Abstract
Inherited retinal degenerations, collectively termed retinitis pigmentosa (RP), constitute one of the leading causes of blindness in the developed world. RP is at present untreatable and the underlying neurodegenerative mechanisms are unknown, even though the genetic causes are often established. Acetylation and deacetylation of histones, carried out by histone acetyltransferases (HATs) and histone deacetylases (HDACs), respectively, affects cellular division, differentiation, death and survival. We found acetylation of histones and probably other proteins to be dramatically reduced in degenerating photoreceptors in the rd1 human homologous mouse model for RP. Using a custom developed in situ HDAC activity assay, we show that overactivation of HDAC classes I/II temporally precedes photoreceptor degeneration. Moreover, pharmacological inhibition of HDACs I/II activity in rd1 organotypic retinal explants decreased activity of poly-ADP-ribose-polymerase and strongly reduced photoreceptor cell death. These findings highlight the importance of protein acetylation for photoreceptor cell death and survival and propose certain HDAC classes as novel targets for the pharmacological intervention in RP.
Similar content being viewed by others
Main
Retinitis pigmentosa (RP) is a group of inherited neurodegenerative diseases that result in selective cell death of retinal photoreceptors. Usually the mutations first lead to degeneration of the rod photoreceptor cells followed by a mutation-independent secondary degeneration of cone photoreceptors. With a prevalence of about 1 : 3500, RP is considered as the main cause of blindness among the working age population in the developed world. At least 40 RP causing mutations have been identified so far, but the metabolic pathways leading to photoreceptor cell death have not been resolved, and no adequate RP treatment is available.1
The rd1 mouse is one of the most studied human homologous RP animal models and carries a loss-of-function mutation in the gene encoding for the β-subunit of rod photoreceptor cGMP phosphodiesterase-6.2 This leads to an accumulation of cGMP, which eventually causes photoreceptor cell death.3, 4 In microarray experiments, we and others found rd1 degeneration to be accompanied by extensive changes in gene expression.5, 6, 7 Although some changes may result from direct and specific effects of cGMP on defined genes,8 it is likely that also more generalized alterations of the transcriptional machinery are involved. Previously, we have shown that rd1 photoreceptor degeneration is in part caused by a strong activation of poly-ADP-ribose-polymerase (PARP),9 which may have a bearing on transcriptional activity.10 However, as PARP activity was found to occur only relatively late during rd1 degeneration, we hypothesized that there might be yet other mechanisms causing dysregulation of gene expression.
Gene regulation is to a large extent governed by epigenetic mechanisms, among which acetylation of histones11 appears to be one of the most important.12 Histone acetylation and deacetylation is mediated by histone acetyltransferases (HATs) and histone deacetylases (HDACs), respectively.13 The HDAC family is subdivided into three main classes (HDAC I, II, and III), depending on their similarity with homologous yeast genes. Class I (HDAC 1–3 and 8) and class II (HDAC 4–7, 9, and 10) are inhibited by trichostatin A (TSA).13 Class III HDACs, also referred to as sirtuins (isoforms: sirt1–7) form a structurally distinct class of NAD+-dependent enzymes that can be inhibited by nicotinamide (NAM).14
Although a number of studies have related transcription of photoreceptor genes and photoreceptor viability with histone acetylation,15, 16, 17 information regarding whether and how HDAC activity connects to degenerating photoreceptors is lacking. Here, we analyzed enzymatic activities of different HDAC classes in situ on retinal tissue sections and studied how various inhibitors affect retinal cell viability. Activity of HDACs I/II was strongly elevated in rd1 photoreceptors and causally related to their death, suggesting HDAC inhibition as a novel approach for neuroprotection in retinal degeneration.
Results
Expression of HDACs in wt and rd1 retina
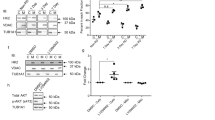
Microarray analysis of the expression of 13 different HDAC genes did not identify any significant differences between wild type (wt) and rd1 (Figure 1a). Immunohistology revealed that HDACs representing all three major classes were present in wt and rd1 retina at post-natal day (P) 11. Both class I HDAC2 (Figure 1a, d) and class II HDAC5 (Figure 1b, e) were prominently expressed in nuclei of the outer nuclear layer (ONL), inner nuclear layer (INL), and ganglion cell layer. In contrast, class III HDAC Sirt2 (Figure 1c, f) was expressed predominantly in non-nuclear structures including photoreceptor segments, neuritic processes in the ONL, and different INL cells. No obvious differences in expression or localization between wt and rd1 at P11 were detected for any of the HDACs.
Micro-array analysis and immunodetection of different HDAC isoforms in wt and rd1 retinae at P11 in vivo. mRNA expression for 14 different HDAC isoforms pertaining to all four HDAC classes was assessed using micro-array analysis. (a) For all studied HDAC isoforms, the ratio of mRNA expression wt/rd1 was not significantly different from 1, indicating that expression was not changed. Values are mean±SEM from five independent hybridization experiments, each containing retinae from four male wt and four rd1 animals. Immunostaining was performed for three different HDAC isoforms representing HDAC classes I–III. HDAC2 (b, e) and HDAC5 (c, f) were expressed in the nuclei of ONL, INL, and GCL, while Sirt2 (d, g) was expressed in photoreceptor segments and neuritic processes in the ONL and different INL cell types. No obvious differences between wt (b-d) and rd1 (e-g) were found. Scale bar: 50 μm
rd1 photoreceptor nuclei show hypoacetylation
Acetylation of lysine residues was studied in wt and rd1 retinae using acetylation-specific antibodies (Abs). In the ONL of wt mice at P11, an Ab detecting general acetylation of lysine residues showed homogeneous staining of the photoreceptor population (Figure 2a-c). In contrast, the P11 rd1 ONL presented staining ‘gaps’ that contained unlabeled photoreceptor nuclei (Figure 2d-f). Such lack of staining encompassed decreased histone acetylation, as confirmed by several Abs directed against specific acetylated histones (Supplementary Figure 1). No obvious signs for hypoacetylation for any of the Abs used were found in the inner retina of neither wt nor rd1. Western blot (WB) of P11 in vivo retinae with the acetyl-lysine Ab (Figure 2g) mainly revealed bands between 12 and 17 kDa that corresponded to the reported molecular weights of different histones and showed numerically decreased acetylation levels in the rd1 retina (wt: 100%; rd1: 89.8%±40, n=3).
