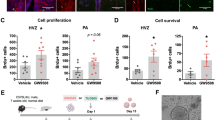
Abstract
Ageing is a result of gradual and overall functional deteriorations across the body; however, it is unknown whether an individual tissue primarily works to mediate the ageing progress and control lifespan. Here we show that the hypothalamus is important for the development of whole-body ageing in mice, and that the underlying basis involves hypothalamic immunity mediated by IκB kinase-β (IKK-β), nuclear factor κB (NF-κB) and related microglia–neuron immune crosstalk. Several interventional models were developed showing that ageing retardation and lifespan extension are achieved in mice by preventing ageing-related hypothalamic or brain IKK-β and NF-κB activation. Mechanistic studies further revealed that IKK-β and NF-κB inhibit gonadotropin-releasing hormone (GnRH) to mediate ageing-related hypothalamic GnRH decline, and GnRH treatment amends ageing-impaired neurogenesis and decelerates ageing. In conclusion, the hypothalamus has a programmatic role in ageing development via immune–neuroendocrine integration, and immune inhibition or GnRH restoration in the hypothalamus/brain represent two potential strategies for optimizing lifespan and combating ageing-related health problems.
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 51 print issues and online access
$199.00 per year
only $3.90 per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on Springer Link
- Instant access to full article PDF
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout






Similar content being viewed by others
References
Miller, R. A. Genes against aging. J. Gerontol. A Biol. Sci. Med. Sci. 67A, 495–502 (2012)
Mattson, M. P. Pathways towards and away from Alzheimer’s disease. Nature 430, 631–639 (2004)
Masoro, E. J. Overview of caloric restriction and ageing. Mech. Ageing Dev. 126, 913–922 (2005)
Finch, C. E. Neurons, glia, and plasticity in normal brain aging. Adv. Gerontol. 10, 35–39 (2002)
Zitnik, G. & Martin, G. M. Age-related decline in neurogenesis: old cells or old environment? J. Neurosci. Res. 70, 258–263 (2002)
Martin, G. M. Epigenetic gambling and epigenetic drift as an antagonistic pleiotropic mechanism of aging. Aging Cell 8, 761–764 (2009)
Bishop, N. A. & Guarente, L. Two neurons mediate diet-restriction-induced longevity in C. elegans . Nature 447, 545–549 (2007)
Fridell, Y. W., Sanchez-Blanco, A., Silvia, B. A. & Helfand, S. L. Targeted expression of the human uncoupling protein 2 (hUCP2) to adult neurons extends life span in the fly. Cell Metab. 1, 145–152 (2005)
Alcedo, J. & Kenyon, C. Regulation of C. elegans longevity by specific gustatory and olfactory neurons. Neuron 41, 45–55 (2004)
Wolkow, C. A., Kimura, K. D., Lee, M. S. & Ruvkun, G. Regulation of C. elegans life-span by insulinlike signaling in the nervous system. Science 290, 147–150 (2000)
Taguchi, A., Wartschow, L. M. & White, M. F. Brain IRS2 signaling coordinates life span and nutrient homeostasis. Science 317, 369–372 (2007)
Li, J., Tang, Y. & Cai, D. IKKβ/NF-κB disrupts adult hypothalamic neural stem cells to mediate a neurodegenerative mechanism of dietary obesity and pre-diabetes. Nature Cell Biol. 14, 999–1012 (2012)
Zhang, X. et al. Hypothalamic IKKβ/NF-κB and ER stress link overnutrition to energy imbalance and obesity. Cell 135, 61–73 (2008)
Purkayastha, S. et al. Neural dysregulation of peripheral insulin action and blood pressure by brain endoplasmic reticulum stress. Proc. Natl Acad. Sci. USA 108, 2939–2944 (2011)
Purkayastha, S., Zhang, G. & Cai, D. Uncoupling the mechanisms of obesity and hypertension by targeting hypothalamic IKK-β and NF-κB. Nature Med. 17, 883–887 (2011)
Okun, E., Griffioen, K. J. & Mattson, M. P. Toll-like receptor signaling in neural plasticity and disease. Trends Neurosci. 34, 269–281 (2011)
Glass, C. K., Saijo, K., Winner, B., Marchetto, M. C. & Gage, F. H. Mechanisms underlying inflammation in neurodegeneration. Cell 140, 918–934 (2010)
Saijo, K. et al. A Nurr1/CoREST pathway in microglia and astrocytes protects dopaminergic neurons from inflammation-induced death. Cell 137, 47–59 (2009)
Saijo, K., Collier, J. G., Li, A. C., Katzenellenbogen, J. A. & Glass, C. K. An ADIOL-ERβ-CtBP transrepression pathway negatively regulates microglia-mediated inflammation. Cell 145, 584–595 (2011)
Saijo, K. & Glass, C. K. Microglial cell origin and phenotypes in health and disease. Nature Rev. Immunol. 11, 775–787 (2011)
Lucin, K. M. & Wyss-Coray, T. Immune activation in brain aging and neurodegeneration: too much or too little? Neuron 64, 110–122 (2009)
Villeda, S. & Wyss-Coray, T. Microglia–a wrench in the running wheel? Neuron 59, 527–529 (2008)
Villeda, S. A. et al. The ageing systemic milieu negatively regulates neurogenesis and cognitive function. Nature 477, 90–94 (2011)
Yoshiyama, Y. et al. Synapse loss and microglial activation precede tangles in a P301S tauopathy mouse model. Neuron 53, 337–351 (2007)
Adler, A. S. et al. Motif module map reveals enforcement of aging by continual NF-κB activity. Genes Dev. 21, 3244–3257 (2007)
Peng, B. et al. Defective feedback regulation of NF-κB underlies Sjogren’s syndrome in mice with mutated κB enhancers of the IκBα promoter. Proc. Natl Acad. Sci. USA 107, 15193–15198 (2010)
