (1997).
Rao, A. & Craig, A.M. Activity regulates the synaptic localization of the NMDA receptor in hippocampal neurons. Neuron 19, 801–812 (1997).
Ehlers, M.D. Reinsertion or degradation of AMPA receptors determined by activity-dependent endocytic sorting. Neuron 28, 511–525 (2000).
Ehlers, M.D. Activity level controls postsynaptic composition and signaling via the ubiquitin-proteasome system. Nat. Neurosci. 6, 231–242 (2003).
Cai, D. et al. Presenilin-1 regulates intracellular trafficking and cell surface delivery of β-amyloid precursor protein. J. Biol. Chem. 278, 3446–3454 (2003).
Wang, H.Y. et al. β-Amyloid(1–42) binds to α7 nicotinic acetylcholine receptor with high affinity. Implications for Alzheimer's disease pathology. J. Biol. Chem. 275, 5626–5632 (2000).
Dineley, K.T. et al. β-amyloid activates the mitogen-activated protein kinase cascade via hippocampal α7 nicotinic acetylcholine receptors: In vitro and in vivo mechanisms related to Alzheimer's disease. J. Neurosci. 21, 4125–4133 (2001).
Levy, R.B. & Aoki, C. α7 nicotinic acetylcholine receptors occur at postsynaptic densities of AMPA receptor-positive and -negative excitatory synapses in rat sensory cortex. J. Neurosci. 22, 5001–5015 (2002).
Shi, J., Townsend, M. & Constantine-Paton, M. Activity-dependent induction of tonic calcineurin activity mediates a rapid developmental downregulation of NMDA receptor currents. Neuron 28, 103–114 (2000).
Stevens, T.R., Krueger, S.R., Fitzsimonds, R.M. & Picciotto, M.R. Neuroprotection by nicotine in mouse primary cortical cultures involves activation of calcineurin and L-type calcium channel inactivation. J. Neurosci. 23, 10093–10099 (2003).
Wang, Y.T. & Salter, M.W. Regulation of NMDA receptors by tyrosine kinases and phosphatases. Nature 369, 233–235 (1994).
Vissel, B., Krupp, J.J., Heinemann, S.F. & Westbrook, G.L. A use-dependent tyrosine dephosphorylation of NMDA receptors is independent of ion flux. Nat. Neurosci. 4, 587–596 (2001).
Pelkey, K.A. et al. Tyrosine phosphatase STEP is a tonic brake on induction of long-term potentiation. Neuron 34, 127–138 (2002).
Paul, S., Nairn, A.C., Wang, P. & Lombroso, P.J. NMDA-mediated activation of the tyrosine phosphatase STEP regulates the duration of ERK signaling. Nat. Neurosci. 6, 34–42 (2003).
Lavezzari, G., McCallum, J., Lee, R. & Roche, K.W. Differential binding of the AP-2 adaptor complex and PSD-95 to the C-terminus of the NMDA receptor subunit NR2B regulates surface expression. Neuropharmacology 45, 729–737 (2003).
Shaywitz, A.J. & Greenberg, M.E. CREB: a stimulus-induced transcription factor activated by a diverse array of extracellular signals. Annu. Rev. Biochem. 68, 821–861 (1999).
Tong, L., Thornton, P.L., Balazs, R. & Cotman, C.W. β-amyloid-(1–42) impairs activity-dependent cAMP-response element-binding protein signaling in neurons at concentrations in which cell survival is not compromised. J. Biol. Chem. 276, 17301–17306 (2001).
Shieh, P.B., Hu, S.C., Bobb, K., Timmusk, T. & Ghosh, A. Identification of a signaling pathway involved in calcium regulation of BDNF expression. Neuron 20, 727–740 (1998).
Tao, X., Finkbeiner, S., Arnold, D.B., Shaywitz, A.J. & Greenberg, M.E. Ca2+ influx regulates BDNF transcription by a CREB family transcription factor-dependent mechanism. Neuron 20, 709–726 (1998).
Riccio, A., Ahn, S., Davenport, C.M., Blendy, J.A. & Ginty, D.D. Mediation by a CREB family transcription factor of NGF-dependent survival of sympathetic neurons. Science 286, 2358–2361 (1999).
Taubenfeld, S.M., Milekic, M.H., Monti, B. & Alberini, C.M. The consolidation of new but not reactivated memory requires hippocampal C/EBPβ. Nat. Neurosci. 4, 813–818 (2001).
Yamamoto-Sasaki, M., Ozawa, H., Saito, T., Rosler, M. & Riederer, P. Impaired phosphorylation of cyclic AMP response element binding protein in the hippocampus of dementia of the Alzheimer type. Brain Res. 824, 300–303 (1999).
Valjent, E. et al. Regulation of a protein phosphatase cascade allows convergent dopamine and glutamate signals to activate ERK in the striatum. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 102, 491–496 (2005).
Alvestad, R.M. et al. Tyrosine dephosphorylation and ethanol inhibition of N-methyl-D-aspartate receptor function. J. Biol. Chem. 278, 11020–11025 (2003).
Schwarze, S.R., Ho, A., Vocero-Akbani, A. & Dowdy, S.F. In vivo protein transduction: delivery of a biologically active protein into the mouse. Science 285, 1569–1572 (1999).
Acknowledgements
We thank M. Greenberg for the gift of phospho-NR2B antibody and G. Thinakaran and S. Sisodia for the gift of stably transfected N2A cells. We also thank J. Shepherd and members of the Greengard and Gouras labs for helpful discussions. This work was supported by the Fisher Foundation for Alzheimer's Research, US National Institutes of Health grant AG09464 (P.G.T. and G.K.G.) and National Institute of Mental Health grant 52711 and 01527 (P.J.L.).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Competing interests
The authors declare no competing financial interests.
Supplementary information
Supplementary Fig. 1
Methyllycaconitine (MLA) inhibits the effect of amyloid-β on NMDA receptors. (PDF 478 kb)
Supplementary Fig. 2
Model of amyloid-β regulation of glutamate receptor trafficking. (PDF 1752 kb)
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Snyder, E., Nong, Y., Almeida, C. et al. Regulation of NMDA receptor trafficking by amyloid-β. Nat Neurosci 8, 1051–1058 (2005). https://doi.org/10.1038/nn1503
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/nn1503
This article is cited by
-
Extrasynaptic NMDA receptors in acute and chronic excitotoxicity: implications for preventive treatments of ischemic stroke and late-onset Alzheimer’s disease
Molecular Neurodegeneration (2023)
-
Neuronal MHC-I complex is destabilized by amyloid-β and its implications in Alzheimer’s disease
Cell & Bioscience (2023)
-
Amyloid β-based therapy for Alzheimer’s disease: challenges, successes and future
Signal Transduction and Targeted Therapy (2023)
-
STIM2 regulates NMDA receptor endocytosis that is induced by short-term NMDA receptor overactivation in cortical neurons
Cellular and Molecular Life Sciences (2023)
-
Anti-Amyloid Immunotherapies for Alzheimer's Disease: A 2023 Clinical Update
Neurotherapeutics (2023)