Decreased acetylation in rd1 photoreceptors in vivo. At P11 immunofluorescence for acetylated lysine residues (green) on wt (a) and rd1 (d) retinae revealed a number of DAPI-stained rd1 photoreceptor nuclei (b, e; blue) with very low levels of protein acetylation. (Merged pictures in c, f, arrowheads indicate nuclei showing low acetylation levels.) WB with the same Ab mainly labeled bands corresponding to the molecular weight of histones (g). Scale bar: 20 μm
HDAC activity is increased in rd1 photoreceptors
To investigate whether the decreased rd1 photoreceptor acetylation was related to increased activity of HDACs, we adapted a technique originally intended to measure tissue homogenates18 for the use on retinal tissue sections.
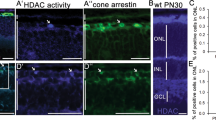
Whole fixed retinal cryosections revealed deacetylation activity. By specifically blocking either HDACs I/II with TSA or HDAC III with NAM, we were able to distinguish the relative contributions of different classes of HDACs to the total activity, and to follow their kinetics with different substrate concentrations. As proof of principle for the HDAC assay, we determined the Km values for total HDAC activity on retinae of rd1 and wt mice (Supplementary Figure 2). The Km value for the fluorogenic substrate of 83 μM at 500 μM NAD+ is in good agreement with previous reports.19 When studied with cellular resolution, both wt and rd1 tissue displayed HDAC activity in photoreceptor segments. All nuclear layers of wt retina were essentially devoid of visible activity (Figure 3a). In contrast, the rd1 ONL carried a subset of cells, displaying typical nuclear morphology of photoreceptors, with highly elevated HDAC activity (Figure 3b). Inhibition of either class I/II HDACs (Figure 3c) or HDAC III (Figure 3d) suggested that most of the excessive HDAC activity in rd1 photoreceptor originated from HDAC I/II. Together, these results implied that rd1 photoreceptor hypoacetylation was due to an excessive activation of HDACs, and most likely HDAC I/II.
HDAC activity in the retina in vivo. HDAC activity was detected in situ in particular in the segment layers of both wt (a) and rd1 (b) retina. In contrast to wt, rd1 retina displayed a subset of ONL cells with strongly increased HDAC activity. Activity of HDAC I/II (c) was studied by inhibition of HDAC III with NAM. Conversely, sirtuin activity (d) was assessed by inhibiting HDACs I/II with TSA. Combined inhibition with TSA and NAM was used as negative control (e). Scale bar: 50 μm
HDAC activity and cell death
To test whether the high HDAC activity observed in rd1 photoreceptors was related to their degeneration, staining for acetylated lysine was combined with the TUNEL assay for dying cells. Most of the cells lacking acetylation (94.3%±7.3 S.E.M., n=3) were also TUNEL positive (Figure 4a–c). In another co-labeling experiment, rd1 HDAC activity colocalized only partially (32.5%±6.7 S.E.M., n=3) with TUNEL-positive cells (Figure 4d–f) implying that the activity generally preceded the final stages of cell death. To confirm this hypothesis, we assessed the number of HDAC activity positive cells in the ONL of wt and rd1 retinas at various time points during the second post-natal week (i.e., during onset and peak of rd1 degeneration). The analysis of the temporal progression of HDAC activity showed a marked increase in the number of HDAC activity positive cells at P9, with a peak in activity already at P11 (Figure 4g). Comparison with previously published data on cell death (TUNEL assay) and PARP activity9 indicated that the peak in HDAC activity preceded the peak of the degeneration by ∼2 days. Overall, this suggested that an acetylation/deacetylation imbalance might have an important role in rd1 photoreceptor degeneration.
Protein acetylation and temporal progression of HDAC activity and cell death in vivo. At P11, immunostaining for acetylated lysine residues (a, green) in rd1 ONL showed characteristic “gaps”, which were partly filled by TUNEL staining (red) for dying cells (b) (merged in c), suggesting hypoacetylation to contribute to photoreceptor cell death. Conversely, the HDAC activity assay (d, f) colocalized in part with TUNEL staining at P11 (e) in the rd1 ONL (merged in f). Scale bar: 20μM. The graph in g shows the temporal progression of HDAC activity (blue line) in wt and rd1 ONL during the second postnatal week, and relates it to the time-course for TUNEL-positive cells (red). Note that the peak of HDAC activity markedly precedes the peak of TUNEL. n⩾3 for each time point and genotype, data for TUNEL assay were previously published in Paquet-Durand et al., 2007 and are shown here for reference purposes only
HDAC I/II inhibitors protect rd1 photoreceptors
We then exposed retinal explants in a short-term culture paradigm (until P11) to inhibitors specific for the three main classes of HDACs and evaluated the outcome on photoreceptor viability using the TUNEL assay.
