Abstract
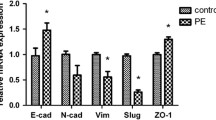
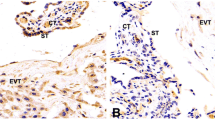
Incomplete invasion of extravillous trophoblasts (EVT) is thought to be associated with complications of pregnancy. Snail, a zinc-finger transcription factor represses the transcription of the cell adhesion molecule E-cadherin. The aim of this study was to investigate the expression of E-cadherin and Snail in placental tissue with preeclampsia or HELLP. Placental tissues were obtained from five patients with HELLP syndrome, seven patients with preeclampsia and seven patients after a normal term birth and analysed for Snail and E-cadherin immunoreactivity with specific monoclonal antibodies. Immunohistochemical staining of the placental tissue was analysed using an immunoreactivity score for the evaluation of staining intensity. In preeclamptic EVT, Snail immunoreactivity showed a significant 1.7-fold increase, accompanied by a significant 1.9-fold reduction of E-cadherin immunoreactivity. A 1.7-fold increase of Snail and in parallel a 1.3-fold reduction of E-cadherin was observed in EVT of HELLP placentas although without statistical significance. Loss of E-cadherin can be observed during epithelial–mesenchymal transition (EMT), a key process in normal development and trophoblast differentiation. Snail represses the transcription of E-cadherin triggering a complete EMT. Results obtained in this study showed changes of Snail and E-cadherin immunoreactivity in preeclamptic placentas that could be accompanied with an altered EMT in trophoblasts.




Similar content being viewed by others
References
Babawale MO, Van Noorden S, Pignatelli M, Stamp GW, Elder MG, Sullivan MH (1996) Morphological interactions of human first trimester placental villi co-cultured with decidual explants. Hum Reprod 11:444–450
Batlle E, Sancho E, Franci C, Dominguez D, Monfar M, Baulida J, Garcia De Herreros A (2000) The transcription factor snail is a repressor of E-cadherin gene expression in epithelial tumour cells. Nat Cell Biol 2:84–89
Benian A, Madazli R, Aksu F, Uzun H, Aydin S (2002) Plasma and placental levels of interleukin-10, transforming growth factor-beta1, and epithelial-cadherin in preeclampsia. Obstet Gynecol 100:327–331
Brown LM, Lacey HA, Baker PN, Crocker IP (2005) E-cadherin in the assessment of aberrant placental cytotrophoblast turnover in pregnancies complicated by pre-eclampsia. Histochem Cell Biol 124:499–506
Cano A, Perez-Moreno MA, Rodrigo I, Locascio A, Blanco MJ, del Barrio MG, Portillo F, Nieto MA (2000) The transcription factor snail controls epithelial–mesenchymal transitions by repressing E-cadherin expression. Nat Cell Biol 2:76–83
Carver EA, Jiang R, Lan Y, Oram KF, Gridley T (2001) The mouse snail gene encodes a key regulator of the epithelial–mesenchymal transition. Mol Cell Biol 21:8184–8188
Cross JC, Werb Z, Fisher SJ (1994) Implantation and the placenta: key pieces of the development puzzle. Science 266:1508–1518
Damsky CH, Librach C, Lim KH, Fitzgerald ML, McMaster MT, Janatpour M, Zhou Y, Logan SK, Fisher SJ (1994) Integrin switching regulates normal trophoblast invasion. Development 120:3657–3666
De Craene B, Gilbert B, Stove C, Bruyneel E, van Roy F, Berx G (2005) The transcription factor snail induces tumor cell invasion through modulation of the epithelial cell differentiation program. Cancer Res 65:6237–6244
Duckitt K, Harrington D (2005) Risk factors for pre-eclampsia at antenatal booking: systematic review of controlled studies. BMJ 330:565
Floridon C, Nielsen O, Holund B, Sunde L, Westergaard JG, Thomsen SG, Teisner B (2000) Localization of E-cadherin in villous, extravillous and vascular trophoblasts during intrauterine, ectopic and molar pregnancy. Mol Hum Reprod 6:943–950
Gotzmann J, Mikula M, Eger A, Schulte-Hermann R, Foisner R, Beug H, Mikulits W (2004) Molecular aspects of epithelial cell plasticity: implications for local tumor invasion and metastasis. Mutat Res 566:9–20
Grau Y, Carteret C, Simpson P (1984) Mutations and chromosomal rearrangements affecting the expression of Snail, a gene involved in embryonic patterning in Drosophila Melanogaster. Genetics 108:347–360
Hay ED (1995) An overview of epithelio–mesenchymal transformation. Acta Anat 154:8–20
Hemavathy K, Ashraf SI, Ip YT (2000) Snail/slug family of repressors: slowly going into the fast lane of development and cancer. Gene 257:1–12
Ikenouchi J, Matsuda M, Furuse M, Tsukita S (2003) Regulation of tight junctions during the epithelium–mesenchyme transition: direct repression of the gene expression of claudins/occludin by Snail. J Cell Sci 116:1959–1967
