Abstract
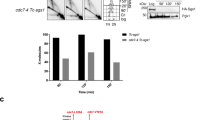
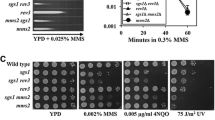
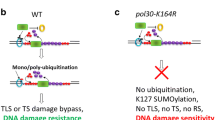
DNA repair is essential to maintain genome integrity. In addition to various DNA repair pathways dealing with specific types of DNA lesions, DNA damage tolerance (DDT) promotes the bypass of DNA replication blocks encountered by the replication fork to prevent cell death. Budding yeast Rad5 plays an essential role in the DDT pathway and its structure indicates that Rad5 recognizes damaged DNA or stalled replication forks, suggesting that Rad5 plays an important role in the DDT pathway choice. It has been reported that Rad5 forms subnuclear foci in the presence of methyl methanesulfonate (MMS) during the S phase. By analyzing the formation of Rad5 foci after MMS treatment, we showed that some specific DNA structures rather than mono-ubiquitination of proliferating cell nuclear antigen are required for the recruitment of Rad5 to the damaged site. Moreover, inactivation of the base excision repair (BER) pathway greatly decreased the Rad5 focus formation, suggesting that Rad5 recognizes specific DNA structures generated by BER. We also identified a negative role of overexpressed translesion synthesis polymerase Polη in the formation of Rad5 foci. Based on these data, we propose a modified DDT pathway model in which Rad5 plays a role in activating the DDT pathway.




Similar content being viewed by others
References
Adamczyk J, Deregowska A, Panek A, Golec E, Lewinska A, Wnuk M (2016) Affected chromosome homeostasis and genomic instability of clonal yeast cultures. Curr Genet 62:405–418. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00294-015-0537-3
Alexander JL, Orr-Weaver TL (2016) Replication fork instability and the consequences of fork collisions from rereplication. Genes Dev 30:2241–2252. https://doi.org/10.1101/gad.288142.116
Ali-Osman F, Rairkar A, Young P (1995) Formation and repair of 1,3-bis-(2-chloroethyl)-1-nitrosourea and cisplatin induced total genomic DNA interstrand crosslinks in human glioma cells. Cancer Biochem Biophys 14:231–241
Andersen PL, Xu F, Xiao W (2008) Eukaryotic DNA damage tolerance and translesion synthesis through covalent modifications of PCNA. Cell Res 18:162–173. https://doi.org/10.1038/cr.2007.114
Ball LG, Zhang K, Cobb JA, Boone C, Xiao W (2009) The yeast Shu complex couples error-free post-replication repair to homologous recombination. Mol Microbiol 73:89–102
Bjoras M, Klungland A, Johansen RF, Seeberg E (1995) Purification and properties of the alkylation repair DNA glycosylase encoded the MAG gene from Saccharomyces cerevisiae. Biochemistry 34:4577–4582
Blastyak A, Pinter L, Unk I, Prakash L, Prakash S, Haracska L (2007) Yeast Rad5 protein required for postreplication repair has a DNA helicase activity specific for replication fork regression. Mol Cell 28:167–175. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.molcel.2007.07.030
Boehm EM, Powers KT, Kondratick CM, Spies M, Houtman JC, Washington MT (2016) The proliferating cell nuclear antigen (PCNA)-interacting protein (PIP) motif of DNA polymerase eta mediates its interaction with the C-terminal domain of Rev1. J Biol Chem 291:8735–8744. https://doi.org/10.1074/jbc.M115.697938
Boiteux S, Guillet M (2004) Abasic sites in DNA: repair and biological consequences in Saccharomyces cerevisiae. DNA Repair 3:1–12
Boiteux S, Jinks-Robertson S (2013) DNA repair mechanisms and the bypass of DNA damage in Saccharomyces cerevisiae. Genetics 193:1025–1064. https://doi.org/10.1534/genetics.112.145219
Boiteux S, Radicella JP (1999) Base excision repair of 8-hydroxyguanine protects DNA from endogenous oxidative stress. Biochimie 81:59–67
Carlile CM, Pickart CM, Matunis MJ, Cohen RE (2009) Synthesis of free and proliferating cell nuclear antigen-bound polyubiquitin chains by the RING E3 ubiquitin ligase Rad5. J Biol Chem 284:29326–29334. https://doi.org/10.1074/jbc.M109.043885
Crosby B, Prakash L, Davis H, Hinkle DC (1981) Purification and characterization of a uracil-DNA glycosylase from the yeast Saccharomyces cerevisiae. Nucleic Acids Res 9:5797–5809