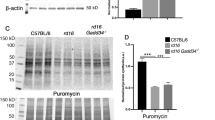
The HDAC I/II inhibitor TSA (1 μM) did not affect the number of TUNEL-positive cells in the ONL of P11 wt retinal cultures (TSA: 1.6±0.2%, n=6 retinal cultures from six different animals versus vehicle controls: 1.7±0.2%, n=9; Figure 5a, b). In the rd1 retina, however, 1 μM TSA significantly decreased the rate of cell death (TSA: 2.2±0.4%, n=12 versus vehicle: 3.5±0.2%, n=27, P<0.001; Figure 5c, d; quantification in panel e). A second HDAC I/II inhibitor, Scriptaid (6 μM), also conferred a significant neuroprotective effect to rd1 photoreceptors (Scriptaid: 2.6±0.1%, n=6, versus vehicle: 3.5±0.2%, n=27, P<0.05). The HDAC III inhibitor NAM (200 μM and 1 mM) had no measurable effect on photoreceptor viability (NAM 200 μM: 3.9±0.2%, n=5 versus vehicle: 3.5±0.2%, n=27; Figure 5e). Neither of the above treatments affected the number of photoreceptor rows (quantification in Figure 5e). Successful in vitro HDAC inhibition by TSA was confirmed using both a tissue-based analysis (WB for acetylated lysine; Figure 5f) and an in situ approach (HDAC activity; Supplementary Figure 3).
HDAC inhibition reduces photoreceptor cell death in vitro. Short-term retinal explant cultures from rd1 and wt animals were exposed to control conditions or 1 μM TSA from P7 to P11 (a-d). In untreated specimens (a, c), TUNEL assay (green) showed the characteristic increase of dying cells in rd1 ONL compared with wt. TSA treatment (b, d) reduced the number of degenerating photoreceptors in rd1, but did not alter viability of wt. The bar graph (e) summarizes effects of TSA, 6 μM Scriptaid, and 200 μM NAM on photoreceptor viability. HDAC I/II inhibitors, TSA and Scriptaid, significantly reduced the amount of dying cells, whereas HDAC III inhibitor NAM had no effect on cell survival. Immunoblotting for acetylated lysine residues (f) showed an increase in protein acetylation after TSA treatment in both wt and rd1 retinae. Long-term cultures of rd1 retinae (until P28; g, h) treated with TSA showed a marked increase in the number of rhodopsin-positive cell bodies and overall size of their ONL when compared with untreated situation (quantification in i). DAPI (blue) was used as nuclear counterstain; actin immunoblotting was used as loading control in f; n⩾6, Scale bars in d and h are 50 and 20 μM respectively
Although we did not observe any negative properties of TSA in our cultures, a previous study on acute wt retinal explants showed proapoptotic effects of TSA at early developmental stages.16 To address the possibility of a transient TSA effect on retinal cell viability, we treated P5 rd1 retinal explants with 1 μM TSA for 24 h, but this did not affect the percentage of TUNEL-positive cells in the P6 in vitro retina (TSA: 1.7±0.2%, vehicle: 1.5±0.3%; n=3; Supplementary Figure 4). Furthermore, when extending the culture period for another 5 days without TSA (P5+1+5=P11), to match with the end point used in our previous experiments, the treated rd1 retina again showed a markedly reduced number of TUNEL-positive cells (TSA: 1.0±0.2%; vehicle: 3.8±0.5%, n=3, P<0.05). At the same time, the number of photoreceptor rows was not significantly affected by the treatment (TSA: 7.1±0.2, vehicle: 7.5±0.1; n=3).
To test whether the strong neuroprotective effect of TSA in the different short-term paradigms would translate into improved long-term survival of photoreceptors, in vitro treatment was prolonged until P28. TSA treatment almost doubled the number of surviving rd1 photoreceptor rows (TSA: 4.1±0.3; vehicle: 2.1±0.2, n=6, P<0.001; Figure 5i).
Expression of rhodopsin was then analyzed as an indication of rod photoreceptor identity. In wt retina, in vivo rhodopsin expression is restricted to the outer segments of rod photoreceptors, whereas in rd1 retina, where outer segments do not develop properly, it is partly mislocalized and also observed throughout the cytoplasm of photoreceptors.20 This phenomenon intensifies under in vitro conditions where rhodopsin mislocalization is observed in both wt and rd1 photoreceptors (Supplementary Figure 5). In long-term TSA-treated explants, rhodopsin expression was found in most of the surviving rd1 photoreceptors, whereas in the untreated situation most remaining ONL cells were rhodopsin negative and most likely predominantly cones (Figure 5g, h). Significantly, rhodopsin-positive photoreceptor outer segments were observed in TSA-treated specimens, when at the same time in the untreated situation, outer segments were completely absent. This supported the idea that TSA indeed upheld survival of rod photoreceptors and promoted growth of rd1 outer segments.
All in all, TSA treatment in both short- and long-term retinal culture demonstrated a strong prosurvival effect, whereas NAM had no such protective effects. The experiments therefore suggested a major contribution of HDAC I/II, but not III, to mutation-induced rd1 photoreceptor death.
HDAC I/II regulate PARP activity
As we had previously found PARP activity to be involved in rd1 photoreceptor cell death,9 we wanted to investigate a possible interaction between HDACs and PARP. When immunostainings for acetylated lysines and for poly-ADP-ribose (PAR) – the product of PARP activity – were combined, the merged images revealed PAR-positive photoreceptor nuclei exclusively in cases where acetylation was absent (Figure 6a–d). Together with the data on the progression of HDAC activity (Figure 4g), this suggested that hypoacetylation and hence HDAC activity was preceding PARP activity.