Kingdom J, Huppertz B, Seaward G, Kaufmann P (2000) Development of the placental villous tree and its consequences for fetal growth. Eur J Obstet Gynecol Reprod Biol 92:35–43
Lala PK, Hamilton GS (1996) Growth factors, proteases and protease inhibitors in the maternal–fetal dialogue. Placenta 17:545–555
Manyonda IT, Whitley GS, Cartwright JE (2001) Trophoblast cell lines: a response to the workshop report by King et al. Placenta 22:262–263
Marzioni D, Banita M, Felici A, Paradinas FJ, Newlands E, De Nictolis M, Muhlhauser J, Castellucci M (2001) Expression of ZO-1 and occludin in normal human placenta and in hydatidiform moles. Mol Hum Reprod 7:279–285
Myatt L, Miodovnik M (1999) Prediction of preeclampsia. Semin Perinatol 23:45–57
Nieto MA (2002) The snail superfamily of zinc-finger transcription factors. Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol 3:155–166
Ohkubo T, Ozawa M (2004) The transcription factor Snail downregulates the tight junction components independently of E-cadherin downregulation. J Cell Sci 117:1675–1685
Peinado H, Ballestar E, Esteller M, Cano A (2004) Snail mediates E-cadherin repression by the recruitment of the Sin3A/histone deacetylase 1 (HDAC1)/HDAC2 complex. Mol Cell Biol 24:306–319
Peinado H, Portillo F, Cano A (2004) Transcriptional regulation of cadherins during development and carcinogenesis. Int J Dev Biol 48:365–375
Perez-Moreno M, Jamora C, Fuchs E (2003) Sticky business: orchestrating cellular signals at adherens junctions. Cell 112:535–548
Pijnenborg R, Dixon G, Robertson WB, Brosens I (1980) Trophoblastic invasion of human decidua from 8 to 18 weeks of pregnancy. Placenta 1:3–19
Pijnenborg R, Anthony J, Davey DA, Rees A, Tiltman A, Vercruysse L, van Assche A (1991) Placental bed spiral arteries in the hypertensive disorders of pregnancy. Br J Obstet Gynaecol 98:648–655
Pijnenborg R (1998) The origin and future of placental bed research. Eur J Obstet Gynecol Reprod Biol 81:185–190
Rath W, Faridi A, Dudenhausen JW (2000) HELLP syndrome. J Perinat Med 28:249–260
Rath W, Bartz C (2004) Treatment of severe preeclampsia and HELLP syndrome. Zentralbl Gynakol 126:293–298
Reister F, Frank HG, Kingdom JC, Heyl W, Kaufmann P, Rath W, Huppertz B (2001) Macrophage-induced apoptosis limits endovascular trophoblast invasion in the uterine wall of preeclamptic women. Lab Invest 81:1143–1152
Remmele W, Stegner HE (1987) Recommendation for uniform definition of an immunoreactive score (IRS) for immunohistochemical estrogen receptor detection (ER-ICA) in breast cancer tissue. Pathologe 8:138–140
Shih Ie M, Hsu MY, Oldt RJ 3rd, Herlyn M, Gearhart JD, Kurman RJ (2002) The role of E-cadherin in the motility and invasion of implantation site intermediate trophoblast. Placenta 23:706–715
Shiverick KT, King A, Frank H, Whitley GS, Cartwright JE, Schneider H (2001) Cell culture models of human trophoblast II: trophoblast cell lines—a workshop report. Placenta 22(Suppl A):S104–S106
Sibai BM, Caritis S, Hauth J (2003) What we have learned about preeclampsia. Semin Perinatol 27:239–246
Sibai BM (2004) Diagnosis, controversies, and management of the syndrome of hemolysis, elevated liver enzymes, and low platelet count. Obstet Gynecol 103:981–991
Thiery JP, Chopin D (1999) Epithelial cell plasticity in development and tumor progression. Cancer Metastasis Rev 18:31–42
Thiery JP (2002) Epithelial–mesenchymal transitions in tumour progression. Nat Rev Cancer 2:442–454
Thiery JP (2003) Epithelial–mesenchymal transitions in development and pathologies. Curr Opin Cell Biol 15:740–746
Vicovac L, Aplin JD (1996) Epithelial–mesenchymal transition during trophoblast differentiation. Acta Anat 156:202–216
Walker JJ (2000) Pre-eclampsia. Lancet 356:1260–1265
Zhou Y, Damsky CH, Fisher SJ (1997) Preeclampsia is associated with failure of human cytotrophoblasts to mimic a vascular adhesion phenotype. One cause of defective endovascular invasion in this syndrome? J Clin Invest 99:2152–2164
Zhou Y, Fisher SJ, Janatpour M, Genbacev O, Dejana E, Wheelock M, Damsky CH (1997) Human cytotrophoblasts adopt a vascular phenotype as they differentiate. A strategy for successful endovascular invasion? J Clin Invest 99:2139–2151
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
K.-F. Becker and U. Jeschke contributed equally to this work.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Blechschmidt, K., Mylonas, I., Mayr, D. et al. Expression of E-cadherin and its repressor Snail in placental tissue of normal, preeclamptic and HELLP pregnancies. Virchows Arch 450, 195–202 (2007). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00428-006-0343-x
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00428-006-0343-x