Abstract
Purpose
To perform serum microRNA expression profiling to identify members of chromosome 19 miRNA cluster involved in preeclampsia development.
Methods
Serum chromosome 19 miRNA cluster microRNA expression profiling was evaluated at 12, 16, and 20 gestational weeks and at the time of preeclampsia diagnosis, in women who developed preeclampsia (WWD-PE; n = 16) and controls (n = 18) using TaqMan low density array plates.
Results
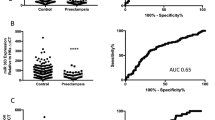
A total of 51 chromosome 19 microRNA cluster members were evaluated. The circulating hsa-miRs 512-3p, 518f-3p, 520c-3p, and 520d-3p, were differentially expressed between groups (P < 0.05). Compared with controls, serum levels of hsa-miR-518f-3p at 20 GW were useful for identifying WWD-Mild-PE (P = 0.035) and WWD-Severe-PE (P = 0.007).
Conclusions
Serum hsa-miRs 512-3p, 518f-3p, 520c-3p, and 520d-3p, are differentially expressed between WWD-PE and controls and their role in the development of preeclampsia should be investigated further.

Similar content being viewed by others
References
Aslam MI (2009) MicroRNAs are novel biomarkers of colorectal cancer. Br J Surg 96(7):702–710
Maccani MA (2009) Epigenetics in the placenta. Am J Reprod Immunol (New York, NY: 1989) 62(2):78–89
Kim VN (2005) MicroRNA biogenesis: coordinated cropping and dicing. Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol 6(5):376–385. https://doi.org/10.1038/nrm1644
Ji L, Brkic J, Liu M, Fu G, Peng C, Wang YL (2013) Placental trophoblast cell differentiation: physiological regulation and pathological relevance to preeclampsia. Mol Aspects Med 34(5):981–1023. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.mam.2012.12.008
Enquobahrie DA, Abetew DF, Sorensen TK, Willoughby D, Chidambaram K, Williams MA (2011) Placental microRNA expression in pregnancies complicated by preeclampsia. Am J Obstet Gynecol 204(2):178 e112-121. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ajog.2010.09.004
Fu G, Brkic J, Hayder H, Peng C (2013) MicroRNAs in human placental development and pregnancy complications. Int J Mol Sci 14(3):5519–5544. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms14035519
Pineles BL, Romero R, Montenegro D, Tarca AL, Han YM, Kim YM, Draghici S, Espinoza J, Kusanovic JP, Mittal P, Hassan SS, Kim CJ (2007) Distinct subsets of microRNAs are expressed differentially in the human placentas of patients with preeclampsia. Am J Obstet Gynecol 196 e261-266(3):261. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ajog.2007.01.008
Chen DB, Wang W (2013) Human placental microRNAs and preeclampsia. Biol Reprod 88(5):130. https://doi.org/10.1095/biolreprod.113.107805
Doridot L, Miralles F, Barbaux S, Vaiman D (2013) Trophoblasts, invasion, and microRNA. Front Genet 4:248. https://doi.org/10.3389/fgene.2013.00248
Morales-Prieto DM, Ospina-Prieto S, Chaiwangyen W, Schoenleben M, Markert UR (2013) Pregnancy-associated miRNA-clusters. J Reprod Immunol 97(1):51–61. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jri.2012.11.001
Ouyang Y, Mouillet JF, Coyne CB, Sadovsky Y (2014) Review: Placenta-specific microRNAs in exosomes—good things come in nano-packages. Placenta 35(Suppl):S69–S73. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.placenta.2013.11.002
Gu Y, Sun J, Groome LJ, Wang Y (2013) Differential miRNA expression profiles between the first and third trimester human placentas. Am J Physiol Endocrinol Metab 304(8):E836–E843. https://doi.org/10.1152/ajpendo.00660.2012
Donker RB, Mouillet JF, Chu T, Hubel CA, Stolz DB, Morelli AE, Sadovsky Y (2012) The expression profile of C19MC microRNAs in primary human trophoblast cells and exosomes. Mol Hum Reprod 18(8):417–424. https://doi.org/10.1093/molehr/gas013
Bullerdiek J, Flor I (2012) Exosome-delivered microRNAs of “chromosome 19 microRNA cluster” as immunomodulators in pregnancy and tumorigenesis. Mol Cytogenet 5(1):27. https://doi.org/10.1186/1755-8166-5-27
Xu P, Zhao Y, Liu M, Wang Y, Wang H, Li YX, Zhu X, Yao Y, Qiao J, Ji L, Wang YL (2014) Variations of microRNAs in human placentas and plasma from preeclamptic pregnancy. Hypertension 63(6):1276–1284. https://doi.org/10.1161/HYPERTENSIONAHA.113.02647
Mouillet JF, Chu T, Hubel CA, Nelson DM, Parks WT, Sadovsky Y (2010) The levels of hypoxia-regulated microRNAs in plasma of pregnant women with fetal growth restriction. Placenta 31(9):781–784. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.placenta.2010.07.001
Li H, Ge Q, Guo L, Lu Z (2013) Maternal plasma miRNAs expression in preeclamptic pregnancies. Biomed Res Int 2013:970265. https://doi.org/10.1155/2013/970265
Wu L, Zhou H, Lin H, Qi J, Zhu C, Gao Z, Wang H (2012) Circulating microRNAs are elevated in plasma from severe preeclamptic pregnancies. Reproduction 143(3):389–397. https://doi.org/10.1530/REP-11-0304