HDAC and PARP activities are connected. In rd1 P11 in vivo specimens, a subset of ONL nuclei showed unusual chromatin condensation as evidenced by DAPI nuclear counterstain (a, blue). In most of these cells a strong accumulation of poly-ADP-ribose (PAR) (b, red) colocalized with hypoacetylation (c, green; merged in d; white arrowheads), suggesting a functional connection between acetylation and PARP activity. In short-term retinal explant cultures at P11, photoreceptors showing PAR accumulation were observed in untreated wt (e) and rd1 retina (g), their number being much higher in the latter case. This number was strongly reduced by TSA treatment in both wt (f) and rd1 retina (h; quantification in i), implying that activation of PARP occurred downstream of HDAC I/II activity. n=3; Scale bar in d, h=20 μM. Some of the PAR immunostaining between ONL and INL relates to IGG staining in blood vessels
We then tested whether HDAC I/II inhibition by TSA indirectly also affected PARP activity. With respect to PAR immunostaining, there was a moderate amount of positive photoreceptor nuclei in wt retinal explant cultures at P11 (wt vehicle: 0.25%±0.1, n=3), and a comparatively much higher number in rd1 explants (rd1 vehicle: 0.9%±0.1; Figure 6e, g). The presence of PAR-positive photoreceptors in wt explants is likely due to the stress that these undergo during culture. In both wt and rd1 explants, the number of PAR-positive cells was reduced by TSA treatment, and this reduction was statistically significant in the rd1 situation (rd1 TSA: 0.3%±0.2, n=3, P<0.05; Figure 6f, h). These results supported the notion that activation of PARP in rd1 photoreceptors occurred downstream of HDAC I/II activity.
Discussion
The activity of HDACs has previously been connected to a variety of different cellular processes, notably regulation of gene expression, cytoskeletal rearrangements, division, and differentiation.13 Here, we show that HDAC activity was causally related to inherited photoreceptor cell death in the rd1 mouse and that this detrimental effect was tied to HDACs I/II. HDACs III did not seem to be involved in the degeneration, which corresponds to observations on weakened HDAC III action in degenerating retina.21 The strong neuroprotection afforded by HDAC I/II inhibitors in both short- and long-term retinal explant cultures proposes them as novel lead compounds to prevent or delay retinal neurodegeneration.
HDAC and gene regulation
Given the extensive effects of acetylation/deacetylation on gene regulation, the observed HDAC hyperactivation would likely result in significantly altered rd1 gene transcription, which matches with previous microarray data.5, 6, 7 On the other hand, we can at present not exclude the possibility that the observed histone deacetylation was due in part also to a decreased activity of HATs. Our observations that rd1 gene alterations include downregulation of the transcription factor CREB6, 8, 22 is of particular interest here, as CREB not only appears to confer neuroprotection6, 8, 22 but also has several links to cellular acetylation events. For example, different HDAC I/II isoforms can recruit protein phosphatase-1 to dephosphorylate and inactivate CREB,23 which might be related to its downregulation in the rd1 retina. Moreover, CREB target gene transcription is facilitated by its co-factor CREB-binding protein (CBP), which has HAT activity,24 and therefore connects CREB activation with histone acetylation. Accordingly, some of the effects on neuronal gene regulation seen when acetylation is increased by HDAC inhibition may be routed through enhanced activity of CREB and CBP.25 The expression of opsin and other photoreceptor genes is controlled by the photoreceptor-specific transcription factor cone-rod-homeobox (CRX).26 In conjunction with histone acetylation and CBP, CRX drives expression of these critical photoreceptor genes in Y79 retinoblastoma cells and in the mouse retina.15, 27
Cross-talk between HDAC and PARP activity
PARP activity is involved in DNA damage repair and hence often seen as a benign factor, although excessive PARP activity may compromise cellular viability.10 Increased PARP activity, as seen in rd1 photoreceptors,9 consumes NAD+ and generates NAM, which in turn negatively regulates HDAC III activity and thereby favors acetylation of its target proteins.14 As HDAC III-dependent deacetylation of the automodification domain of PARP blocks its activity,28 low NAD+ levels could trigger a positive feedback loop accounting for both the high PARP activity and the low HDAC III activity observed in rd1 photoreceptors. Yet other reports demonstrate that acetylation by p300/CBP promotes the ability of PARP-1 to act as a co-activator in transcription30, whereas acetylation by histone acetyltransferases PCAF and GCN5L reduces PARP-2 catalytic activity.29, 30 The findings highlight a possibility for hyperactive HDAC I/II to intervene with various PARP types, perhaps causing abnormal stimulation of these enzymes. In such a scheme, HDAC I/II activity would be upstream of PARP activation in rd1 photoreceptor degeneration, which is in accord with our results, where TSA treatment reduced accumulation of PAR. In addition, PARP activity accompanies the event of dying, TUNEL-positive photoreceptors and colocalizes to a large extent with them,9 whereas in this study, TUNEL colocalization with HDAC activity was only minor. This again implies that HDAC activity was upstream of PARP activation.
HDAC activity in cell death and survival
Experimental evidence suggests that both overactivation of HDACs I/II or their inhibition promotes cell death.13 Similarly, HDAC III activity can have both pro- and antiapoptotic effects depending on cell type and proliferation state,31 and the right balance between the activities of different HDAC classes therefore seems to be crucial for maintaining cellular viability.13 In addition, individual members of each HDAC class could have distinct cell type-specific roles,32 perhaps related to their expression levels, which may in part explain the opposing effects of HDAC inhibitors observed in different neurodegeneration paradigms.12 The protective effects of TSA and Scriptaid comply with a number of studies on post-mitotic neurons, where HDAC inhibitors also conferred neuroprotection,12, 33, 34 possibly in part due to the prevention of oxidative stress35 and reactivation of CREB signaling.36, 37 Furthermore, it is conceivable that in the rd1 situation HDAC inhibition may induce expression or increase the stability of neuroprotective genes and proteins that are not directly related to the pathological mechanism. In this context, the chaperone HSP90, which is a target for HDAC-dependent deacetylation, appears to have a prominent role in neurodegeneration. Acetylation at its K294 residue inhibits HSP9038 and hence HDAC inhibitors indirectly also block HSP90 activity.39 Interestingly, HSP90 inhibition induces an upregulation of the neuroprotective chaperone HSP70 and strongly increases neuronal survival.40, 41 Our finding that decreased histone acetylation combines with increased HDAC activity corresponds to very similar observations made in motorneurons in a mouse model for amyotrophic lateral sclerosis, where HDAC inhibition also resulted in neuroprotection.36 In the in vivo retina, HDAC inhibition has been shown to promote survival of ganglion cells after optic nerve crush.37
Conclusion
The mechanisms governing inherited photoreceptor cell death have remained elusive to date.1 Our discovery that HDAC activity was involved in photoreceptor degeneration may thus help to close a major gap of knowledge between the immediate effects of a single gene mutation2 and the observed massive changes at the transcriptional level.6 Moreover, increased HDAC activity appeared to be responsible for an activation of PARP in degenerating rd1 photoreceptors. The exact interplay between PARP and HDAC activity warrants further studies, as it may potentially explain crucial events in the pathological process. This study not only brings up HDAC activity as a ‘missing link,’ uniting several other findings on the mechanisms of photoreceptor cell death, but also highlights HDACs as novel targets for the development of neuroprotective therapies aimed to halt or delay inherited retinal degeneration in humans.
