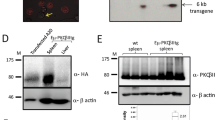
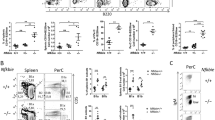
Abstract
Phosphoinositide 3-kinase (PI3K) and phosphatase and tensin homolog (PTEN) phosphatase serve essential functions in the regulation of cell growth, differentiation and survival by modulating intracellular phosphatidylinositol-3,4,5-trisphosphate (PI-3,4,5-P3) concentrations. Here we show that the conditional deletion of Pten in B cells led to the preferential generation of marginal zone (MZ) B cells and B1 cells. PTEN-deficient B cells were hyperproliferative in response to mitogenic stimuli, and exhibited a lower threshold for activation through the B cell antigen receptor. Inactivation of PTEN rescued germinal center, MZ B and B1 cell formation in CD19−/− mice, arguing that recruitment and activation of PI3K are the dominant roles for CD19 in these B cell subpopulations. These findings establish the central role of PI-3,4,5-P3 regulation in the differentiation of peripheral B cell subsets.
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 12 print issues and online access
$209.00 per year
only $17.42 per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on Springer Link
- Instant access to full article PDF
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout






Similar content being viewed by others
References
Martin, F., Oliver, A.M. & Kearney, J.F. Marginal zone and B1 B cells unite in the early response against T-independent blood-borne particulate antigens. Immunity 14, 617–629 (2001).
Berland, R. & Wortis, H.H. Origins and functions of B-1 cells with notes on the role of CD5. Annu. Rev. Immunol. 20, 253–300 (2002).
Fruman, D.A., Satterthwaite, A.B. & Witte, O.N. Xid-like phenotypes: a B cell signalosome takes shape. Immunity 13, 1–3 (2000).
Turner, M. & Billadeau, D.D. VAV proteins as signal integrators for multi-subunit immune-recognition receptors. Nat. Rev. Immunol. 2, 476–486 (2002).
Anderson, K.E., Coadwell, J., Stephens, L.R. & Hawkins, P.T. Translocation of PDK-1 to the plasma membrane is important in allowing PDK-1 to activate protein kinase B. Curr. Biol. 8, 684–691 (1998).
Fruman, D.A. & Cantley, L.C. Phosphoinositide 3-kinase in immunological systems. Semin. Immunol. 14, 7–18 (2002).
Fruman, D.A. et al. Impaired B cell development and proliferation in absence of phosphoinositide 3-kinase p85α. Science 283, 393–397 (1999).
Suzuki, H. et al. Xid-like immunodeficiency in mice with disruption of the p85α subunit of phosphoinositide 3-kinase. Science 283, 390–392 (1999).
Okkenhaug, K. et al. Impaired B and T cell antigen receptor signaling in p110δ PI 3-kinase mutant mice. Science 297, 1031–1034 (2002).
Clayton, E. et al. A crucial role for the p110δ subunit of phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase in B cell development and activation. J. Exp. Med. 196, 753–763 (2002).
Tuveson, D.A., Carter, R.H., Soltoff, S.P. & Fearon, D.T. CD19 of B cells as a surrogate kinase insert region to bind phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase. Science 260, 986–989 (1993).
Wang, Y. et al. The physiologic role of CD19 cytoplasmic tyrosines. Immunity 17, 501–514 (2002).
Buhl, A.M., Pleiman, C.M., Rickert, R.C. & Cambier, J.C. Qualitative regulation of B cell antigen receptor signaling by CD19: selective requirement for PI3-kinase activation, inositol-1,4,5-trisphosphate production and Ca2+ mobilization. J. Exp. Med. 186, 1897–1910 (1997).
Buhl, A.M. & Cambier, J.C. Phosphorylation of CD19 Y484 and Y515, and linked activation of phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase, are required for B cell antigen receptor-mediated activation of Bruton's tyrosine kinase. J. Immunol. 162, 4438–4446 (1999).
Otero, D.C., Omori, S.A. & Rickert, R.C. CD19-dependent activation of Akt kinase in B-lymphocytes. J. Biol. Chem. 276, 1474–1478 (2001).
Fujimoto, M. et al. Complementary roles for CD19 and Bruton's tyrosine kinase in B lymphocyte signal transduction. J. Immunol. 168, 5465–5476 (2002).