Donigan KA, Cerritelli SM, McDonald JP, Vaisman A, Crouch RJ, Woodgate R (2015) Unlocking the steric gate of DNA polymerase eta leads to increased genomic instability in Saccharomyces cerevisiae. DNA Repair 35:1–12. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.dnarep.2015.07.002
Ehrenfeld GM et al (1987) Copper-dependent cleavage of DNA by bleomycin. Biochemistry 26:931–942
Enervald E, Lindgren E, Katou Y, Shirahige K, Strom L (2013) Importance of Poleta for damage-induced cohesion reveals differential regulation of cohesion establishment at the break site and genome-wide. PLoS Genet 9:e1003158. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pgen.1003158
Fasullo MT, Sun M (2017) Both RAD5-dependent and independent pathways are involved in DNA damage-associated sister chromatid exchange in budding yeast. AIMS genetics 4:84–102. https://doi.org/10.3934/genet.2017.2.84
Fields S, Song O (1989) A novel genetic system to detect protein-protein interactions. Nature 340:245–246. https://doi.org/10.1038/340245a0
Fromme JC, Banerjee A, Verdine GL (2004) DNA glycosylase recognition and catalysis. Curr Opin Struct Biol 14:43–49. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.sbi.2004.01.003
Gangavarapu V, Haracska L, Unk I, Johnson RE, Prakash S, Prakash L (2006) Mms2-Ubc13-dependent and -independent roles of Rad5 ubiquitin ligase in postreplication repair and translesion DNA synthesis in Saccharomyces cerevisiae. Mol Cell Biol 26:7783–7790. https://doi.org/10.1128/MCB.01260-06
Gilljam KM et al (2009) Identification of a novel, widespread, and functionally important PCNA-binding motif. J Cell Biol 186:645–654. https://doi.org/10.1083/jcb.200903138
Guillet M, Boiteux S (2002) Endogenous DNA abasic sites cause cell death in the absence of Apn1, Apn2 and Rad1/Rad10 in Saccharomyces cerevisiae. Embo J 21:2833–2841. https://doi.org/10.1093/emboj/21.11.2833
Haracska L, Prakash S, Prakash L (2002) Yeast Rev1 protein is a G template-specific DNA polymerase. J Biol Chem 277:15546–15551. https://doi.org/10.1074/jbc.M112146200
Hishiki A, Hara K, Ikegaya Y, Yokoyama H, Shimizu T, Sato M, Hashimoto H (2015) Structure of a novel DNA-binding domain of Helicase-like transcription factor (HLTF) and its functional implication in DNA damage tolerance. J Biol Chem 290:13215–13223. https://doi.org/10.1074/jbc.M115.643643
Hoege C, Pfander B, Moldovan GL, Pyrowolakis G, Jentsch S (2002) RAD6-dependent DNA repair is linked to modification of PCNA by ubiquitin and. SUMO Nature 419:135–141. https://doi.org/10.1038/nature00991
Horton JK et al (2013) Preventing oxidation of cellular XRCC1 affects PARP-mediated DNA damage responses. DNA Repair 12:774–785. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.dnarep.2013.06.004
Hsiang YH, Hertzberg R, Hecht S, Liu LF (1985) Camptothecin induces protein-linked DNA breaks via mammalian DNA topoisomerase I. J Biol Chem 260:14873–14878
Iyer LM, Babu MM, Aravind L (2006) The HIRAN domain and recruitment of chromatin remodeling and repair activities to damaged. DNA Cell Cycle 5:775–782. https://doi.org/10.4161/cc.5.7.2629
James P, Halladay J, Craig EA (1996) Genomic libraries and a host strain designed for highly efficient two-hybrid selection in yeast. Genetics 144:1425–1436
Johnson AW, Demple B (1988) Yeast DNA 3′-repair diesterase is the major cellular apurinic apyrimidinic endonuclease—substrate-specificity and kinetics. J Biol Chem 263:18017–18022
Johnson RE, Henderson ST, Petes TD, Prakash S, Bankmann M, Prakash L (1992) Saccharomyces cerevisiae RAD5-encoded DNA repair protein contains DNA helicase and zinc-binding sequence motifs and affects the stability of simple repetitive sequences in the genome. Mol Cell Biol 12:3807–3818
Johnson RE, Kondratick CM, Prakash S, Prakash L (1999a) hRAD30 mutations in the variant form of xeroderma pigmentosum. Science 285:263–265
Johnson RE, Prakash S, Prakash L (1999b) Requirement of DNA polymerase activity of yeast Rad30 protein for its biological function. J Biol Chem 274:15975–15977