Material and Methods
Animals
Animals were housed under standard white cyclic lighting, had free access to food and water, and were used irrespective of gender. C3H rd1/rd1 (rd1) and control C3H wt mice were used.42 All procedures were performed in accordance with the local ethics committee in Lund (permits M225-04 and M242-07), the Tübingen University (§4 registration from 23–01–08), and the ARVO statement for the use of animals in ophthalmic and visual research. All efforts were made to minimize the number of animals used and their suffering. Because of the critical changes at P11,22, 43 most comparisons between rd1 and wt were carried out at this age. Day of birth was considered as P0.
Microarray analyis
Details of the transcription assay performed on a custom-made mouse gene chip were described in Azadi et al.6 Two times up- or downregulation in at least three out of five hybridizations was considered as significant variation. Results not pertaining to this study are published elsewhere.
In vitro retinal explant cultures
Retinae from P5 rd1 and wt animals were used to generate retinal explants as described before.4, 44 In brief, animals were killed and the eyes enucleated in an aseptic environment. Afterwards, the entire eyes were incubated in R16 serum-free culture medium (Invitrogen Life Technologies, Paisley, UK; 07490743A) containing 0.12% proteinase K (MP Biomedicals, Solon, OH, USA; 193504) at 37 °C for 15 min, to allow preparation of retinal cultures with RPE attached. Proteinase K was inactivated with 10% fetal calf serum (Invitrogen Life Technologies; PET10108165) in R16 medium, and the eyes dissected aseptically in a Petri dish containing R16 medium. The anterior segment, lens, vitreous, sclera, and choroids were carefully removed, and the retina was cut perpendicular to its edges, resulting in a cloverleaf-like shape. Subsequently, the retina was transferred to a Millicell culture dish filter insert (Millipore AB, Solna, Sweden; PIHA03050) with the retinal pigment epithelium layer facing the membrane. The insert was put into a six-well culture plate and incubated in R16 nutrient medium at 37 °C. Every second day, the full volume of nutrient medium, 1.5 ml per dish, was replaced with fresh medium.
The first 2 days, the retina was left in R16 culture medium without treatment to adapt to culture conditions. At P7, cultures were either exposed to different treatments (TSA 1 μM, Scriptaid 6 μM, NAM 200 μM, and 1000 μM; all from Sigma, Munich, Germany), or kept as untreated control. NAM is a constituent of the culturing medium and present at about 22 μM, which should be less than half the reported IC50 value in cell-free studies.45 Explants were cultured until P11 for short-term cultures (P5+2+4), or until P28, for long-term cultures (P5+2+21). Culturing was stopped by 2 h fixation in 4% paraformaldehyde (PFA), washed 4 × 15 min in phosphate-buffered saline (PBS), then cryoprotected first with PBS +10% sucrose, and subsequently with PBS +25% sucrose. Explants were frozen and embedded in Jung tissue freezing medium (Leica Microsystems, Nussloch, Germany) for cryosectioning (12 μm).
HDAC assay
HDAC activity assays were performed on cryosections of 4% PFA P11 fixed eyes. The assay is based on an adaptation of the Fluor de Lys Fluorescent Assay System (Biomol, Hamburg, Germany). Retinal sections were exposed to different concentrations of Fluor de Lys-SIRT2 deacetylase substrate (Biomol) with 2 or 100 μM TSA (Sigma, Steinheim, Germany), 2 mM NAM (Sigma), and 500 μM NAD+ (Biomol) in assay buffer (50 mM Tris/HCl, pH 8.0; 137 mM NaCl; 2.7 mM KCl; 1 mM MgCl2; 1 mg/ml BSA) and 0.1% NP40 and 0.5 × Developer II (Biomol). Images were captured at indicated time points with a fixed exposure time of 2 s using a Zeiss (Jena, Germany) Axiophot microscope ( × 20 magnification) and Zeiss Axiovision 4.2 software; densitometry was performed with the aid of ImageJ (National Institutes of Health, Bethesda, MD, USA). The reaction rate was determined in at least four independent experiments, as the slope of the linear regression fitted to the data points in the linear range of a time course, using SigmaPlot (Systat software, Erkrath, Germany) software. For the calculation of Km values, the slope of time courses with different substrate concentrations was plotted against the corresponding substrate concentrations; a hyperbolic regression fitted to the data points revealed Km values and Vmax.
In situ deacetylation activity was determined on retinal sections incubated for 3 h with 200 μM Fluor de Lys-SIRT2 deacetylase substrate in assay buffer with/without inhibitors. Sections were then washed in PBS and fixed in methanol at −80 °C for 20 min. × 0.5 developer (Biomol) in assay buffer was applied and pictures taken immediately in an Apotome microscope (Zeiss), at × 20 using the DAPI filter.
