Abstract
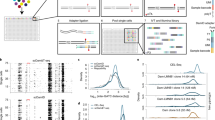
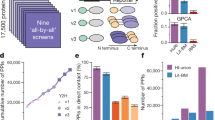
To accelerate high-density interactome mapping, we developed a yeast two-hybrid interaction screening approach involving short-read second-generation sequencing (Y2H-seq) with improved sensitivity and a quantitative scoring readout allowing rapid interaction validation. We applied Y2H-seq to investigate enzymes involved in protein methylation, a largely unexplored post-translational modification. The reported network of 523 interactions involving 22 methyltransferases or demethylases is comprehensively annotated and validated through coimmunoprecipitation experiments and defines previously undiscovered cellular roles of nonhistone protein methylation.
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 12 print issues and online access
$259.00 per year
only $21.58 per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on Springer Link
- Instant access to full article PDF
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout



Similar content being viewed by others
References
Venkatesan, K. et al. Nat. Methods 6, 83–90 (2009).
Schwartz, A.S., Yu, J., Gardenour, K.R., Finley, R.L. Jr. & Ideker, T. Nat. Methods 6, 55–61 (2009).
Yu, H. et al. Nat. Methods 8, 478–480 (2011).
Vinayagam, A. et al. Sci. Signal. 4, rs8 (2011).
Hegele, A. et al. Mol. Cell 45, 567–580 (2012).
Erce, M.A., Pang, C.N., Hart-Smith, G. & Wilkins, M.R. Proteomics 12, 564–586 (2012).
Lee, Y.H. & Stallcup, M.R. Mol. Endocrinol. 23, 425–433 (2009).
Bedford, M.T. & Clarke, S.G. Mol. Cell 33, 1–13 (2009).
Huang, J. & Berger, S.L. Curr. Opin. Genet. Dev. 18, 152–158 (2008).
Chen, C., Nott, T.J., Jin, J. & Pawson, T. Nat. Rev. Mol. Cell Biol. 12, 629–642 (2011).
Lan, F., Nottke, A.C. & Shi, Y. Curr. Opin. Cell Biol. 20, 316–325 (2008).
Worseck, J.M., Grossmann, A., Weimann, M., Hegele, A. & Stelzl, U. Methods Mol. Biol. 812, 63–87 (2012).
Lewis, J.D. et al. BMC Genomics 13, 8 (2012).
Passos, D.O., Bressan, G.C., Nery, F.C. & Kobarg, J. FEBS J. 273, 3946–3961 (2006).
Yang, Y. & Bedford, M.T. Mol. Cell 48, 487–488 (2012).
Côté, J., Boisvert, F.M., Boulanger, M.C., Bedford, M.T. & Richard, S. Mol. Biol. Cell 14, 274–287 (2003).
Zhang, Y. et al. EMBO J. 22, 1801–1810 (2003).
Goehler, H. et al. Mol. Cell 15, 853–865 (2004).
David, M., Dzamba, M., Lister, D., Ilie, L. & Brudno, M. Bioinformatics 27, 1011–1012 (2011).
Stelzl, U. et al. Cell 122, 957–968 (2005).
Huang, da W., Sherman, B.T. & Lempicki, R.A. Nat. Protoc. 4, 44–57 (2009).
Palidwor, G.A. et al. PLoS Comput. Biol. 5, e1000304 (2009).
Passos, D.O., Quaresma, A.J. & Kobarg, J. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 346, 517–525 (2006).
Lee, J. & Bedford, M.T. EMBO Rep. 3, 268–273 (2002).
Lee, J., Cheng, D. & Bedford, M.T. Methods Mol. Biol. 284, 195–208 (2004).
Acknowledgements
We thank B. Lukaszewska-McGreal from the MPIMG–mass spectrometry group and D. Roth and S. Paturej from the MPIMG–next-generation sequencing team for their experimental support. The work was supported by the Max Planck Society and the German Ministry of Science (NGFNp, NeuroNet-TP3 01GS08171; BMBF, 0315082).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
M.W. performed Y2H screens. A.G. and U.S. developed the screening protocol. J.W. and A.G. analyzed the sequencing data. Z.Ö. contributed to cloning, Y2H and protein purification experiments. P.B. performed the co-IP experiments. M.W. and N.B. performed the methylation assays. D.M. performed the mass spectrometry analysis. T.V., B.T., E.E.W. and S.S. contributed tools and reagents. M.W., J.W. and U.S. analyzed the data and generated the figures. U.S. conceived and supervised the study and wrote the manuscript. All authors provided feedback on the manuscript.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Competing interests
The authors declare no competing financial interests.
Supplementary information
Supplementary Text and Figures
Supplementary Figures 1–6 and Supplementary Tables 1,2,4,6 and 7 (PDF 1171 kb)
Supplementary Tables 3 and 5
PPI data. Columns are as follows: Symbol_p NCBI ENTREZ GeneID of the prey protein; GeneID_p, NCBI Entrez symbol of the prey protein;Symbol_b, NCBI Entrez Gene ID of the bait protein (PMTs and PDeMs);GeneID_b, NCBI Entrez Gene ID of the bait protein (PMTs and PDeMs); Y2HRetest, retest result (sum of the fraction of bait-prey combinations found over tested); Matrix, interaction found in the matrix approach; Y2H-seq, interaction found in the Y2H-seq approach. (XLS 100 kb)
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Weimann, M., Grossmann, A., Woodsmith, J. et al. A Y2H-seq approach defines the human protein methyltransferase interactome. Nat Methods 10, 339–342 (2013). https://doi.org/10.1038/nmeth.2397
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/nmeth.2397
This article is cited by
-
Myeloid cell nuclear differentiation antigen controls the pathogen-stimulated type I interferon cascade in human monocytes by transcriptional regulation of IRF7
Nature Communications (2022)
-
Removing auto-activators from yeast-two-hybrid assays by conditional negative selection
Scientific Reports (2021)
-
Modulation of chromatin remodeling proteins SMYD1 and SMARCD1 promotes contractile function of human pluripotent stem cell-derived ventricular cardiomyocyte in 3D-engineered cardiac tissues
Scientific Reports (2019)
-
rec-YnH enables simultaneous many-by-many detection of direct protein–protein and protein–RNA interactions
Nature Communications (2018)
-
Protein interaction perturbation profiling at amino-acid resolution
Nature Methods (2017)