Johnson RE, Haracska L, Prakash S, Prakash L (2001) Role of DNA polymerase eta in the bypass of a (6 – 4) TT photoproduct. Mol Cell Biol 21:3558–3563. https://doi.org/10.1128/MCB.21.10.3558-3563.2001
Kile AC et al (2015) HLTF’s ancient HIRAN domain binds 3′ DNA ends to drive replication fork. Reversal Mol Cell 58:1090–1100. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.molcel.2015.05.013
Kobbe D et al (2016) AtRAD5A is a DNA translocase harboring a HIRAN domain which confers binding to branched DNA structures and is required for DNA repair in vivo. Plant J Cell Mol Biol. https://doi.org/10.1111/tpj.13283
Kuang L, Kou H, Xie Z, Zhou Y, Feng X, Wang L, Wang Z (2013) A non-catalytic function of Rev1 in translesion DNA synthesis and mutagenesis is mediated by its stable interaction with Rad. 5. DNA Repair 12:27–37. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.dnarep.2012.10.003
Lemontt JF (1971) Mutants of yeast defective in mutation induced by ultraviolet light. Genetics 68:21–33
Lindahl T, Nyberg B (1972) Rate of depurination of native deoxyribonucleic acid. Biochemistry 11:3610–3618
Lindahl T, Wood RD (1999) Quality control by DNA repair. Science 286:1897–1905
Lorick KL, Jensen JP, Fang S, Ong AM, Hatakeyama S, Weissman AM (1999) RING fingers mediate ubiquitin-conjugating enzyme (E2)-dependent ubiquitination. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 96:11364–11369
MacNeill SA (2016) PCNA-binding proteins in the archaea: novel functionality beyond the conserved core. Curr Genet 62:527–532. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00294-016-0577-3
Masutani C et al (1999) The XPV (xeroderma pigmentosum variant) gene encodes human DNA polymerase eta. Nature 399:700–704. https://doi.org/10.1038/21447
McDonald JP, Levine AS, Woodgate R (1997) The Saccharomyces cerevisiae RAD30 gene, a homologue of Escherichia coli dinB and umuC, is DNA damage inducible and functions in a novel error-free postreplication repair mechanism. Genetics 147:1557–1568
Mukhopadhyay S, Clark DR, Watson NB, Zacharias W, McGregor WG (2004) REV1 accumulates in DNA damage-induced nuclear foci in human cells and is implicated in mutagenesis by benzo[a]pyrenediolepoxide. Nucleic Acids Res 32:5820–5826. https://doi.org/10.1093/nar/gkh903
Nelson JR, Lawrence CW, Hinkle DC (1996) Deoxycytidyl transferase activity of yeast REV1 protein. Nature 382:729–731. https://doi.org/10.1038/382729a0
Ortiz-Bazan MA, Gallo-Fernandez M, Saugar I, Jimenez-Martin A, Vazquez MV, Tercero JA (2014) Rad5 plays a major role in the cellular response to DNA damage during chromosome replication. Cell Rep 9:460–468. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.celrep.2014.09.005
Pages V (2016) Single-strand gap repair involves both RecF and RecBCD pathways. Curr Genet 62:519–521. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00294-016-0575-5
Pages V, Bresson A, Acharya N, Prakash S, Fuchs RP, Prakash L (2008) Requirement of Rad5 for DNA polymerase zeta-dependent translesion synthesis in Saccharomyces cerevisiae. Genetics 180:73–82. https://doi.org/10.1534/genetics.108.091066
Parker JL, Ulrich HD (2009) Mechanistic analysis of PCNA poly-ubiquitylation by the ubiquitin protein ligases Rad18 and Rad5. Embo J 28:3657–3666. https://doi.org/10.1038/emboj.2009.303
Parker JL, Bielen AB, Dikic I, Ulrich HD (2007) Contributions of ubiquitin- and PCNA-binding domains to the activity of Polymerase eta in Saccharomyces cerevisiae. Nucleic Acids Res 35:881–889. https://doi.org/10.1093/nar/gkl1102
Pastushok L, Xiao W (2004) DNA postreplication repair modulated by ubiquitination and sumoylation. Adv Protein Chem 69:279–306
Poklar N, Pilch DS, Lippard SJ, Redding EA, Dunham SU, Breslauer KJ (1996) Influence of cisplatin intrastrand crosslinking on the conformation, thermal stability, and energetics of a 20-mer DNA duplex. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 93:7606–7611