TUNEL assay
The terminal deoxynucleotidyl transferase dUTP nick end labeling (TUNEL) assay was performed on cryosections from treated and untreated rd1 retinas, using an in situ cell death detection kit conjugated with tetra-methyl-rhodamine or fluorescein isothiocyanate (Roche Diagnostics, Mannheim, Germany). For controls, terminal deoxynucleotidyl transferase enzyme was either omitted from the labeling solution (negative control), or sections were pretreated for 30 min with DNAse I (Roche Diagnostics, 3 U/ml) in 50 mM Tris-HCl, pH 7.5, 1 mg/ml BSA to induce DNA-strand breaks (positive control). Negative control showed no staining at all, whereas positive control stained all nuclei in all layers of the retina.9
Immunostaining
Frozen retinal sections from P11 animals or cultured retinae were dried for 30–60 min at 37 °C. Subsequently, the tissue was rehydrated in PBS, and preincubated for 1 h at room temperature (RT) in blocking solution, containing 10% normal serum, and 0.1 or 0.3% Triton in PBS (PBST). Immunohistochemistry was performed overnight at 4 °C, using primary Abs (acetylated lysine; acetylated H2A, H2B, H3, H4; Sirt2; HDAC2; HDAC5; PAR) diluted 1 : 100 in blocking solution. Primary Abs were purchased from Cell Signaling (Danvers, MA, USA) except PAR Ab (Alexis Biochemicals, Lörrach, Germany) and Rhodopsin Ab (Millipore, Schwalbach, Germany). The tissue was rinsed with PBST, and incubated for 1 h with a corresponding secondary Ab, Alexa 488 (1 : 200–1 : 750, Invitrogen), diluted in PBST. Sections were rinsed in PBS, and mounted in Vectashield with DAPI (Vector Laboratories, Burlingame, CA, USA).
Western Blot
Retinae from P11 animals were enucleated and stored at −80 °C. Later on, the tissue was homogenized in buffer (10 mM Tris, 1 mM EDTA, 150 mM NaCl, 1 mM Na3VO4, 50 nM okadaic acid, 2% SDS, 10% glycerol, 0.0625 M Tris-HCl, and protease inhibitor cocktail 10 μl/ml (Calbiochem, Darmstadt, Germany); pH 6.8) with a Heidolph DIAX 600 homogenizer (Heidolph, Schwabach, Germany) or a manual homogenizer (glass to glass). Retinal explant cultures, both treated and untreated with TSA, from wt and rd1 mice were homogenized using the same process. Bradford assay was used to measure protein concentration. Proteins were then separated by SDS-PAGE 4–12% gradient gel (at 55 V), and transferred to a PVDF membrane (Amersham Biosciences, Buckinghamshire, UK). Membranes were incubated in Roti block (Roth, Karlsruhe, Germany) blocking buffer for 3 h at RT. After washing, primary Abs (acetylated lysine; acetylated H2A, H2B, H3, H4; actin) were added at a dilution of 1 : 1000 in buffer containing TBS-T and 5% dried milk (Roth), and incubated overnight at 4 °C. Primary Abs were purchased from Cell Signaling, except for actin Ab which was from Chemicon (Schwalbach, Germany). After washing, the membranes were treated with buffer containing HRP-conjugated secondary Ab (Amersham Biosciences) overnight at 4 °C. The membranes were developed using Hyperfilm (Amersham Biosciences) detection system. Quantification was performed after film scanning using ImageJ (NIH).
Microscopy, cell counting, and statistics
Morphological observations and routine light microscopy were performed on a Zeiss Imager Z1 Apotome Microscope, equipped with a Zeiss Axiocam digital camera. Images were captured using Zeiss Axiovision 4.7 software; image overlays and contrast enhancement were performed using Adobe Photoshop CS3. Images shown in figures are representative for least three different animals for each genotype/treatment. Percentages of TUNEL-positive cells were assessed and calculated in a blinded manner as reported previously.4, 9 The mean value for photoreceptor rows in the ONL after in vitro culture was determined using DAPI nuclear counterstaining. Values are given as mean±S.E.M. Statistical significance was tested using one-way ANOVA with Bonferroni correction and Prism (GraphPad Software, San Diego, CA, USA), significance levels were P<0.05 (*), P<0.01 (**), and P<0.001 (***).
Conflict of interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Abbreviations
- ab:
-
antibody
- abs:
-
antibodies
- CBP:
-
CREB-binding-protein
- CREB:
-
cyclic AMP-response-element-binding
- CRX:
-
cone-rod-homeobox
- GCL:
-
ganglion cell layer
- HDAC:
-
histone deacetylase
- INL:
-
inner nuclear layer
- NAD+:
-
nicotinamide dinucleotide
- NAM:
-
nicotinamide
- ONL:
-
outer nuclear layer
- P:
-
post-natal day
- PFA:
-
paraformaldehyde
- PBS:
-
phosphate buffered saline
- PDE6:
-
phosphodiesterase-6
- PAR:
-
poly-ADP-ribose
- PARP:
-
poly-ADP-ribose-polymerase
- RP:
-
retinitis pigmentosa
- SEM:
-
standard error of the mean
- TUNEL:
-
terminal deoxynucleotidyl transferase dUTP nick end labelling
- TSA:
-
trichostatin A
- WB:
-
western blot
References
Sancho-Pelluz J, Arango-Gonzalez B, Kustermann S, Romero FJ, van Veen T, Zrenner E et al. Photoreceptor cell death mechanisms in inherited retinal degeneration. Mol Neurobiol 2008; 38: 253–269.
Bowes C, Li T, Danciger M, Baxter LC, Applebury ML, Farber DB . Retinal degeneration in the rd mouse is caused by a defect in the beta subunit of rod cGMP-phosphodiesterase. Nature 1990; 347: 677–680.
Farber DB, Lolley RN . Cyclic guanosine monophosphate: elevation in degenerating photoreceptor cells of the C3H mouse retina. Science 1974; 186: 449–451.
Paquet-Durand F, Hauck SM, van Veen T, Ueffing M, Ekstrom P . PKG activity causes photoreceptor cell death in two retinitis pigmentosa models. J Neurochem 2009; 108: 796–810.
