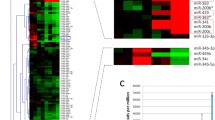
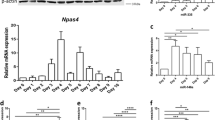
Abstract
Using microarray analysis, we detected microRNA-124 (miR-124) to be abundantly expressed in the olfactory bulb (OB). miR-124 regulates adult neurogenesis in the subventricular zone (SVZ). However, much less is known about its role in newborn OB neurons. Here, using both gain-of-function and loss-of-function approaches, we demonstrate that brain-specific miR-124 affects dendritic morphogenesis and spine density in newborn OB neurons. Functional Annotation Clustering of miR-124 targets was enriched in “cell morphogenesis involved in neuron differentiation.”






Similar content being viewed by others
References
Akerblom M, Sachdeva R, Barde I, Verp S, Gentner B, Trono D, Jakobsson J (2012) MicroRNA-124 is a subventricular zone neuronal fate determinant. The Journal of neuroscience : the official journal of the Society for Neuroscience 32(26):8879–8889
Akerblom M, Petri R, Sachdeva R, Klussendorf T, Mattsson B, Gentner B, Jakobsson J (2014) microRNA-125 distinguishes developmentally generated and adult-born olfactory bulb interneurons. Development 141(7):1580–1588
Alonso M, Viollet C, Gabellec MM, Meas-Yedid V, Olivo-Marin JC, Lledo PM (2006) Olfactory discrimination learning increases the survival of adult-born neurons in the olfactory bulb. The Journal of neuroscience : the official journal of the Society for Neuroscience 26(41):10508–10513
Arvanitis DN, Jungas T, Behar A, Davy A (2010) Ephrin-B1 reverse signaling controls a posttranscriptional feedback mechanism via miR-124. Mol Cell Biol 30(10):2508–2517
Baudet ML, Zivraj KH, Abreu-Goodger C, Muldal A, Armisen J, Blenkiron C, Goldstein LD, Miska EA, Holt CE (2011) miR-124 acts through CoREST to control onset of Sema3A sensitivity in navigating retinal growth cones. Nat Neurosci 15(1):29–38
Bindea G, Mlecnik B, Hackl H, Charoentong P, Tosolini M, Kirilovsky A, Fridman WH, Pages F, Trajanoski Z, Galon J (2009) ClueGO: a cytoscape plug-in to decipher functionally grouped gene ontology and pathway annotation networks. Bioinformatics 25(8):1091–1093
Bindea G, Galon J, Mlecnik B (2013) CluePedia cytoscape plugin: pathway insights using integrated experimental and in silico data. Bioinformatics 29(5):661–663
Carleton A, Petreanu LT, Lansford R, Alvarez-Buylla A, Lledo PM (2003) Becoming a new neuron in the adult olfactory bulb. Nat Neurosci 6(5):507–518
Cheng LC, Pastrana E, Tavazoie M, Doetsch F (2009) miR-124 regulates adult neurogenesis in the subventricular zone stem cell niche. Nat Neurosci 12(4):399–408
Davila NG, Blakemore LJ, Trombley PQ (2003) Dopamine modulates synaptic transmission between rat olfactory bulb neurons in culture. J Neurophysiol 90(1):395–404
Forero DA, van der Ven K, Callaerts P, Del-Favero J (2010) miRNA genes and the brain: implications for psychiatric disorders. Hum Mutat 31(11):1195–1204
Franke K, Otto W, Johannes S, Baumgart J, Nitsch R, Schumacher S (2012) miR-124-regulated RhoG reduces neuronal process complexity via ELMO/Dock180/Rac1 and Cdc42 signalling. EMBO J 31(13):2908–2921
Gao FB (2010) Context-dependent functions of specific microRNAs in neuronal development. Neural Dev 5:25
Gentner B, Schira G, Giustacchini A, Amendola M, Brown BD, Ponzoni M, Naldini L (2009) Stable knockdown of microRNA in vivo by lentiviral vectors. Nat Methods 6(1):63–66
Gu X, Meng S, Liu S, Jia C, Fang Y, Li S, Fu C, Song Q, Lin L, Wang X (2014) miR-124 represses ROCK1 expression to promote neurite elongation through activation of the PI3K/Akt signal pathway. Journal of molecular neuroscience : MN 52(1):156–165
Gurtan AM, Sharp PA (2013) The role of miRNAs in regulating gene expression networks. J Mol Biol 425(19):3582–3600
Krichevsky AM, King KS, Donahue CP, Khrapko K, Kosik KS (2003) A microRNA array reveals extensive regulation of microRNAs during brain development. RNA 9(10):1274–1281
Kuroda H, Kutner RH, Bazan NG, Reiser J (2009) Simplified lentivirus vector production in protein-free media using polyethylenimine-mediated transfection. J Virol Methods 157(2):113–121
Kutner RH, Zhang XY, Reiser J (2009) Production, concentration and titration of pseudotyped HIV-1-based lentiviral vectors. Nat Protoc 4(4):495–505
Lazarini F, Lledo PM (2011) Is adult neurogenesis essential for olfaction? Trends Neurosci 34(1):20–30
Ledderose C, Mohnle P, Limbeck E, Schutz S, Weis F, Rink J, Briegel J, Kreth S (2012) Corticosteroid resistance in sepsis is influenced by microRNA-124-induced downregulation of glucocorticoid receptor-alpha. Crit Care Med 40(10):2745–2753
Lemasson M, Saghatelyan A, Olivo-Marin JC, Lledo PM (2005) Neonatal and adult neurogenesis provide two distinct populations of newborn neurons to the mouse olfactory bulb. J Neurosci 25(29):6816–6825
Li JH, Liu S, Zhou H, Qu LH, Yang JH (2014) starBase v2.0: decoding miRNA-ceRNA, miRNA-ncRNA and protein-RNA interaction networks from large-scale CLIP-Seq data. Nucleic Acids Res 42(Database issue):D92–D97