Yang Q, Lu J, Wang S, Li H, Ge Q, Lu Z (2011) Application of next-generation sequencing technology to profile the circulating microRNAs in the serum of preeclampsia versus normal pregnant women. Clin Chim Acta Int J Clin Chem 412(23–24):2167–2173. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cca.2011.07.029
Ura B, Feriotto G, Monasta L, Bilel S, Zweyer M, Celeghini C (2014) Potential role of circulating microRNAs as early markers of preeclampsia. Taiwan J Obstet Gynecol 53(2):232–234. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.tjog.2014.03.001
Herzog EM, Eggink AJ, Willemsen SP, Slieker RC, Wijnands KPJ, Felix JF, Chen J, Stubbs A, van der Spek PJ, van Meurs JB, Steegers-Theunissen RPM (2017) Early- and late-onset preeclampsia and the tissue-specific epigenome of the placenta and newborn. Placenta 58:122–132. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.placenta.2017.08.070
Garza-Veloz I, Castruita-De la Rosa C, Cortes-Flores R, Martinez-Gaytan V, Rivera-Munoz JE, Garcia-Mayorga EA, Meza-Lamas E, Rojas-Martinez A, Ortiz-Lopez R, Martinez-Fierro ML (2011) No association between polymorphisms/haplotypes of the vascular endothelial growth factor gene and preeclampsia. BMC Pregnancy Childbirth 11:35. https://doi.org/10.1186/1471-2393-11-35
Martinez-Fierro ML, Garza-Veloz I, Carrillo-Sanchez K, Martinez-Gaytan V, Cortes-Flores R, Ochoa-Torres MA, Guerrero GG, Rodriguez-Sanchez IP, Cancela-Murrieta CO, Zamudio-Osuna M, Badillo-Almaraz JI, Castruita-De la Rosa C (2014) Expression levels of seven candidate genes in human peripheral blood mononuclear cells and their association with preeclampsia. Hypertens Pregnancy 33(2):191–203. https://doi.org/10.3109/10641955.2013.853777
Morales-Prieto DM, Chaiwangyen W, Ospina-Prieto S, Schneider U, Herrmann J, Gruhn B, Markert UR (2012) MicroRNA expression profiles of trophoblastic cells. Placenta 33(9):725–734. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.placenta.2012.05.009
Sheikh AM, Small HY, Currie G, Delles C (2016) Systematic review of micro-RNA expression in pre-eclampsia identifies a number of common pathways associated with the disease. PLoS ONE 11(8):e0160808. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0160808
Hromadnikova I, Kotlabova K, Ivankova K, Krofta L (2017) First trimester screening of circulating C19MC microRNAs and the evaluation of their potential to predict the onset of preeclampsia and IUGR. PLoS ONE 12(2):e0171756. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0171756
Luque A, Farwati A, Crovetto F, Crispi F, Figueras F, Gratacos E, Aran JM (2014) Usefulness of circulating microRNAs for the prediction of early preeclampsia at first-trimester of pregnancy. Sci Rep 4:4882. https://doi.org/10.1038/srep04882
Hromadnikova I, Kotlabova K, Ondrackova M, Kestlerova A, Novotna V, Hympanova L, Doucha J, Krofta L (2013) Circulating C19MC microRNAs in preeclampsia, gestational hypertension, and fetal growth restriction. Mediat Inflamm 2013:186041. https://doi.org/10.1155/2013/186041
Acknowledgements
The authors thank all of the study participants. We are grateful to the clinical staff of the Urban Health Center of Zacatecas “José Castro Villagrana” and the Hospital de la Mujer Zacatecana for their invaluable assistance in patient recruitment. We also gratefully acknowledge the support of Dr. Raymundo Orozco-Covarrubias, Dr. José Luis Durán-Aguayo, Dr. Martín Cardona-Domínguez, Dr. Rosbel Vázquez Castro, and Dr. Raúl Hernández-León (SSZ) in patient enrolment. The invaluable accompaniment and support of Dr. Pug MF throughout the work will always be acknowledged: we will always remember you.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
All authors participated throughout the study and during the preparation of the manuscript, as follows: Protocol/project development: MLM-F, VF-M, YO-C. Data collection or management: MLM-F, IG-V, CG-A, OYB-C, IPR-S, RC-M. Data analysis: MLM-F, CG-A, ID-E, JIB-A, JMO-R, LOS-S. Manuscript writing/editing/approval: MLM-F, IG-V, CG-A, ID-E, OYB-C, VF-M, GPH-D, MRR-P, IPR-S, RC-M, JMO-R, LOS-S, JIB-A, YO-C.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors report no conflicts of interest.
Funding
This work was funded in part by the following CONACYT Grants to M.L.M.F: -SEP-CB-2009-01-0128567, -FOMIX M0024-2013-01-203220, -SS/IMSS/ISSSTE-2010-138721, -SS/IMSS/ISSSTE-2012-01-181124, and -INFR-225520, and to I.GV: INFR-2015-01-254106.
Ethical approval
All procedures performed in studies involving human participants were in accordance with the ethical standards of the institutional research committee and with the 1964 Helsinki declaration and its later amendments.
Electronic supplementary material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Martinez-Fierro, M.L., Garza-Veloz, I., Gutierrez-Arteaga, C. et al. Circulating levels of specific members of chromosome 19 microRNA cluster are associated with preeclampsia development. Arch Gynecol Obstet 297, 365–371 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00404-017-4611-6
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00404-017-4611-6