Rohrer B, Pinto FR, Hulse KE, Lohr HR, Zhang L, Almeida JS . Multidestructive pathways triggered in photoreceptor cell death of the rd mouse as determined through gene expression profiling. J Biol Chem 2004; 279: 41903–41910.
Azadi S, Paquet-Durand F, Medstrand P, van Veen T, Ekstrom PA . Up-regulation and increased phosphorylation of protein kinase C (PKC) delta, mu and theta in the degenerating rd1 mouse retina. Mol Cell Neurosci 2006; 31: 759–773.
Hackam AS, Strom R, Liu D, Qian J, Wang C, Otteson D et al. Identification of gene expression changes associated with the progression of retinal degeneration in the rd1 mouse. Invest Ophthalmol Vis Sci 2004; 45: 2929–2942.
Pilz RB, Broderick KE . Role of cyclic GMP in gene regulation. Front Biosci 2005; 10: 1239–1268.
Paquet-Durand F, Silva J, Talukdar T, Johnson LE, Azadi S, van Veen T et al. Excessive activation of poly(ADP-ribose) polymerase contributes to inherited photoreceptor degeneration in the retinal degeneration mouse 1. J Neurosci 2007; 27: 10311–10319.
Schreiber V, Dantzer F, Ame JC, de Murcia G . Poly(ADP-ribose): novel functions for an old molecule. Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol 2006; 7: 517–528.
Egger G, Liang G, Aparicio A, Jones PA . Epigenetics in human disease and prospects for epigenetic therapy. Nature 2004; 429: 457–463.
Morrison BE, Majdzadeh N, D’Mello SR . Histone deacetylases: focus on the nervous system. Cell Mol Life Sci 2007; 64: 2258–2269.
Haberland M, Montgomery RL, Olson EN . The many roles of histone deacetylases in development and physiology: implications for disease and therapy. Nat Rev Genet 2009; 10: 32–42.
Kruszewski M, Szumiel I . Sirtuins (histone deacetylases III) in the cellular response to DNA damage—facts and hypotheses. DNA Repair (Amst) 2005; 4: 1306–1313.
Peng GH, Chen S . Crx activates opsin transcription by recruiting HAT-containing co-activators and promoting histone acetylation. Hum Mol Genet 2007; 16: 2433–2452.
Wallace DM, Donovan M, Cotter TG . Histone deacetylase activity regulates apaf-1 and caspase 3 expression in the developing mouse retina. Invest Ophthalmol Vis Sci 2006; 47: 2765–2772.
Chen B, Cepko CL . Requirement of histone deacetylase activity for the expression of critical photoreceptor genes. BMC Dev Biol 2007; 7: 78.
Wood JG, Rogina B, Lavu S, Howitz K, Helfand SL, Tatar M et al. Sirtuin activators mimic caloric restriction and delay ageing in metazoans. Nature 2004; 430: 686–689.
Fan Y, Ludewig R, Scriba GK . 9-Fluorenylmethoxycarbonyl-labeled peptides as substrates in a capillary electrophoresis-based assay for sirtuin enzymes. Anal Biochem 2009; 387: 243–248.
Bowes C, van Veen T, Farber DB . Opsin, G-protein and 48-kDa protein in normal and rd mouse retinas: developmental expression of mRNAs and proteins and light/dark cycling of mRNAs. Exp Eye Res 1988; 47: 369–390.
Jaliffa C, Ameqrane I, Dansault A, Leemput J, Vieira V, Lacassagne E et al. Sirt1 involvement in rd10 mouse retinal degeneration. Invest Ophthalmol Vis Sci 2009; 50: 3562–3572.
Paquet-Durand F, Azadi S, Hauck SM, Ueffing M, van Veen T, Ekstrom P . Calpain is activated in degenerating photoreceptors in the rd1 mouse. J Neurochem 2006; 96: 802–814.
Gao J, Siddoway B, Huang Q, Xia H . Inactivation of CREB mediated gene transcription by HDAC8 bound protein phosphatase. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 2009; 379: 1–5.
Kalkhoven E . CBP and p300: HATs for different occasions. Biochem Pharmacol 2004; 68: 1145–1155.
Vecsey CG, Hawk JD, Lattal KM, Stein JM, Fabian SA, Attner MA et al. Histone deacetylase inhibitors enhance memory and synaptic plasticity via CREB: CBP-dependent transcriptional activation. J Neurosci 2007; 27: 6128–6140.
Hennig AK, Peng GH, Chen S . Regulation of photoreceptor gene expression by Crx-associated transcription factor network. Brain Res 2008; 1192: 114–133.
Palhan VB, Chen S, Peng GH, Tjernberg A, Gamper AM, Fan Y et al. Polyglutamine-expanded ataxin-7 inhibits STAGA histone acetyltransferase activity to produce retinal degeneration. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 2005; 102: 8472–8477.
Rajamohan SB, Pillai VB, Gupta M, Sundaresan NR, Birukov KG, Samant S et al. SIRT1 promotes cell survival under stress by deacetylation-dependent deactivation of poly (ADP-ribose) polymerase 1. Mol Cell Biol 2009; 29: 4116–4129.
Haenni SS, Hassa PO, Altmeyer M, Fey M, Imhof R, Hottiger MO . Identification of lysines 36 and 37 of PARP-2 as targets for acetylation and auto-ADP-ribosylation. Int J Biochem Cell Biol 2008; 40: 2274–2283.
Hassa PO, Haenni SS, Buerki C, Meier NI, Lane WS, Owen H et al. Acetylation of poly(ADP-ribose) polymerase-1 by p300/CREB-binding protein regulates coactivation of NF-kappaB-dependent transcription. J Biol Chem 2005; 280: 40450–40464.
Gan L, Mucke L . Paths of convergence: sirtuins in aging and neurodegeneration. Neuron 2008; 58: 10–14.