Prakash L (1981) Characterization of postreplication repair in Saccharomyces cerevisiae and effects of rad6, rad18, rev3 and rad52 mutations. Mol General Gene MGG 184:471–478
Prakash S, Prakash L (2002) Translesion DNA synthesis in eukaryotes: a one- or two-polymerase affair. Genes Dev 16:1872–1883. https://doi.org/10.1101/gad.1009802
Prakash S, Johnson RE, Prakash L (2005) Eukaryotic translesion synthesis DNA polymerases: specificity of structure and function. Annu Rev Biochem 74:317–353. https://doi.org/10.1146/annurev.biochem.74.082803.133250
Rothstein RJ (1983) One-step gene disruption in yeast. Methods Enzymol 101:202–211
Sale JE, Lehmann AR, Woodgate R (2012) Y-family DNA polymerases and their role in tolerance of cellular DNA damage. Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol 13:141–152. https://doi.org/10.1038/nrm3289
Scharer OD, Jiricny J (2001) Recent progress in the biology, chemistry and structural biology of DNA glycosylases. BioEssays News Rev Mol Cell Dev Biol 23:270–281. https://doi.org/10.1002/1521-1878(200103)23:3<270::AID-BIES1037>3.0.CO;2-J
Sung P, Prakash L, Weber S, Prakash S (1987) The RAD3 gene of Saccharomyces cerevisiae encodes a DNA-dependent ATPase. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 84:6045–6049
Unk I, Haracska L, Johnson RE, Prakash S, Prakash L (2000) Apurinic endonuclease activity of yeast Apn2 protein. J Biol Chem 275:22427–22434. https://doi.org/10.1074/jbc.M002845200
Unk I, Haracska L, Gomes XV, Burgers PM, Prakash L, Prakash S (2002) Stimulation of 3′–>5′ exonuclease and 3′-phosphodiesterase activities of yeast apn2 by proliferating cell nuclear antigen. Mol Cell Biol 22:6480–6486
van der Kemp PA, Thomas D, Barbey R, de Oliveira R, Boiteux S (1996) Cloning and expression in Escherichia coli of the OGG1 gene of Saccharomyces cerevisiae, which codes for a DNA glycosylase that excises 7,8-dihydro-8-oxoguanine and 2,6-diamino-4-hydroxy-5-N-methylformamidopyrimidine. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 93:5197–5202
Warbrick E, Heatherington W, Lane DP, Glover DM (1998) PCNA binding proteins in Drosophila melanogaster: the analysis of a conserved PCNA binding domain. Nucleic Acids Res 26:3925–3932
Xiao W, Chow BL, Hanna M, Doetsch PW (2001) Deletion of the MAG1 DNA glycosylase gene suppresses alkylation-induced killing and mutagenesis in yeast cells lacking AP endonucleases. Mutat Res/DNA Repair 487:137–147
Xu H, Zhang P, Liu L, Lee MY (2001) A novel PCNA-binding motif identified by the panning of a random peptide display library. Biochemistry 40:4512–4520
Xu X, Blackwell S, Lin A, Li F, Qin Z, Xiao W (2015) Error-free DNA-damage tolerance in Saccharomyces cerevisiae. Mutat Res Rev Mutat Res 764:43–50. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.mrrev.2015.02.001
Xu X et al (2016) Involvement of budding yeast Rad5 in translesion DNA synthesis through physical interaction with Rev1. Nucleic Acids Res 44:5231–5245. https://doi.org/10.1093/nar/gkw183
Zhang H, Lawrence CW (2005) The error-free component of the RAD6/RAD18 DNA damage tolerance pathway of budding yeast employs sister-strand recombination. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 102:15954–15959. https://doi.org/10.1073/pnas.0504586102
Acknowledgements
This work was supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (Grant number 31371264); CAS Interdisciplinary Innovation Team; and the Newton Advanced Fellowship from the Royal Society (Grant number NA140085). Q. W and W. X were supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (Grant number 31670068).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
There are no conflicts of interest.
Additional information
Communicated by M. Kupiec.
Electronic supplementary material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Fan, Q., Xu, X., Zhao, X. et al. Rad5 coordinates translesion DNA synthesis pathway by recognizing specific DNA structures in saccharomyces cerevisiae. Curr Genet 64, 889–899 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00294-018-0807-y
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00294-018-0807-y