Engel, P. et al. Abnormal B lymphocyte development, activation, and differentiation in mice that lack or overexpress the CD19 signal transduction molecule. Immunity 3, 39–50 (1995).
Rickert, R.C., Rajewsky, K. & Roes, J. Impairment of T-cell-dependent B-cell responses and B-1 cell development in CD19-deficient mice. Nature 376, 352–355 (1995).
Martin, F. & Kearney, J.F. Positive selection from newly formed to marginal zone B cells depends on the rate of clonal production, CD19, and btk. Immunity 12, 39–49 (2000).
Rameh, L.E. & Cantley, L.C. The role of phosphoinositide 3-kinase lipid products in cell function. J. Biol. Chem. 274, 8347–8350 (1999).
Leslie, N.R. & Downes, C.P. PTEN: the down side of PI 3-kinase signalling. Cell. Signal. 14, 285–295 (2002).
Stambolic, V. et al. Negative regulation of PKB/Akt-dependent cell survival by the tumor suppressor PTEN. Cell 95, 29–39 (1998).
Groszer, M. et al. Negative regulation of neural stem/progenitor cell proliferation by the Pten tumor suppressor gene in vivo. Science 294, 2186–2189 (2001).
Lesche, R. et al. Cre/loxP-mediated inactivation of the murine Pten tumor suppressor gene. Genesis 32, 148–149 (2002).
Rickert, R.C., Roes, J. & Rajewsky, K. B lymphocyte-specific, Cre-mediated mutagenesis in mice. Nucleic Acids Res. 25, 1317–1318 (1997).
Rickert, P., Weiner, O.D., Wang, F., Bourne, H.R. & Servant, G. Leukocytes navigate by compass: roles of PI3Kγ and its lipid products. Trends Cell. Biol. 10, 466–473 (2000).
Cariappa, A. et al. The follicular versus marginal zone B lymphocyte cell fate decision is regulated by Aiolos, Btk, and CD21. Immunity 14, 603–615 (2001).
Lu, T.T. & Cyster, J.G. Integrin-mediated long-term B cell retention in the splenic marginal zone. Science 297, 409–412 (2002).
Oliver, A.M., Martin, F., Gartland, G.L., Carter, R.H. & Kearney, J.F. Marginal zone B cells exhibit unique activation, proliferative and immunoglobulin secretory responses. Eur. J. Immunol. 27, 2366–2374 (1997).
Jones, S.M. & Kazlauskas, A. Growth-factor-dependent mitogenesis requires two distinct phases of signalling. Nat. Cell Biol. 3, 165–172 (2001).
Fearon, D.T. & Carroll, M.C. Regulation of B lymphocyte responses to foreign and self-antigens by the CD19/CD21 complex. Annu. Rev. Immunol. 18, 393–422 (2000).
Beitz, L.O., Fruman, D.A., Kurosaki, T., Cantley, L.C. & Scharenberg, A.M. SYK is upstream of phosphoinositide 3-kinase in B cell receptor signaling. J. Biol. Chem. 274, 32662–32666 (1999).
Kurosaki, T. Regulation of B-cell signal transduction by adaptor proteins. Nat. Rev. Immunol. 2, 354–363 (2002).
Okada, T., Maeda, A., Iwamatsu, A., Gotoh, K. & Kurosaki, T. BCAP: the tyrosine kinase substrate that connects B cell receptor to phosphoinositide 3-kinase activation. Immunity 13, 817–827 (2000).
Yamazaki, T. et al. Essential immunoregulatory role for BCAP in B cell development and function. J. Exp. Med. 195, 535–545 (2002).
Funamoto, S., Meili, R., Lee, S., Parry, L. & Firtel, R.A. Spatial and temporal regulation of 3-phosphoinositides by PI 3-kinase and PTEN mediates chemotaxis. Cell 109, 611–623 (2002).
Iijima, M. & Devreotes, P. Tumor suppressor PTEN mediates sensing of chemoattractant gradients. Cell 109, 599–610 (2002).
Giancotti, F.G. & Ruoslahti, E. Integrin signaling. Science 285, 1028–1032 (1999).
Reiske, H.R. et al. Requirement of phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase in focal adhesion kinase-promoted cell migration. J. Biol. Chem. 274, 12361–12366 (1999).
