Abstract
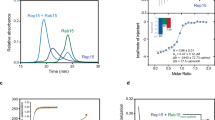
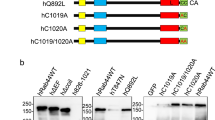
MAMMALIAN cells express many ras-like low molecular mass GTP-binding proteins (rab proteins)1–6 that are highly homologous to the Yptl and Sec4 proteins involved in controlling secretion in yeast7-9. Owing to their structural similarity and to their variety, rab proteins have been postulated to act as specific regulators of membrance traffic in exocytosis and endocytosis10, and rab5 has been shown to be involved in early endosome fusion in vitro11. In agreement with their postulated functions, all rab proteins studied so far have been found in distinct subcompartments along the exocytic or endocytic pathways5,11–13. To define the region mediating their specific localization, we transiently expressed rab2, rab5 and rab7 hybrid proteins in BHK cells, and determined their intracellular localization by immunofluorescence confocal microscopy and subcellular fractionation. Here we present evidence that the highly variable C-terminal domain contains structural elements necessary for the association of rab proteins with their specific target membranes in the endocytic pathway.
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 51 print issues and online access
$199.00 per year
only $3.90 per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on Springer Link
- Instant access to full article PDF
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Touchot, N., Chardin, P. & Tavitian, A. Proc. natn. Acad. Sci. U.S.A. 84, 8210–8214 (1987).
Bucci, C. et al. Nucleic Acids Res. 16, 9979–9993 (1988).
Matsui, Y. et al. J. biol. Chem. 263, 11071–11074 (1988).
Zahraoui, A., Touchot, N., Chardin, P. & Tavitian, A. J. biol. Chem. 264, 12394–12401 (1989).
Chavrier, P., Parton, R. G., Hauri, H. P., Simons, K. & Zerial, M. Cell 62, 317–329 (1990).
Chavrier, P., Vingron, M., Sander, C., Simons, K. & Zerial, M. Molec. cell. Biol. 10, 6578–6585 (1990).
Gallwitz, D., Donath, C. & Sander, C. Nature 306, 704–707 (1983).
Salminen, A. & Novick, P. J. Cell 49, 527–538 (1987).
Segev, N., Mulholland, J. & Botstein, D. Cell 52, 915–924 (1988).
Bourne, H. R., Sanders, D. A. & McCormick, F. Nature 348, 125–132 (1990).
Gorvel, J. P., Chavrier, P., Zerial, M. & Gruenberg, J. Cell 64, 915–925 (1991).
Goud, B., Zahraoui, A., Tavitian, A. & Saraste, J. Nature 345, 553–556 (1990).
Fischer von Mollard, G. et al. Proc. natn. Acad. Sci. U.S.A. 87, 1988–1992 (1990).
Willumsen, B. M., Norris, K., Papageorge, A. G., Hubbert, N. L. & Lowy, D. R. EMBO J. 3, 2581–2585 (1984).
Deschenes, R. J. & Broach, J. R. Molec. cell. Biol. 7, 2344–2351 (1987).
Molenaar, C. M. T., Prange, R. & Gallwitz, D. EMBO J. 7, 971–976 (1988).
Walworth, N. C., Goud, B., Kastan Kabcenell, A. & Novick, P. J. EMBO J. 8, 1685–1693 (1989).
Gutierrez, L., Magee, A. I., Marshall, C. J. & Hancock, J. F. EMBO J. 8, 1093–1098 (1989).
Hancock, J. F., Magee, A. I., Childs, J. E. & Marshall, C. J. Cell 57, 1167–1177 (1989).
Fuerst, T. R., Niles, E. G., Studier, F. W. & Moss, B. Proc. natn. Acad. Sci. U.S.A. 83, 8122–8126 (1986).
Zerial, M., Melancon, P., Schneider, C. & Garoff, H. EMBO J. 5, 1543–1550 (1986).
Hopkins, C. R. Cell 35, 321–330 (1983).
Schmid, S. L., Fuchs, R., Male, P. & Mellman, I. Cell 52, 73–83 (1988).
Hancock, J. F., Paterson, H. & Marshall, C. J. Cell 63, 133–139 (1989).
Horton, R. M., Hunt, H. D., Ho, S. N., Pullen, J. K. & Pease, L. R. Gene 77, 61–68 (1989).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Chavrier, P., Gorvel, JP., Stelzer, E. et al. Hypervariable C-termmal domain of rab proteins acts as a targeting signal. Nature 353, 769–772 (1991). https://doi.org/10.1038/353769a0
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/353769a0
This article is cited by
-
Molecular characterization of Rab5A, and involvement in innate immunity in Yellow River Carp Cyprinus carpio
Aquaculture International (2024)
-
JRAB/MICAL-L2 undergoes liquid–liquid phase separation to form tubular recycling endosomes
Communications Biology (2021)
-
Computer-aided identification of lung cancer inhibitors through homology modeling and virtual screening
Egyptian Journal of Medical Human Genetics (2019)
-
Molecular Insights into the Roles of Rab Proteins in Intracellular Dynamics and Neurodegenerative Diseases
NeuroMolecular Medicine (2018)
-
Secretory RAB GTPase 3C modulates IL6-STAT3 pathway to promote colon cancer metastasis and is associated with poor prognosis
Molecular Cancer (2017)
Comments
By submitting a comment you agree to abide by our Terms and Community Guidelines. If you find something abusive or that does not comply with our terms or guidelines please flag it as inappropriate.