Li G, Yang J, Ling S (2015) Formaldehyde exposure alters miRNA expression profiles in the olfactory bulb. Inhal Toxicol 27(8):387–393
Liang Y, Ridzon D, Wong L, Chen C (2007) Characterization of microRNA expression profiles in normal human tissues. BMC Genomics 8:166
Luikart BW, Bensen AL, Washburn EK, Perederiy JV, Su KG, Li Y, Kernie SG, Parada LF, Westbrook GL (2011) miR-132 mediates the integration of newborn neurons into the adult dentate gyrus. PLoS One 6(5):e19077
Notter T, Panzanelli P, Pfister S, Mircsof D, Fritschy JM (2014) A protocol for concurrent high-quality immunohistochemical and biochemical analyses in adult mouse central nervous system. Eur J Neurosci 39(2):165–175
Pathania M, Torres-Reveron J, Yan L, Kimura T, Lin TV, Gordon V, Teng ZQ, Zhao X, Fulga TA, Van Vactor D, Bordey A (2012) miR-132 enhances dendritic morphogenesis, spine density, synaptic integration, and survival of newborn olfactory bulb neurons. PLoS One 7(5):e38174
Rajasethupathy P, Fiumara F, Sheridan R, Betel D, Puthanveettil SV, Russo JJ, Sander C, Tuschl T, Kandel E (2009) Characterization of small RNAs in Aplysia reveals a role for miR-124 in constraining synaptic plasticity through CREB. Neuron 63(6):803–817
Sanuki R, Onishi A, Koike C, Muramatsu R, Watanabe S, Muranishi Y, Irie S, Uneo S, Koyasu T, Matsui R, Cherasse Y, Urade Y, Watanabe D, Kondo M, Yamashita T, Furukawa T (2011) miR-124a is required for hippocampal axogenesis and retinal cone survival through Lhx2 suppression. Nat Neurosci 14(9):1125–1134
Schneider Gasser EM, Straub CJ, Panzanelli P, Weinmann O, Sassoe-Pognetto M, Fritschy JM (2006) Immunofluorescence in brain sections: simultaneous detection of presynaptic and postsynaptic proteins in identified neurons. Nat Protoc 1(4):1887–1897
Schratt G (2009a) Fine-tuning neural gene expression with microRNAs. Curr Opin Neurobiol 19(2):213–219
Schratt G (2009b) microRNAs at the synapse. Nat Rev Neurosci 10(12):842–849
Sempere LF, Freemantle S, Pitha-Rowe I, Moss E, Dmitrovsky E, Ambros V (2004) Expression profiling of mammalian microRNAs uncovers a subset of brain-expressed microRNAs with possible roles in murine and human neuronal differentiation. Genome Biol 5(3):R13
Swanson AM, Shapiro LP, Whyte AJ, Gourley SL (2013) Glucocorticoid receptor regulation of action selection and prefrontal cortical dendritic spines. Communicative & integrative biology 6(6):e26068
Vo N, Klein ME, Varlamova O, Keller DM, Yamamoto T, Goodman RH, Impey S (2005) A cAMP-response element binding protein-induced microRNA regulates neuronal morphogenesis. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 102(45):16426–16431
Wayman GA, Davare M, Ando H, Fortin D, Varlamova O, Cheng HY, Marks D, Obrietan K, Soderling TR, Goodman RH, Impey S (2008) An activity-regulated microRNA controls dendritic plasticity by down-regulating p250GAP. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 105(26):9093–9098
Whitman MC, Greer CA (2009) Adult neurogenesis and the olfactory system. Prog Neurobiol 89(2):162–175
Xu XL, Li Y, Wang F, Gao FB (2008) The steady-state level of the nervous-system-specific microRNA-124a is regulated by dFMR1 in drosophila. The Journal of neuroscience : the official journal of the Society for Neuroscience 28(46):11883–11889
Xue Q, Yu C, Wang Y, Liu L, Zhang K, Fang C, Liu F, Bian G, Song B, Yang A, Ju G, Wang J (2016) miR-9 and miR-124 synergistically affect regulation of dendritic branching via the AKT/GSK3beta pathway by targeting Rap2a. Sci Rep 6:26781
Yoo AS, Staahl BT, Chen L, Crabtree GR (2009) MicroRNA-mediated switching of chromatin-remodelling complexes in neural development. Nature 460(7255):642–646
Yu JY, Chung KH, Deo M, Thompson RC, Turner DL (2008) MicroRNA miR-124 regulates neurite outgrowth during neuronal differentiation. Exp Cell Res 314(14):2618–2633
Zhao YN, Li WF, Li F, Zhang Z, Dai YD, Xu AL, Qi C, Gao JM, Gao J (2013) Resveratrol improves learning and memory in normally aged mice through microRNA-CREB pathway. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 435(4):597–602
Acknowledgements
We are grateful to the Core Facilities of Zhejiang University Institute of Neuroscience for the technical assistance.
Author’s Contributions
Guifa Li carried out the sample collection, participated in the array analysis, and drafted the manuscript. Shucai Ling participated in the cell culture and drafted the manuscript. All authors have read and approved the final manuscript.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
All experiments were approved by the Animal Advisory Committee at Zhejiang University and conducted in accordance with the US National Institutes of Health Guidelines for the Care and Use of Laboratory Animals.
Conflict of Interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Li, G., Ling, S. MiR-124 Promotes Newborn Olfactory Bulb Neuron Dendritic Morphogenesis and Spine Density. J Mol Neurosci 61, 159–168 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12031-016-0873-x
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12031-016-0873-x