Harrison, D. E. et al. Rapamycin fed late in life extends lifespan in genetically heterogeneous mice. Nature 460, 392–395 (2009)
Barger, S. W. et al. Tumor necrosis factors α and β protect neurons against amyloid β-peptide toxicity: evidence for involvement of a κ B-binding factor and attenuation of peroxide and Ca2+ accumulation. Proc. Natl Acad. Sci. USA 92, 9328–9332 (1995)
Bruce, A. J. et al. Altered neuronal and microglial responses to excitotoxic and ischemic brain injury in mice lacking TNF receptors. Nature Med. 2, 788–794 (1996)
Taoufik, E. et al. Transmembrane tumour necrosis factor is neuroprotective and regulates experimental autoimmune encephalomyelitis via neuronal nuclear factor-κB. Brain 134, 2722–2735 (2011)
Kaltschmidt, B. et al. NF-κB regulates spatial memory formation and synaptic plasticity through protein kinase A/CREB signaling. Mol. Cell. Biol. 26, 2936–2946 (2006)
Meffert, M. K., Chang, J. M., Wiltgen, B. J., Fanselow, M. S. & Baltimore, D. NF-κB functions in synaptic signaling and behavior. Nature Neurosci. 6, 1072–1078 (2003)
O’Mahony, A. et al. NF-κB/Rel regulates inhibitory and excitatory neuronal function and synaptic plasticity. Mol. Cell. Biol. 26, 7283–7298 (2006)
Huang, W., Ghisletti, S., Perissi, V., Rosenfeld, M. G. & Glass, C. K. Transcriptional integration of TLR2 and TLR4 signaling at the NCoR derepression checkpoint. Mol. Cell 35, 48–57 (2009)
Kawahara, T. L. et al. SIRT6 links histone H3 lysine 9 deacetylation to NF-κB-dependent gene expression and organismal life span. Cell 136, 62–74 (2009)
Michishita, E. et al. SIRT6 is a histone H3 lysine 9 deacetylase that modulates telomeric chromatin. Nature 452, 492–496 (2008)
Meng, Q. & Cai, D. Defective hypothalamic autophagy directs the central pathogenesis of obesity via the IκB kinase β (IKKβ)/NF-κB pathway. J. Biol. Chem. 286, 32324–32332 (2011)
Banks, W. A. et al. Effects of a growth hormone-releasing hormone antagonist on telomerase activity, oxidative stress, longevity, and aging in mice. Proc. Natl Acad. Sci. USA 107, 22272–22277 (2010)
Tillerson, J. L. & Miller, G. W. Grid performance test to measure behavioral impairment in the MPTP-treated-mouse model of parkinsonism. J. Neurosci. Methods 123, 189–200 (2003)
Mueller, J. M. & Pahl, H. L. Assaying NF-κB and AP-1 DNA-binding and transcriptional activity. Methods Mol. Biol. 99, 205–216 (2000)
Flurkey, K., Papaconstantinou, J., Miller, R. A. & Harrison, D. E. Lifespan extension and delayed immune and collagen aging in mutant mice with defects in growth hormone production. Proc. Natl Acad. Sci. USA 98, 6736–6741 (2001)
Ramanadham, S. et al. Age-related changes in bone morphology are accelerated in group VIA phospholipase A2 (iPLA2β)-null mice. Am. J. Pathol. 172, 868–881 (2008)
Meylan, E. et al. Requirement for NF-κB signalling in a mouse model of lung adenocarcinoma. Nature 462, 104–107 (2009)
Wang, C., Li, Q., Redden, D. T., Weindruch, R. & Allison, D. B. Statistical methods for testing effects on “maximum lifespan”. Mech. Ageing Dev. 125, 629–632 (2004)
Acknowledgements
We thank other Cai laboratory members for technical assistance, and L. Farhana, D. Stocco, L. Eckhardt, T. Ohshima, A. Lin and D. Tantin for reagents. This study was supported by National Institutes of Health (NIH) grants R01 AG 031774, R01 DK078750, and American Diabetes Association grant 1-12-BS-20 (all to D.C.). D.C. is a recipient of Irma T. Hirschl Scholarship.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
D.C. conceived project and designed the study; G.Z., J.L., S.P., Y.T., H.Z. and Y.Y. performed experiments with assistance from B.L. and G.L. All authors carried out data analyses and interpretations; D.C. organized experimentation and wrote the paper.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Competing interests
The authors declare no competing financial interests.
Supplementary information
Supplementary Figures
This file contains Supplementary Figures 1-13. (PDF 2686 kb)
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Zhang, G., Li, J., Purkayastha, S. et al. Hypothalamic programming of systemic ageing involving IKK-β, NF-κB and GnRH. Nature 497, 211–216 (2013). https://doi.org/10.1038/nature12143
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/nature12143
This article is cited by
-
Squalamine reverses age-associated changes of firing patterns of myenteric sensory neurons and vagal fibres
Communications Biology (2024)
-
Glucose dysregulation in antipsychotic-naive first-episode psychosis: in silico exploration of gene expression signatures
Translational Psychiatry (2024)
-
A comprehensive model for the biochemistry of ageing, senescence and longevity
Biogerontology (2024)
-
Current understanding of essential trace elements in intrahepatic cholestasis of pregnancy
BioMetals (2024)
-
Heterochronic parabiosis reprograms the mouse brain transcriptome by shifting aging signatures in multiple cell types
Nature Aging (2023)
Comments
By submitting a comment you agree to abide by our Terms and Community Guidelines. If you find something abusive or that does not comply with our terms or guidelines please flag it as inappropriate.