Chen B, Cepko CL . HDAC4 regulates neuronal survival in normal and diseased retinas. Science 2009; 323: 256–259.
Leng Y, Liang MH, Ren M, Marinova Z, Leeds P, Chuang DM . Synergistic neuroprotective effects of lithium and valproic acid or other histone deacetylase inhibitors in neurons: roles of glycogen synthase kinase-3 inhibition. J Neurosci 2008; 28: 2576–2588.
Bolger TA, Yao TP . Intracellular trafficking of histone deacetylase 4 regulates neuronal cell death. J Neurosci 2005; 25: 9544–9553.
Ryu H, Lee J, Olofsson BA, Mwidau A, Dedeoglu A, Escudero M et al. Histone deacetylase inhibitors prevent oxidative neuronal death independent of expanded polyglutamine repeats via an Sp1-dependent pathway. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 2003; 100: 4281–4286.
Rouaux C, Panteleeva I, Rene F, Gonzalez de Aguilar JL, Echaniz-Laguna A, Dupuis L et al. Sodium valproate exerts neuroprotective effects in vivo through CREB-binding protein-dependent mechanisms but does not improve survival in an amyotrophic lateral sclerosis mouse model. J Neurosci 2007; 27: 5535–5545.
Biermann J, Grieshaber P, Goebel U, Martin G, Thanos S, Di Giovanni S, Lagréze WA . Valproic acid-mediated neuroprotection and regeneration in injured retinal ganglion cells. Invest Ophthalmol Vis Sci. 2010; 51: 526–534. Epub 2009 Jul 23.
Scroggins BT, Robzyk K, Wang D, Marcu MG, Tsutsumi S, Beebe K et al. An acetylation site in the middle domain of Hsp90 regulates chaperone function. Mol Cell 2007; 25: 151–159.
Kekatpure VD, Dannenberg AJ, Subbaramaiah K . HDAC6 modulates Hsp90 chaperone activity and regulates activation of aryl hydrocarbon receptor signaling. J Biol Chem 2009; 284: 7436–7445.
Shen HY, He JC, Wang Y, Huang QY, Chen JF . Geldanamycin induces heat shock protein 70 and protects against MPTP-induced dopaminergic neurotoxicity in mice. J Biol Chem 2005; 280: 39962–39969.
Wen XR, Li C, Zong YY, Yu CZ, Xu J, Han D et al. Dual inhibitory roles of geldanamycin on the c-Jun NH2-terminal kinase 3 signal pathway through suppressing the expression of mixed-lineage kinase 3 and attenuating the activation of apoptosis signal-regulating kinase 1 via facilitating the activation of Akt in ischemic brain injury. Neuroscience 2008; 156: 483–497.
Sanyal S, Bal AK . Comparative light and electron microscopic study of retinal histogenesis in normal and rd mutant mice. Z Anat Entwicklungsgesch 1973; 142: 219–238.
Hauck SM, Ekstrom PA, Ahuja-Jensen P, Suppmann S, Paquet-Durand F, van Veen T et al. Differential modification of phosducin protein in degenerating rd1 retina is associated with constitutively active Ca2+/calmodulin kinase II in rod outer segments. Mol Cell Proteomics 2006; 5: 324–336.
Sanz MM, Johnson LE, Ahuja S, Ekstrom PA, Romero J, van Veen T . Significant photoreceptor rescue by treatment with a combination of antioxidants in an animal model for retinal degeneration. Neuroscience 2007; 145: 1120–1129.
Bitterman KJ, Anderson RM, Cohen HY, Latorre-Esteves M, Sinclair DA . Inhibition of silencing and accelerated aging by nicotinamide, a putative negative regulator of yeast sir2 and human SIRT1. J Biol Chem 2002; 277: 45099–45107.
Acknowledgements
We thank H Abdalle, B Klefbohm, K Dengler, and S Kurz-Bernhard for excellent technical assistance and Y Arsenijevic, M-T Perez, and B Wissinger for helpful comments and discussions. This study was supported by grants from the EU (RETNET: MRTN-CT-2003–504003, EVI-GENORET: LSHG-CT-2005–512036, NEUROTRAIN: MEST-CT-2005–020235), Fundación Oftalmológica del Mediterráneo (FOM), KMA, Synfrämjandets Forskningsfond, Stiftelsen för synskadade i f.d. Malmöhus län, Foundation Fighting Blindness (FFB), Swedish Medical Research Council (VRM), Crafoord foundation, Kerstan Foundation, Torsten och Ragnar Söderbergs Foundation, and Deutsche Forschungsgemeinschaft (DFG; PA1751/1–1).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Edited by A Verkhratsky
Supplementary Information accompanies the paper on Cell Death and Disease website (http://www.nature.com/cddis)
Rights and permissions
This article is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial-No Derivative Works 3.0 License. To view a copy of this license, visit http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by-nc-nd/3.0/
About this article
Cite this article
Sancho-Pelluz, J., Alavi, M., Sahaboglu, A. et al. Excessive HDAC activation is critical for neurodegeneration in the rd1 mouse. Cell Death Dis 1, e24 (2010). https://doi.org/10.1038/cddis.2010.4
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/cddis.2010.4
Keywords
This article is cited by
-
T-type voltage-gated channels, Na+/Ca2+-exchanger, and calpain-2 promote photoreceptor cell death in inherited retinal degeneration
Cell Communication and Signaling (2024)
-
Dysregulation of histone deacetylases in ocular diseases
Archives of Pharmacal Research (2024)
-
Roles of Histone Acetyltransferases and Deacetylases in the Retinal Development and Diseases
Molecular Neurobiology (2023)
-
HDAC inhibition ameliorates cone survival in retinitis pigmentosa mice
Cell Death & Differentiation (2021)
-
CRISPR-Based Genome Editing as a New Therapeutic Tool in Retinal Diseases
Molecular Biotechnology (2021)