Abstract
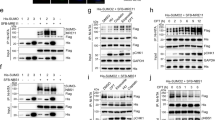
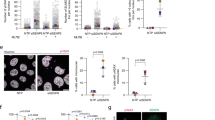
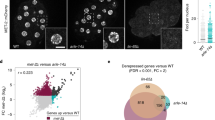
SUMOylation promotes targeting of HP1α to pericentric heterochromatin. Here we identify the SUMO-specific protease SENP7 in mouse as a maintenance factor for HP1α accumulation at this location. SENP7 interacts directly with HP1α, localizes at HP1-enriched pericentric domains and can deconjugate SUMOylated HP1α in vivo. Depletion of SENP7 delocalizes HP1α from pericentric heterochromatin without affecting H3K9me3 levels. We propose that following targeting of HP1α, a subsequent deSUMOylation event enables HP1α retention at these domains.
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 12 print issues and online access
$189.00 per year
only $15.75 per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on Springer Link
- Instant access to full article PDF
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout



Similar content being viewed by others
References
Singh, P.B. et al. Nucleic Acids Res. 19, 789–794 (1991).
Kwon, S.H. & Workman, J.L. Mol. Cells 26, 217–227 (2008).
Nozawa, R.S. et al. Nat. Cell Biol. 12, 719–727 (2010).
Grewal, S.I. & Jia, S. Nat. Rev. Genet. 8, 35–46 (2007).
Maison, C. et al. Nat. Genet. 43, 220–227 (2011).
Kim, J.H. & Baek, S.H. Biochim. Biophys. Acta 1792, 155–162 (2009).
Yeh, E.T. J. Biol. Chem. 284, 8223–8227 (2009).
Mukhopadhyay, D. & Dasso, M. Trends Biochem. Sci. 32, 286–295 (2007).
Hay, R.T. Trends Cell Biol. 17, 370–376 (2007).
Wilkinson, K.A. & Henley, J.M. Biochem. J. 428, 133–145 (2010).
Shen, L.N., Geoffroy, M.C., Jaffray, E.G. & Hay, R.T. Biochem. J. 421, 223–230 (2009).
Maison, C. et al. Nat. Genet. 30, 329–334 (2002).
Peters, A.H. et al. Cell 107, 323–337 (2001).
Prasanth, S.G., Shen, Z., Prasanth, K.V. & Stillman, B. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 107, 15093–15098 (2010).
Mikolajczyk, J. et al. J. Biol. Chem. 282, 26217–26224 (2007).
Lee, Y.K., Thomas, S.N., Yang, A.J. & Ann, D.K. J. Biol. Chem. 282, 1595–1606 (2007).
Acknowledgements
We thank R. Hay (University of Dundee) for reagents, C. Gazin for preliminary MS data, S. Cantaloube for technical help, A. vandenBerg for critical reading of the manuscript, members of the UMR218 unit for discussions and the Curie Imaging platform for microscopy facility. K. Romeo received support from Université Pierre et Marie Curie (UPMC) and Ministère de l'Enseignement Supérieur et de la Recherche. This work was supported by la Ligue Nationale contre le Cancer (Equipe labellisée Ligue 2010), the European Commission Network of Excellence EpiGeneSys (HEALTH-F4-2010-257082 to G.A.), European Research Council Advanced Grant 2009-AdG_20090506 “Eccentric” to G.A. and ANR “ECenS” ANR-09-BLAN-0257-01 to G.A.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
J.-P.Q., C.M. and G.A. conceived and designed the experiments. K.R., C.M., D.B., M.D. and J.-P.Q. conducted the experiments. J.-P.Q., C.M., K.R. and G.A. analyzed the data. J.-P.Q., C.M. and G.A. wrote the paper.
Corresponding authors
Ethics declarations
Competing interests
The authors declare no competing financial interests.
Supplementary information
Supplementary Text and Figures
Supplementary Figures 1–6 and Supplementary Methods (PDF 4259 kb)
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Maison, C., Romeo, K., Bailly, D. et al. The SUMO protease SENP7 is a critical component to ensure HP1 enrichment at pericentric heterochromatin. Nat Struct Mol Biol 19, 458–460 (2012). https://doi.org/10.1038/nsmb.2244
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/nsmb.2244
This article is cited by
-
The SUMOylation and ubiquitination crosstalk in cancer
Journal of Cancer Research and Clinical Oncology (2023)
-
Verloren negatively regulates the expression of IMD pathway dependent antimicrobial peptides in Drosophila
Scientific Reports (2021)
-
The poly-SUMO2/3 protease SENP6 enables assembly of the constitutive centromere-associated network by group deSUMOylation
Nature Communications (2019)
-
Activity-dependent neuroprotective protein recruits HP1 and CHD4 to control lineage-specifying genes
Nature (2018)
-
Novel SUMO-Protease SENP7S Regulates β-catenin Signaling and Mammary Epithelial Cell Transformation
Scientific Reports (2017)