Klingbeil, C.K. et al. Targeting Pyk2 to β 1-integrin-containing focal contacts rescues fibronectin-stimulated signaling and haptotactic motility defects of focal adhesion kinase-null cells. J. Cell. Biol. 152, 97–110 (2001).
Guinamard, R., Okigaki, M., Schlessinger, J. & Ravetch, J.V. Absence of marginal zone B cells in Pyk-2-deficient mice defines their role in the humoral response. Nat. Immunol. 1, 31–36 (2000).
Lam, E.W. et al. Cyclin D3 compensates for loss of cyclin D2 in mouse B-lymphocytes activated via the antigen receptor and CD40. J. Biol. Chem. 275, 3479–3484 (2000).
Solvason, N. et al. Cyclin D2 is essential for BCR-mediated proliferation and CD5 B cell development. Int. Immunol. 12, 631–638 (2000).
Glassford, J. et al. Vav is required for cyclin D2 induction and proliferation of mouse B lymphocytes activated via the antigen receptor. J. Biol. Chem. 276, 41040–41048 (2001).
Su, T.T. & Rawlings, D.J. Transitional B lymphocyte subsets operate as distinct checkpoints in murine splenic B cell development. J. Immunol. 168, 2101–2110 (2002).
Schwartz, M.A. & Assoian, R.K. Integrins and cell proliferation: regulation of cyclin-dependent kinases via cytoplasmic signaling pathways. J. Cell. Sci. 114, 2553–2560 (2001).
Brunet, A. et al. Akt promotes cell survival by phosphorylating and inhibiting a Forkhead transcription factor. Cell 96, 857–868 (1999).
Kops, G.J. et al. Direct control of the Forkhead transcription factor AFX by protein kinase B. Nature 398, 630–634 (1999).
Medema, R.H., Kops, G.J., Bos, J.L. & Burgering, B.M. AFX-like Forkhead transcription factors mediate cell-cycle regulation by Ras and PKB through p27kip1. Nature 404, 782–787 (2000).
Blain, S.W. & Massague, J. Breast cancer banishes p27 from nucleus. Nat. Med. 8, 1076–1078 (2002).
del Peso, L., Gonzalez-Garcia, M., Page, C., Herrera, R. & Nunez, G. Interleukin-3-induced phosphorylation of BAD through the protein kinase Akt. Science 278, 687–689 (1997).
Helgason, C.D. et al. A dual role for Src homology 2 domain-containing inositol-5-phosphatase (SHIP) in immunity: aberrant development and enhanced function of B lymphocytes in SHIP−/− mice. J. Exp. Med. 191, 781–794 (2000).
Brauweiler, A. et al. Differential regulation of B cell development, activation, and death by the Src homology 2 domain-containing 5′ inositol phosphatase (SHIP). J. Exp. Med. 191, 1545–1554 (2000).
Acknowledgements
We thank G. Bokoch (The Scripps Research Institute) for providing anti-Rac1, Rac2 antisera; M. David for discussions and members of the Rickert lab for critical evaluation of the manuscript. Supported by National Institutes of Health Grant AI41649 (to R.C.R.) and by a grant from the University of California Cancer Research Coordinating Committee (to R.C.R.). A.N.A. was supported by the Cell, Molecular and Genetic Training Program Grant (NIH, GM07246).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Competing interests
The authors declare no competing financial interests.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Anzelon, A., Wu, H. & Rickert, R. Pten inactivation alters peripheral B lymphocyte fate and reconstitutes CD19 function. Nat Immunol 4, 287–294 (2003). https://doi.org/10.1038/ni892
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/ni892
This article is cited by
-
B Cell Aberrance in Lupus: the Ringleader and the Solution
Clinical Reviews in Allergy & Immunology (2022)
-
Metabolic gatekeepers to safeguard against autoimmunity and oncogenic B cell transformation
Nature Reviews Immunology (2019)
-
Immune Dysregulation and Disease Pathogenesis due to Activating Mutations in PIK3CD—the Goldilocks’ Effect
Journal of Clinical Immunology (2019)
-
Innate B cells cleave to the marginal zone
Nature Immunology (2017)
-
Mechanisms of central tolerance for B cells
Nature Reviews Immunology (2017)